Security News

Web hosting giant GoDaddy says unknown attackers have stolen source code and installed malware on its servers after breaching its cPanel shared hosting environment. While GoDaddy discovered the security breach in early December 2022 following customer reports that their sites were being used to redirect to random domains, the attackers had access to the company's network for multiple years.
Suspected North Korean nation-state actors targeted a journalist in South Korea with a malware-laced Android app as part of a social engineering campaign. The findings come from South Korea-based non-profit Interlab, which coined the new malware RambleOn.

ReversingLabs wrote about Havoc earlier this month in connection with a malicious npm package called Aabquerys, noting that it was created by a malware developer called C5pider. Now researchers with Zscaler's ThreatLabz threat intelligence unit say Havoc is being used in a campaign targeting a government organization.

A new Mirai botnet variant tracked as 'V3G4' targets 13 vulnerabilities in Linux-based servers and IoT devices to use in DDoS attacks. The malware spreads by brute-forcing weak or default telnet/SSH credentials and exploiting hardcoded flaws to perform remote code execution on the target devices.

Cybersecurity experts at Minerva recently made a stunning discovery of a new malware tagged Beep that has the features to evade detection and analysis by security software. While Beep is in its early stage of development and still lacks some essential malware attack capabilities, Minerva's report shows that it can enable threat actors to download and inject additional payloads on infected systems using three major components: a dropper, an injector and a payload. The differentiating factor between Beep and other malware is its ability to beat detection using unique evasion techniques.

A new attack campaign launched by an unknown threat actor targets the U.S. with two malware families: MortalKombat ransomware and Laplas Clipper. Figure A. Once executed, the loader downloads another ZIP file from a server belonging to the attackers' infrastructure, whose content might be MortalKombat ransomware or Laplas Clipper malware.

Hackers are deploying a new malware named 'Frebniss' on Microsoft's Internet Information Services that stealthily executes commands sent via web requests. Microsoft IIS is a web server software that acts as a web server and a web app hosting platform for services like Outlook on the Web for Microsoft Exchange.

Chinese-speaking individuals in Southeast and East Asia are the targets of a new rogue Google Ads campaign that delivers remote access trojans such as FatalRAT to compromised machines. The attacks involve purchasing ad slots to appear in Google search results that direct users searching for popular applications to rogue websites hosting trojanized installers, ESET said in a report published today.
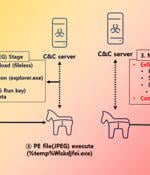
The North Korea-linked threat actor tracked as APT37 has been linked to a piece of new malware dubbed M2RAT in attacks targeting its southern counterpart, suggesting continued evolution of the group's features and tactics. APT37, also tracked under the monikers Reaper, RedEyes, Ricochet Chollima, and ScarCruft, is linked to North Korea's Ministry of State Security unlike the Lazarus and Kimsuky threat clusters that are part of the Reconnaissance General Bureau.

A new financially motivated campaign that commenced in December 2022 has seen the unidentified threat actor behind it deploying a novel ransomware strain dubbed MortalKombat and a clipper malware known as Laplas. The starting point that kicks off the multi-stage attack chain is a phishing email bearing a malicious ZIP file that's used as a pathway to deliver either the clipper or the ransomware.