Security News

A high-severity security flaw has been disclosed in the Python URL parsing function that could be exploited to bypass domain or protocol filtering methods implemented with a blocklist, ultimately resulting in arbitrary file reads and command execution. "Urlparse has a parsing problem when the entire URL starts with blank characters," the CERT Coordination Center said in a Friday advisory.

CEO, fresh with funds, lays out the dependency dilemma Interview Open source security biz Socket is extending its source code dependency checker, which previously addressed only JavaScript and...

Python security fixes often happen through "Silent" code commits, without an associated Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures identifier, according to a group of computer security researchers. In a preprint paper titled, "Exploring Security Commits in Python," Shiyu Sun, Shu Wang, Xinda Wang, Yunlong Xing, Kun Sun from George Mason University, and Elisa Zhang from Dougherty Valley High School, all in the United States, propose a remedy: a database of security commits called PySecDB to make Python code repairs more visible to the community.

A new fileless attack dubbed PyLoose has been observed striking cloud workloads with the goal of delivering a cryptocurrency miner, new findings from Wiz reveal. "The attack consists of Python code that loads an XMRig Miner directly into memory using memfd, a known Linux fileless technique," security researchers Avigayil Mechtinger, Oren Ofer, and Itamar Gilad said.

A security researcher and system administrator has developed a tool that can help users check for manifest mismatches in packages from the NPM JavaScript software registry. The problem is with the inconsistent information between a package's manifest data as displayed in the NPM registry and the data present in the 'package.

Researchers have discovered a novel attack on the Python Package Index repository that employs compiled Python code to sidestep detection by application security tools. PYC files are compiled bytecode files that are generated by the Python interpreter when a Python program is executed.
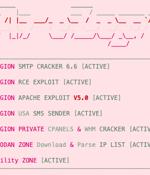
An emerging Python-based credential harvester and a hacking tool named Legion is being marketed via Telegram as a way for threat actors to break into various online services for further exploitation. The malware is suspected to be linked to another malware family called AndroxGh0st that was first documented by cloud security services providerLacework in December 2022.

A malicious Python package on the Python Package Index repository has been found to use Unicode as a trick to evade detection and deploy an info-stealing malware. The package in question, named onyxproxy, was uploaded to PyPI on March 15, 2023, and comes with capabilities to harvest and exfiltrate credentials and other valuable data.

A malicious Python package on PyPI uses Unicode as an obfuscation technique to evade detection while stealing and exfiltrating developers' account credentials and other sensitive data from compromised devices. The malicious package, named "Onyxproxy," uses a combination of different Unicode fonts in the source code to help it bypass automated scans and defenses that identify potentially malicious functions based on string matching.

A malicious Python package uploaded to the Python Package Index has been found to contain a fully-featured information stealer and remote access trojan. The package, named colourfool, was identified by Kroll's Cyber Threat Intelligence team, with the company calling the malware Colour-Blind.