Security News
A new set of trojanized apps spread via the Google Play Store has been observed distributing the notorious Joker malware on compromised Android devices. Despite continued attempts on the part of Google to scale up its defenses, the apps have been continually iterated to search for gaps and slip into the app store undetected.

Google is rolling out a new Data Safety section on the Play Store, Android's official app repository, where developers must declare what data their software collects from users of their apps. Not only will developers declare what data they collect, but also what data they share with third parties, essentially disclosing the purpose behind the collection.
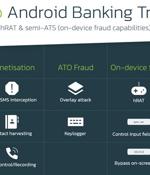
A number of rogue Android apps that have been cumulatively installed from the official Google Play Store more than 50,000 times are being used to target banks and other financial entities. Like other Android banking trojans, the rogue apps are nothing more than droppers, whose primary function is to deploy the malicious payload embedded within them.
As many as seven malicious Android apps discovered on the Google Play Store masqueraded as antivirus solutions to deploy a banking trojan called SharkBot. "SharkBot steals credentials and banking information," Check Point researchers Alex Shamshur and Raman Ladutska said in a report shared with The Hacker News.

Security researchers tracking the mobile app ecosystem have noticed a recent spike in trojan infiltration on the Google Play Store, with one of the apps having over 500,000 installs and available to download. Most of these apps belong to a family of trojan malware used in various scams, resulting in financial losses and also loss of sensitive personal information. The threats discovered on the Play Store by Dr. Web's analysts include cryptocurrency management apps, social benefit aid tools, Gasprom investment clones, photo editors, and a launcher themed after iOS 15.
The threat actor behind a nascent Android banking trojan named SharkBot has managed to evade Google Play Store security barriers by masquerading as an antivirus app. Where SharkBot stands apart is in its ability to carry out the unauthorized transactions via Automatic Transfer Systems, which stands in contrast to TeaBot, which requires a live operator to interact with the infected devices to conduct the malicious activities.
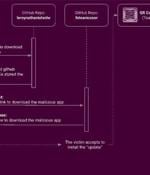
An Android banking trojan designed to steal credentials and SMS messages has been observed sneaking past Google Play Store protections to target users of more than 400 banking and financial apps from Russia, China, and the U.S. "TeaBot RAT capabilities are achieved via the device screen's live streaming plus the abuse of Accessibility Services for remote interaction and key-logging," Cleafy researchers said in a report. Also known by the name Anatsa, TeaBot first emerged in May 2021, camouflaging its malicious functions by posing as seemingly innocuous PDF document and QR code scanner apps that are distributed via the official Google Play Store instead of third-party apps stores or via fraudulent websites.

The TeaBot banking trojan - also known as "Anatsa" - has been spotted on the Google Play store, researchers from Cleafy have discovered. Hank Schless, senior manager of security solutions at Lookout, explained via email that attackers "Usually stick to utility apps like QR code scanners, flashlights, photo filters, or PDF scanners because these are apps that people download out of necessity and likely won't put as much time into looking at reviews that might impact their decision to download.".

The TeaBot banking trojan was spotted once again in Google Play Store where it posed as a QR code app and spread to more than 10,000 devices. The trojanized apps include the promised functionality, so user reviews on the Play Store are positive.
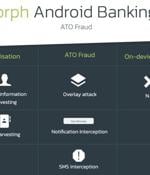
A new Android banking trojan with over 50,000 installations has been observed distributed via the official Google Play Store with the goal of targeting 56 European banks and carrying out harvesting sensitive information from compromised devices. Xenomorph, like Alien and ERMAC, is yet another example of an Android banking trojan that's focused on circumventing Google Play Store's security protections by masquerading as productivity apps such as "Fast Cleaner" to trick unaware victims into installing the malware.