Security News

The U.S. National Security Agency released today guidance on how to defend against BlackLotus UEFI bootkit malware attacks. In May, Microsoft released security updates to address a Secure Boot zero-day vulnerability that was used to bypass patches released for CVE-2022-21894, the Secure Boot bug initially abused in BlackLotus attacks last year.

Microsoft has released security updates to address a Secure Boot zero-day vulnerability exploited by BlackLotus UEFI malware to infect fully patched Windows systems. According to a Microsoft Security Response Center blog post, the security flaw was used to bypass patches released for CVE-2022-21894, another Secure Boot bug abused in BlackLotus attacks last year.

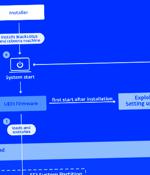
Microsoft has shared guidance to help organizations check if hackers targeted or compromised machines with the BlackLotus UEFI bootkit by exploiting the CVE-2022-21894 vulnerability. Analyzing devices compromised with BlackLotus, the Microsoft Incident Response team identified several points in the malware installation and execution process that allow its detection.

5 open source Burp Suite penetration testing extensions you should check outWhen it comes to assessing the security of computer systems, penetration testing tools are critical for identifying vulnerabilities that attackers may exploit. LastPass breach: Hacker accessed corporate vault by compromising senior developer's home PCLastPass is, once again, telling customers about a security incident related to the August 2022 breach of its development environment and subsequent unauthorized access to the company's third-party cloud storage service that hosted backups.

The developers of the BlackLotus UEFI bootkit have improved the malware with Secure Boot bypass capabilities that allow it to infected even fully patched Windows 11 systems. BlackLotus is the first public example of UEFI malware that can avoid the Secure Boot mechanism, thus being able to disable security protections that come with the operating system.

ESET researchers have published the first analysis of a UEFI bootkit capable of circumventing UEFI Secure Boot, a critical platform security feature. "Our investigation started with a few hits on what turned out to be the BlackLotus user-mode component - an HTTP downloader - in our telemetry late in 2022. After an initial assessment, code patterns found in the samples brought us to the discovery of six BlackLotus installers. This allowed us to explore the whole execution chain and to realize that what we were dealing with here is not just regular malware," says Martin Smolár, the ESET researcher who led the investigation into the bootkit.
A stealthy Unified Extensible Firmware Interface bootkit called BlackLotus has become the first publicly known malware capable of bypassing Secure Boot defenses, making it a potent threat in the cyber landscape. "This bootkit can run even on fully up-to-date Windows 11 systems with UEFI Secure Boot enabled," Slovak cybersecurity company ESET said in a report shared with The Hacker News.

Acer has fixed a high-severity vulnerability affecting multiple laptop models that could enable local attackers to deactivate UEFI Secure Boot on targeted systems. Attackers with high privileges can abuse it in low-complexity attacks that require no user interaction to alter UEFI Secure Boot settings by modifying the BootOrderSecureBootDisable NVRAM variable to disable Secure Boot.
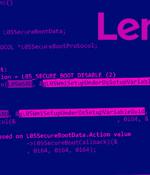
PC maker Lenovo has addressed yet another set of three shortcomings in the Unified Extensible Firmware Interface firmware affecting several Yoga, IdeaPad, and ThinkBook devices. "The vulnerabilities allow disabling UEFI Secure Boot or restoring factory default Secure Boot databases: all simply from an OS," Slovak cybersecurity firm ESET explained in a series of tweets.

Lenovo has fixed two high-severity vulnerabilities impacting various ThinkBook, IdeaPad, and Yoga laptop models that could allow an attacker to deactivate UEFI Secure Boot. UEFI Secure Boot is a verification system that ensures no malicious code can be loaded and executed during the computer boot process.