Security News

The threat actor behind the information-stealing malware known as Typhon Reborn has resurfaced with an updated version that packs in improved capabilities to evade detection and resist analysis. Based on another stealer malware called Prynt Stealer, Typhon is also capable of delivering the XMRig cryptocurrency miner.
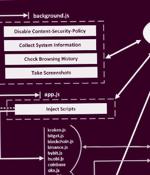
Chromium-based web browsers are the target of a new malware called Rilide that masquerades itself as a seemingly legitimate extension to harvest sensitive data and siphon cryptocurrency. "Rilide malware is disguised as a legitimate Google Drive extension and enables threat actors to carry out a broad spectrum of malicious activities, including monitoring."

The threat actor known as Arid Viper has been observed using refreshed variants of its malware toolkit in its attacks targeting Palestinian entities since September 2022. Also known by the names APT-C-23 and Desert Falcon, the hacking group has been linked to attacks aimed at Palestine and the Middle East at least since 2014.

eFile.com, an IRS-authorized e-file software service provider used by many for filing their tax returns, has been caught serving JavaScript malware. Security researchers state the malicious JavaScript file existed on eFile.com website for weeks.

A piece of new information-stealing malware called OpcJacker has been spotted in the wild since the second half of 2022 as part of a malvertising campaign. "OpcJacker's main functions include keylogging, taking screenshots, stealing sensitive data from browsers, loading additional modules, and replacing cryptocurrency addresses in the clipboard for hijacking purposes," Trend Micro researchers Jaromir Horejsi and Joseph C. Chen said.

Automated malware campaigns will drastically change the reaction speed of malware gangs. The technology to run malware campaigns and automatically bypass new defenses is most definitely doable nowadays, but thus far, we haven't seen anything of the kind.

The AlienFox toolkit is being hawked on Telegram as a way to compromise misconfigured hosts on cloud services platforms and harvest sensitive information like API keys and other secrets, according to security shop SentinelOne. While the AlienFox scripts can be used against a range of web services, they primarily target cloud-based and software-as-a-service email hosting services, Delamotte wrote.

Multiple malware botnets actively target Cacti and Realtek vulnerabilities in campaigns detected between January and March 2023, spreading ShellBot and Moobot malware. The targeted flaws are CVE-2021-35394, a critical remote code execution vulnerability in Realtek Jungle SDK, and CVE-2022-46169, a critical command injection flaw in the Cacti fault management monitoring tool.
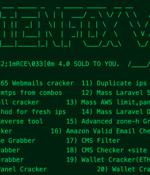
A new "Comprehensive toolset" called AlienFox is being distributed on Telegram as a way for threat actors to harvest credentials from API keys and secrets from popular cloud service providers. "The spread of AlienFox represents an unreported trend towards attacking more minimal cloud services, unsuitable for crypto mining, in order to enable and expand subsequent campaigns," SentinelOne security researcher Alex Delamotte said in a report shared with The Hacker News.

Google Cloud's recently acquired security outfit Mandiant has named a new nasty from North Korea: a cyber crime gang it calls APT43 and accuses of a five-year rampage. "Mandiant assesses with high confidence that APT43 is a moderately sophisticated cyber operator that supports the interests of the North Korean regime," states a report on the gang released on Wednesday.