Security News
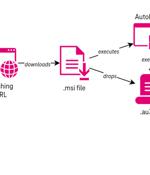
A new malspam campaign has been observed deploying an off-the-shelf malware called DarkGate. "The current spike in DarkGate malware activity is plausible given the fact that the developer of the malware has recently started to rent out the malware to a limited number of affiliates," Telekom Security said in a report published last week.

Genshin Impact developer miHoYohas responded to an in-game hacking situation that has caused problems recently in its player community, warning that they would take legal action against those responsible. Genshin Impact is a massively popular anime-style open-world exploration game available for Android, iOS, PS4, and Windows with over 60 million active players.
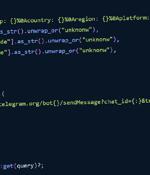
In yet another sign that developers continue to be targets of software supply chain attacks, a number of malicious packages have been discovered on the Rust programming language's crate registry. It's not clear what the end goal of the campaign was, but the suspicious modules were found to harbor functionalities to capture the operating system information and transmit the data to a hard-coded Telegram channel via the messaging platform's API. This suggests that the campaign may have been in its early stages and that the threat actor may have been casting a wide net to compromise as many developer machines as possible to deliver rogue updates with improved data exfiltration capabilities.

More than a dozen malicious packages have been discovered on the npm package repository since the start of August 2023 with capabilities to deploy an open-source information stealer called Luna Token Grabber on systems belonging to Roblox developers. "The malicious packages reproduce code from the legitimate noblox.js package but add malicious, information-stealing functions," software threat researcher Lucija Valentić said in a Tuesday analysis.

Apple last year introduced a security feature called App Management that's designed to prevent one application from modifying another without authorization under macOS Ventura - but a developer claims it's not very good at its job under some circumstances. "If an app is modified by something that isn't signed by the same development team and isn't allowed by an NSUpdateSecurityPolicy, macOS will block the modification and notify the user that an app wants to manage other apps," explained Justin Sagurton of Apple's privacy engineering team, in a video presentation at the fruity computer seller's 2022 Worldwide Developers Conference.

In these fraudulent schemes, criminals either obtain direct access to NFT developer social media accounts or create look-alike accounts to promote "Exclusive" new NFT releases, often employing misleading advertising campaigns that create a sense of urgency to pull them off. "Links provided in these announcements are phishing links directing victims to a spoofed website that appears to be a legitimate extension of a particular NFT project," the FBI said in an advisory last week.

Cybersecurity researchers have discovered a new bunch of malicious packages on the npm package registry that are designed to exfiltrate sensitive developer information. Software supply chain firm...

Google's plans to introduce the Web Environment Integrity API on Chrome has been met with fierce backlash from internet software developers, drawing criticism for limiting user freedom and undermining the core principles of the open web. Google says this is not a privacy risk as it does not enable cross-site user tracking and won't interfere with browser or plugins/extensions functionality.

Apple has announced plans to require developers to submit reasons to use certain APIs in their apps starting later this year with the release of iOS 17, iPadOS 17, macOS Sonoma, tvOS 17, and watchOS 10 to prevent their abuse for data collection. The iPhone maker said it's making the move to ensure that such APIs are not abused by app developers to collect device signals to carry out fingerprinting, which could be employed to uniquely identify users across different apps and websites for other purposes such as targeted advertising.

He sheds light on the significance of positive security culture, the reasons behind recurrent vulnerabilities, strategies for incorporating secure coding training without hampering development processes, the effectiveness of gamified learning experiences, the need for the regular refreshment of secure development training, and innovative methods to encourage developers to improve their secure coding techniques. How important is fostering a security culture within development teams for secure coding practices?