Security News

Google's latest update to the Chrome browser fixes a varying number of bugs, depending on whether you're on Android, Windows or Mac, and depending on whether you're running the "Stable channel" or the "Extended stable channel". The Stable channel is the very latest version, including all new browser features, currently numbered Chrome 103.

While people were celebrating the Fourth of July holiday in the United States, Google quietly rolled out a stable channel update for Chrome to patch an actively exploited zero-day vulnerability, the fourth such flaw the vendor has had to patch in its browser product so far this year. Chrome 103 for Android and Version 103.0.5060.114 for Windows and Mac, outlined in separate blog posts published Monday, fix a heap buffer overflow flaw in WebRTC, the engine that gives the browser its real-time communications capability.

Google on Monday shipped security updates to address a high-severity zero-day vulnerability in its Chrome web browser that it said is being exploited in the wild. The shortcoming, tracked as CVE-2022-2294, relates to a heap overflow flaw in the WebRTC component that provides real-time audio and video communication capabilities in browsers without the need to install plugins or download native apps.

Google has issued an unexpected update to its Chrome browser to address a zero-day WebRTC flaw that is actively being exploited. The fix is installing Chrome 103.0.5060.114 for Windows and Chrome 103.0.5060.71 for Android, both of which will appear soon.

Google has released Chrome 103.0.5060.114 for Windows users to address a high-severity zero-day vulnerability exploited by attackers in the wild, the fourth Chrome zero-day patched in 2022. This update was available immediately when BleepingComputer checked for new updates by going into Chrome menu > Help > About Google Chrome.
Google on Friday pledged to update its location history system so that visits to medical clinics and similarly sensitive places are automatically deleted. Google keeps a log of its users whereabouts, via its Location History functionality, and provides some controls to delete all or part of those records, or switch it off.
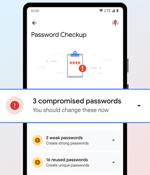
Google on Thursday announced a slew of improvements to its password manager service aimed at creating a more consistent look and feel across different platforms. The updates are also expected to automatically group multiple passwords for the same sites as well as introduce an option to manually add passwords.

One of the commissioners of the U.S. Federal Communications Commission has renewed calls asking for Apple and Google to boot the popular video-sharing platform TikTok from their app stores citing "Its pattern of surreptitious data practices." "It is clear that TikTok poses an unacceptable national security risk due to its extensive data harvesting being combined with Beijing's apparently unchecked access to that sensitive data," Brendan Carr, a Republican member of the FCC, wrote in a letter to Apple and Google's chief executives.

Google's Threat Analysis Group on Thursday disclosed it had acted to block as many as 36 malicious domains operated by hack-for-hire groups from India, Russia, and the U.A.E. In a manner analogous to the surveillanceware ecosystem, hack-for-hire firms equip their clients with capabilities to enable targeted attacks aimed at corporates as well as activists, journalists, politicians, and other high-risk users. "The hack-for-hire landscape is fluid, both in how the attackers organize themselves and in the wide range of targets they pursue in a single campaign at the behest of disparate clients," Shane Huntley, director of Google TAG, said in a report.

Google has added API security tools and Workspace admin alerts about potentially risky configuration changes such as super admin passwords resets. Google's answer to these problems includes two API security features available in preview: one that identifies API misconfigurations and another that detects bots.