Security News
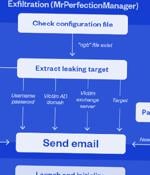
The Iranian nation-state hacking group known as OilRig has continued to target government organizations in the Middle East as part of a cyber espionage campaign that leverages a new backdoor to exfiltrate data. "The campaign abuses legitimate but compromised email accounts to send stolen data to external mail accounts controlled by the attackers," Trend Micro researchers Mohamed Fahmy, Sherif Magdy, and Mahmoud Zohdy said.

Cisco has released security updates this week to address a high-severity vulnerability in the Cisco IOx application hosting environment that can be exploited in command injection attacks. "An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by deploying and activating an application in the Cisco IOx application hosting environment with a crafted activation payload file," Cisco explains in a security advisory published on Wednesday.

The attackers were focused on maintaining persistence on exploited devices by using the custom malware to patch the FortiOS logging processes so that specific log entries could be removed or to disable the logging process altogether. Yesterday, Mandiant published a report about a suspected Chinese espionage campaign leveraging the FortiOS flaw since October 2022 using a new 'BOLDMOVE' malware explicitly designed for attacks on FortiOS devices.
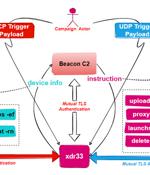
Unidentified threat actors have deployed a new backdoor that borrows its features from the U.S. Central Intelligence Agency's Hive multi-platform malware suite, the source code of which was released by WikiLeaks in November 2017. "This is the first time we caught a variant of the CIA Hive attack kit in the wild, and we named it xdr33 based on its embedded Bot-side certificate CN=xdr33," Qihoo Netlab 360's Alex Turing and Hui Wang said in a technical write-up published last week.

Security researchers are warning that patching critical vulnerabilities allowing access to the network is insufficient to defend against ransomware attacks. One case is a Lorenz ransomware attack that reached completion months after the hackers gained access to the victim's network using an exploit for a critical bug in a telephony system.

The Russian cyberespionage group known as Turla has been observed piggybacking on attack infrastructure used by a decade-old malware to deliver its own reconnaissance and backdoor tools to targets in Ukraine. Google-owned Mandiant, which is tracking the operation under the uncategorized cluster moniker UNC4210, said the hijacked servers correspond to a variant of a commodity malware called ANDROMEDA that was uploaded to VirusTotal in 2013.

A previously undocumented Python backdoor targeting VMware ESXi servers has been spotted, enabling hackers to execute commands remotely on a compromised system. VMware ESXi is a virtualization platform commonly used in the enterprise to host numerous servers on one device while using CPU and memory resources more effectively.

A new Go-based malware threat that researchers call Redigo has been targeting Redis servers vulnerable to CVE-2022-0543 to plant a stealthy backdoor and allow command execution. Today, AquaSec reports that its Redis honeypots vulnerable to CVE-2022-0543 caught a new piece of malware that is not detected as a threat by antivirus engines on Virus Total.

The North Korea-linked ScarCruft group has been attributed to a previously undocumented backdoor called Dolphin that the threat actor has used against targets located in its southern counterpart. "The backdoor has a wide range of spying capabilities, including monitoring drives and portable devices and exfiltrating files of interest, keylogging and taking screenshots, and stealing credentials from browsers," ESET researcher Filip Jurčacko said in a new report published today.

The North Korea-linked ScarCruft group has been attributed to a previously undocumented backdoor called Dolphin that the threat actor has used against targets located in its southern counterpart. "The backdoor has a wide range of spying capabilities, including monitoring drives and portable devices and exfiltrating files of interest, keylogging and taking screenshots, and stealing credentials from browsers," ESET researcher Filip Jurčacko said in a new report published today.