Security News

It may come as a surprise to absolutely nobody that experts say, in revealing the most prevalent and likely tactics to meddle with elections this year, that state-sponsored cybercriminals pose the biggest threat. As leaders of major international powers, both of these elections are likely to be targeted by foreign adversaries, and according to security giant Mandiant's latest report on election security trends, defenders should be aware of the four Ds. DDoS attacks, data theft and leaks, disinformation, and deepfakes lead the way as the most likely types of attacks to be trialed during this year's elections, researchers say, all of which have the potential to impact voter outcomes.

The Iran-affiliated threat actor tracked as MuddyWater (aka Mango Sandstorm or TA450) has been linked to a new phishing campaign in March 2024 that aims to deliver a legitimate Remote Monitoring...

An Iran-nexus threat actor known as UNC1549 has been attributed with medium confidence to a new set of attacks targeting aerospace, aviation, and defense industries in the Middle East, including...

Hackers backed by Iran and Hezbollah staged cyber attacks designed to undercut public support for the Israel-Hamas war after October 2023. This includes destructive attacks against key Israeli...

OpenAI has shut down five accounts it asserts were used by government agents to generate phishing emails and malicious software scripts as well as research ways to evade malware detection. "We disrupted five state-affiliated malicious actors: two China-affiliated threat actors known as Charcoal Typhoon and Salmon Typhoon; the Iran-affiliated threat actor known as Crimson Sandstorm; the North Korea-affiliated actor known as Emerald Sleet; and the Russia-affiliated actor known as Forest Blizzard," the OpenAI team wrote.

Iran's anti-Israel cyber operations are providing a window into the techniques the country may deploy in the run-up to the 2024 US Presidential elections, Microsoft says. An analysis of Iran's activity, published by Microsoft Threat Analysis Center today, concluded that Iran may again target US elections as it did in 2020, using more sophisticated techniques from a wealth of different groups.

Hacktivists reportedly disrupted services at about 70 percent of Iran's gas stations in a politically motivated cyberattack. Iran's oil minister Javad Owji confirmed on Monday the IT systems of the nation's petrol stations had been attacked as Iranian media told of long queues at the pumps and traffic jams - particularly in Tehran - as folks tried and failed to fill up.

A group with links to Iran targeted transportation, logistics, and technology sectors in the Middle East, including Israel, in October 2023 amid a surge in Iranian cyber activity since the onset of the Israel-Hamas war. The attacks have been attributed by CrowdStrike to a threat actor it tracks under the name Imperial Kitten, and which is also known as Crimson Sandstorm, TA456, Tortoiseshell, and Yellow Liderc.
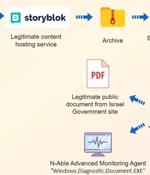
The Iranian nation-state actor known as MuddyWater has been linked to a new spear-phishing campaign targeting two Israeli entities to ultimately deploy a legitimate remote administration tool from...

The Iran-linked OilRig threat actor targeted an unnamed Middle East government between February and September 2023 as part of an eight-month-long campaign. The attack led to the theft of files and...