Security News

Cybersecurity researchers have found that entry points could be abused across multiple programming ecosystems like PyPI, npm, Ruby Gems, NuGet, Dart Pub, and Rust Crates to stage software supply...
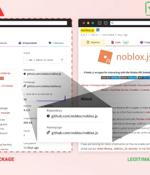
Roblox developers are the target of a persistent campaign that seeks to compromise systems through bogus npm packages, once again underscoring how threat actors continue to exploit the trust in...

Threat actors with ties to North Korea have been observed publishing a set of malicious packages to the npm registry, indicating "coordinated and relentless" efforts to target developers with...
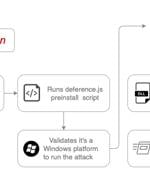
The North Korea-linked threat actor known as Moonstone Sleet has continued to push malicious npm packages to the JavaScript package registry with the aim of infecting Windows systems, underscoring the persistent nature of their campaigns. The security arm of the cloud monitoring firm is tracking the threat actor under the name Stressed Pungsan, which exhibits overlaps with a newly discovered North Korean malicious activity cluster dubbed Moonstone Sleet.
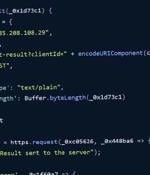
Cybersecurity researchers have identified two malicious packages on the npm package registry that concealed backdoor code to execute malicious commands sent from a remote server. The packages in question - img-aws-s3-object-multipart-copy and legacyaws-s3-object-multipart-copy - have been downloaded 190 and 48 times each.

Unknown threat actors have been found propagating trojanized versions of jQuery on npm, GitHub, and jsDelivr in what appears to be an instance of a "Complex and persistent" supply chain attack. As many as 68 packages have been linked to the campaign.

Cybersecurity researchers have uncovered a new suspicious package uploaded to the npm package registry that's designed to drop a remote access trojan (RAT) on compromised systems. The package in...
An ongoing social engineering campaign is targeting software developers with bogus npm packages under the guise of a job interview to trick them into downloading a Python backdoor. Cybersecurity...

New research has discovered over 800 packages in the npm registry which have discrepancies from their registry entries, out of which 18 have been found to exploit a technique called manifest...

A set of fake npm packages discovered on the Node.js repository has been found to share ties with North Korean state-sponsored actors, new findings from Phylum show. The packages are named...