Security News

New research into the infrastructure behind an emerging DDoS botnet named Abcbot has uncovered links with a cryptocurrency-mining botnet attack that came to light in December 2020. Attacks involving Abcbot, first disclosed by Qihoo 360's Netlab security team in November 2021, are triggered via a malicious shell script that targets insecure cloud instances operated by cloud service providers such as Huawei, Tencent, Baidu, and Alibaba Cloud to download malware that co-opts the machine to a botnet, but not before terminating processes from competing threat actors and establishing persistence.

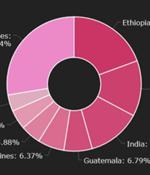
Cryptocurrency users in Ethiopia, Nigeria, India, Guatemala, and the Philippines are being targeted by a new variant of the Phorpiex botnet called Twizt that has resulted in the theft of virtual coins amounting to $500,000 over the last one year. Israeli security firm Check Point Research, which detailed the attacks, said the latest evolutionary version "Enables the botnet to operate successfully without active servers," adding it supports no less than 35 wallets associated with different blockchains, including Bitcoin, Ethereum, Dash, Dogecoin, Litecoin, Monero, Ripple, and Zilliqa, to facilitate crypto theft.
The botnet uses a tactic called crypto clipping, which relies on malware to steal cryptocurrency during a transaction, says Check Point Research. A new botnet variant discovered by cyber threat intelligence provider Check Point Research employs a unique method to steal cryptocurrency from its victims.

The previously shutdown Phorpiex botnet has re-emerged with new peer-to-peer command and control infrastructure, making the malware more difficult to disrupt. The source code for the Phorpiex botnet is being sold on the darknet... pic.

The botnet known as Dark Mirai has been observed exploiting a new vulnerability on the TP-Link TL-WR840N EU V5, a popular inexpensive home router released in 2017. According to a report by researchers at Fortinet, who have been following Dark Mirai activity, the botnet added the particular RCE in its arsenal only two weeks after TP-Link released the firmware update.

Google took steps to shut down the Glupteba botnet, at least for now. So Google is also suing the botnet's operators.

MikroTik is a Latvian manufacturer of routers and wireless ISPs who has sold over 2,000,000 devices globally. In August, the Mēris botnet exploited vulnerabilities in MikroTik routers to create an army of devices that performed a record-breaking DDoS attack on Yandex.

Google on Tuesday said it took steps to disrupt the operations of a sophisticated "Multi-component" botnet called Glupteba that approximately infected more than one million Windows computers across the globe and stored its command-and-control server addresses on Bitcoin's blockchain as a resilience mechanism. As part of the efforts, Google's Threat Analysis Group said it partnered with the CyberCrime Investigation Group over the past year to terminate around 63 million Google Docs that were observed to have distributed the malware, alongside 1,183 Google Accounts, 908 Cloud Projects, and 870 Google Ads accounts that were associated with its distribution.

Although a patch was released in September, any still-vulnerable Hikvision IP Network Video Recorder products are being actively targeted by the Mirai-based botnet known as Moobot. FortiGuard Labs has released a report detailing how the Moobot botnet is leveraging a known remote code execution vulnerability in Hikvision products to spread a Moobot, which carries out distributed denial of service attacks.

A Mirai-based botnet called 'Moobot' is spreading aggressively via exploiting a critical command injection flaw in the webserver of many Hikvision products. Among the various payloads that leverage CVE-2021-36260, Fortinet found a downloader masked as "MacHelper," which fetches and executes Moobot with the "Hikivision" parameter.