Security News

Microsoft has released security updates to address a Secure Boot zero-day vulnerability exploited by BlackLotus UEFI malware to infect fully patched Windows systems. According to a Microsoft Security Response Center blog post, the security flaw was used to bypass patches released for CVE-2022-21894, another Secure Boot bug abused in BlackLotus attacks last year.

Microsoft has released security updates to address a Secure Boot zero-day vulnerability exploited by BlackLotus UEFI malware to infect fully patched Windows systems. According to a Microsoft Security Response Center blog post, the security flaw was used to bypass patches released for CVE-2022-21894, another Secure Boot bug abused in BlackLotus attacks last year.

The development of the Snake malware started under the name "Uroburos" in late 2003, while the first versions of the implant were seemingly finalized by early 2004, with Russian state hackers deploying the malware in attacks immediately after. The malware is linked to a unit within Center 16 of the FSB, the notorious Russian Turla hacking group, and was disrupted following a coordinated effort named Operation MEDUSA. Among the computers ensnared in the Snake peer-to-peer botnet, the FBI also found devices belonging to NATO member governments.

In the early stages of the war in Ukraine in 2022, PIPEDREAM, a known malware was quietly on the brink of wiping out a handful of critical U.S. electric and liquid natural gas sites. PIPEDREAM is an attack toolkit with unmatched and unprecedented capabilities developed for use against industrial control systems.
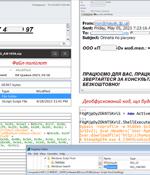
An ongoing phishing campaign with invoice-themed lures is being used to distribute the SmokeLoader malware in the form of a polyglot file, according to the Computer Emergency Response Team of Ukraine. In a related advisory, Ukraine's cybersecurity authority also revealed details of destructive attacks orchestrated by a group known as UAC-0165 against public sector organizations.

A new Android malware called 'FluHorse' has been discovered, targeting users in Eastern Asia with malicious apps that imitate legitimate versions. The apps mimicked by the FluHorse carrier apps are 'ETC,' a toll-collection app used in Taiwan, and 'VPBank Neo,' a banking app in Vietnam.

Various sectors in East Asian markets have been subjected to a new email phishing campaign that distributes a previously undocumented strain of Android malware called FluHorse that abuses the Flutter software development framework. "The malware features several malicious Android applications that mimic legitimate applications, most of which have more than 1,000,000 installs," Check Point said in a technical report.

A new Android subscription malware named Fleckpe has been unearthed on the Google Play Store, amassing more than 620,000 downloads in total since 2022. Kaspersky, which identified 11 apps on the official app storefront, said the malware masqueraded as legitimate photo editing apps, camera, and smartphone wallpaper packs.

A new Android subscription malware named 'Fleckpe' has been spotted on Google Play, the official Android app store, disguised as legitimate apps downloaded over 620,000 times. Kaspersky reveals that Fleckpe is the newest addition to the realm of malware that generates unauthorized charges by subscribing users to premium services, joining the ranks of other malicious Android malware, such as Jocker and Harly.
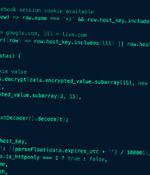
Meta said it took steps to take down more than 1,000 malicious URLs from being shared across its services that were found to leverage OpenAI's ChatGPT as a lure to propagate about 10 malware families since March 2023. The development comes against the backdrop of fake ChatGPT web browser extensions being increasingly used to steal users' Facebook account credentials with an aim to run unauthorized ads from hijacked business accounts.