Security News
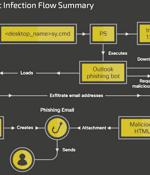
Spanish-speaking users in Latin America have been at the receiving end of a new botnet malware dubbed Horabot since at least November 2020. "Horabot enables the threat actor to control the victim's Outlook mailbox, exfiltrate contacts' email addresses, and send phishing emails with malicious HTML attachments to all addresses in the victim's mailbox," Cisco Talos researcher Chetan Raghuprasad said.

CVE-2023-28771, the critical command injection vulnerability affecting many Zyxel firewalls, is being actively exploited by a Mirai-like botnet, and has been added to CISA's Known Exploited Vulnerabilities catalog. CVE-2023-28771 is a vulnerability that allows unauthenticated attackers to execute OS commands remotely by sending crafted IKE packets to an affected device.

The U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency has added a recently patched critical security flaw in Zyxel gear to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities catalog, citing evidence of active exploitation. Federal agencies in the U.S. are mandated to update their devices by June 21, 2023.

Botnets are also getting easier to build and deploy because, much like legitimate software development, malicious botnets can be created using existing codebases. One example of how little technical sophistication is required is evinced by a botnet dubbed Dark Frost by researchers at Akamai web services.

If you're running an Apache NiFi instance exposed on the internet and you have not secured access to it, the underlying host may already be covertly cryptomining on someone else's behalf. "Routers make bad cryptomining servers. Cryptomining may be what they end up doing if the lateral movement doesn't get them anywhere."

A new botnet called Dark Frost has been observed launching distributed denial-of-service attacks against the gaming industry. "The Dark Frost botnet, modeled after Gafgyt, QBot, Mirai, and other malware strains, has expanded to encompass hundreds of compromised devices," Akamai security researcher Allen West said in a new technical analysis shared with The Hacker News.

A nascent botnet called Andoryu has been found to exploit a now-patched critical security flaw in the Ruckus Wireless Admin panel to break into vulnerable devices. While the malware is known to weaponize remote code execution flaws in GitLab and Lilin DVR for propagation, the addition of CVE-2023-25717 shows that Andoryu is actively expanding its exploit arsenal to ensnare more devices into the botnet.

A new malware botnet named 'AndoryuBot' is targeting a critical-severity flaw in the Ruckus Wireless Admin panel to infect unpatched Wi-Fi access points for use in DDoS attacks.Tracked as CVE-2023-25717, the flaw impacts all Ruckus Wireless Admin panels version 10.4 and older, allowing remote attackers to perform code execution by sending unauthenticated HTTP GET requests to vulnerable devices.

The US government's Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency is adding three more flaws to its list of known-exploited vulnerabilities, including one involving TP-Link routers that is being targeted by the operators of the notorious Mirai botnet. Trend Micro's Zero Day Initiative threat-hunting group early last week wrote in a report that in mid-April miscreants behind the please-can't-it-just-die Mirai botnet were beginning to exploit the flaw primarily by attacking devices in Eastern Europe, though the campaign soon expanded beyond that region.

A US court has recently unsealed a restraining order against a gang of alleged cybercrooks operating outside the country, based on a formal legal complaint from internet giant Google. Interestingly the court order also authorises Google to identify network providers whose services directly or indirectly make this criminality possible, and to "[request] that those persons and entities take reasonable best efforts" to stop the malware and the data theft in its tracks.