Security News
Cybersecurity researchers have uncovered a privilege escalation vulnerability in Google Cloud that could enable malicious actors tamper with application images and infect users, leading to supply chain attacks. The issue, dubbed Bad.Build, is rooted in the Google Cloud Build service, according to cloud security firm Orca, which discovered and reported the issue.
Improve your cloud security with these 9 proven strategies. Uptycs, alongside renowned expert Lee Atchison, share their list of comprehensive tactics to mitigate risks facing modern development teams.

A critical design flaw in the Google Cloud Build service discovered by cloud security firm Orca Security can let attackers escalate privileges, providing them with almost nearly-full and unauthorized access to Google Artifact Registry code repositories. Dubbed Bad.Build, this flaw could enable the threat actors to impersonate the service account for the Google Cloud Build managed continuous integration and delivery service to run API calls against the artifact registry and take control over application images.

The U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency has shared a factsheet providing details on free tools and guidance for securing digital assets after switching to the cloud from on-premises environments. The highlighted tools complement the built-in tools provided by cloud service providers and help reinforce the resilience of network infrastructures, strengthen security measures, promptly identify malicious compromises, meticulously map potential threat vectors, and effectively pinpoint malicious activity in the aftermath of a breach.

A criminal crew with a history of deploying malware to harvest credentials from Amazon Web Services accounts may expand its attention to organizations using Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud Platform. The crooks used to target primarily AWS users, and now seem to be looking for ways into Azure and Google Cloud accounts.
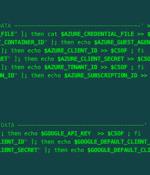
A malicious actor has been linked to a cloud credential stealing campaign in June 2023 that's focused on Azure and Google Cloud Platform services, marking the adversary's expansion in targeting beyond Amazon Web Services. They also overlap with an ongoing TeamTNT campaign disclosed by Aqua called Silentbob that leverages misconfigured cloud services to drop malware as part of what's said to be a testing effort, while also linking SCARLETEEL attacks to the threat actor, citing infrastructure commonalities.
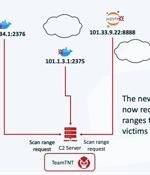
As many as 196 hosts have been infected as part of an aggressive cloud campaign mounted by the TeamTNT group called Silentbob. "The botnet run by TeamTNT has set its sights on Docker and Kubernetes environments, Redis servers, Postgres databases, Hadoop clusters, Tomcat and Nginx servers, Weave Scope, SSH, and Jupyter applications," Aqua security researchers Ofek Itach and Assaf Morag said in a report shared with The Hacker News.

Only 22% of IT professionals reported that more than 60% of their sensitive data in the cloud is encrypted. According to the findings, on average, only 45% of cloud data is currently encrypted.

A new fileless attack dubbed PyLoose has been observed striking cloud workloads with the goal of delivering a cryptocurrency miner, new findings from Wiz reveal. "The attack consists of Python code that loads an XMRig Miner directly into memory using memfd, a known Linux fileless technique," security researchers Avigayil Mechtinger, Oren Ofer, and Itamar Gilad said.

Google Cloud's AML AI represents an advancement in the fight against money laundering. In this Help Net Security interview, Anna Knizhnik, Director, Product Management, Cloud AI, Financial Services, at Google Cloud, explains how Google Cloud's AML AI outperforms current systems, lowers operational costs, enhances governance, and improves the customer experience by reducing false positives and minimizing compliance verification checks.