Security News

Cybersecurity researchers are warning of "Imposter packages" mimicking popular libraries available on the Python Package Index repository. The 41 malicious PyPI packages have been found to pose as typosquatted variants of legitimate modules such as HTTP, AIOHTTP, requests, urllib, and urllib3.

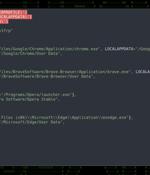
Malicious actors have published more than 451 unique Python packages on the official Python Package Index repository in an attempt to infect developer systems with clipper malware. Targeted web browsers include Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, Brave, and Opera, with the malware modifying browser shortcuts to load the add-on automatically upon launch using the "-load-extension" command line switch.

Four different rogue packages in the Python Package Index have been found to carry out a number of malicious actions, including dropping malware, deleting the netstat utility, and manipulating the SSH authorized keys file. "Most of these packages had well thought out names, to purposely confuse people," Security researcher and journalist Ax Sharma said.
Cybersecurity researchers have unearthed a new Python-based attack campaign that leverages a Python-based remote access trojan to gain control over compromised systems since at least August 2022. LNK files retrieves two text files from a remote server that are subsequently renamed to.

A new Python-based malware has been spotted in the wild featuring remote access trojan capabilities to give its operators control over the breached systems. The PY#RATION malware is distributed via a phishing campaign that uses password-protected ZIP file attachments containing two shortcut.

Dec. 31, 2022, the PyTorch machine learning framework announced on its website that one of its packages had been compromised via the PyPI repository. According to the PyTorch team, a malicious torchtriton dependency package was uploaded to the PyPI code repository on Friday, Dec. 30, 2022, at around 4:40 p.m. The malicious package had the same package name as the one shipped on the PyTorch nightly package index.

An active malware campaign is targeting the Python Package Index and npm repositories for Python and JavaScript with typosquatted and fake modules that deploy a ransomware strain, marking the latest security issue to affect software supply chains. According to Phylum, the rogue packages embed source code that retrieves Golang-based ransomware binary from a remote server depending on the victim's operating system and microarchitecture.

A previously undocumented Python backdoor targeting VMware ESXi servers has been spotted, enabling hackers to execute commands remotely on a compromised system. VMware ESXi is a virtualization platform commonly used in the enterprise to host numerous servers on one device while using CPU and memory resources more effectively.
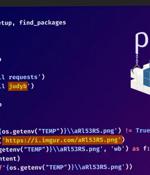
An ongoing supply chain attack has been leveraging malicious Python packages to distribute malware called W4SP Stealer, with over hundreds of victims ensnared to date. "The threat actor is still active and is releasing more malicious packages," Checkmarx researcher Jossef Harush said in a technical write-up, calling the adversary WASP. "The attack seems related to cybercrime as the attacker claims that these tools are undetectable to increase sales."

WASP malware is using steganography and polymorphism to evade detection with malicious Python packages designed to steal credentials, personal information, and cryptocurrency. Researchers from Phylum and Check Point earlier this month reported seeing new malicious packages on PyPI, a package index for Python developers.