Security News

"The C2 server serves as a botnet-as-a-service controlling nearly 230,000 vulnerable MikroTik routers," Avast's senior malware researcher, Martin Hron, said in a write-up, potentially linking it to what's now called the M?ris botnet. The botnet is known to exploit a known vulnerability in the Winbox component of MikroTik routers, enabling the attackers to gain unauthenticated, remote administrative access to any affected device.

ASUS routers have emerged as the target of a nascent botnet called Cyclops Blink, almost a month after it was revealed the malware abused WatchGuard firewall appliances as a stepping stone to gain remote access to breached networks. Intelligence agencies from the U.K. and the U.S. have characterized Cyclops Blink as a replacement framework for VPNFilter, another malware that has exploited network devices, primarily small office/home office routers, and network-attached storage devices.

The modular botnet known as Cyclops Blink, linked to the same advanced persistent threat behind the NotPetya wiper attacks, is expanding its device targeting to include ASUS routers. "Our investigation shows that there are more than 200 Cyclops Blink victims around the world. Typical countries of infected WatchGuard devices and ASUS routers are the United States, India, Italy, Canada, and a long list of other countries, including Russia."
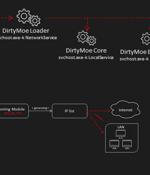
"The worming module targets older well-known vulnerabilities, e.g., EternalBlue and Hot Potato Windows privilege escalation," Avast researcher Martin Chlumecký said in a report published Wednesday. "One worm module can generate and attack hundreds of thousands of private and public IP addresses per day; many victims are at risk since many machines still use unpatched systems or weak passwords."

A new Linux botnet is using the infamous Log4j vulnerability to install rootkits and steal data. Researchers at Chinese internet security company Qihoo's 360's Network Security Research Lab discovered the botnet family, which they dubbed B1txor20, as it was infecting new hosts via the Log4j vulnerability.
First observed propagating through the Log4j vulnerability on February 9, 2022, the malware leverages a technique called DNS tunneling to build communication channels with command-and-control servers by encoding data in DNS queries and responses. B1txor20, while also buggy in some ways, currently supports the ability to obtain a shell, execute arbitrary commands, install a rootkit, open a SOCKS5 proxy, and functions to upload sensitive information back to the C2 server.

The newly found malware, dubbed B1txor20 by researchers at Qihoo 360's Network Security Research Lab, focuses its attacks on Linux ARM, X64 CPU architecture devices. The botnet uses exploits targeting the Log4J vulnerability to infect new hosts, a very appealing attack vector seeing that dozens of vendors use the vulnerable Apache Log4j logging library.

The Qakbot botnet is getting more dangerous, sinking its fangs into email threads and injecting malicious modules to pump up the core botnet's powers. On Thursday, Sophos published a deep dive into the botnet, describing how researchers have recently seen it spreading through email thread hijacking - an attack in which malware operators malspam replies to ongoing email threads.

The insidious Emotet botnet, which staged a return in November 2021 after a 10-month-long hiatus, is once again exhibiting signs of steady growth, amassing a swarm of over 100,000 infected hosts for perpetrating its malicious activities."While Emotet has not yet attained the same scale it once had, the botnet is showing a strong resurgence with a total of approximately 130,000 unique bots spread across 179 countries since November 2021," researchers from Lumen's Black Lotus Labs said in a report.

Hey webop geeks, you are already dead, a note claiming to be left by the REvil ransomware gang declared, embedded into the attack itself as a string of text in the URL for the extortion demand. In a post that detailed mitigation of a recent attack that hit up to 2.5 Mrps on a single website, Imperva's Nelli Klepfish shared several chest-thumping ransom notes - a screen capture of one is included below - that its targeted customer received before the attack started.