Security News
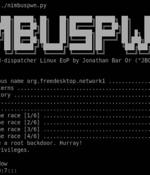
Microsoft on Tuesday disclosed a set of two privilege escalation vulnerabilities in the Linux operating system that could potentially allow threat actors to carry out an array of nefarious activities. Collectively called "Nimbuspwn," the flaws "Can be chained together to gain root privileges on Linux systems, allowing attackers to deploy payloads, like a root backdoor, and perform other malicious actions via arbitrary root code execution," Jonathan Bar Or of the Microsoft 365 Defender Research Team said in a report.

How well do your Linux security practices stack up in today's challenging operating environment? Are you following the correct processes to keep systems up-to-date and protected against the latest threats? Now you can find out thanks to research independently conducted by the Ponemon Institute. The research sponsored by TuxCare sought to understand better how organizations are currently managing the security and stability of their Linux-based systems.

Readers will be introduced to their own virtual hacking lab and will learn about different flavors of Kali Linux installed onto different platforms. This book is suitable for those who are passionate about securing things in an offensive way and can be useful for aspiring red teamers.

How many times have you been working on a Linux server and wished you had the means to safely store passwords? Having such a feature available to your headless servers would be such a time saver. SEE: Password breach: Why pop culture and passwords don't mix.

The Hive ransomware operation has converted their VMware ESXi Linux encryptor to the Rust programming language and added new features to make it harder for security researchers to snoop on victim's ransom negotiations. Ransomware gang's Linux encryptors typically target the VMware ESXI virtualization platforms as they are the most commonly used in the enterprise.

In kernel version 5.17, both /dev/random and /dev/urandom have been replaced with a new — identical — algorithm based on the BLAKE2 hash function, which is an excellent security improvement.

A new Linux botnet is using the infamous Log4j vulnerability to install rootkits and steal data. Researchers at Chinese internet security company Qihoo's 360's Network Security Research Lab discovered the botnet family, which they dubbed B1txor20, as it was infecting new hosts via the Log4j vulnerability.
First observed propagating through the Log4j vulnerability on February 9, 2022, the malware leverages a technique called DNS tunneling to build communication channels with command-and-control servers by encoding data in DNS queries and responses. B1txor20, while also buggy in some ways, currently supports the ability to obtain a shell, execute arbitrary commands, install a rootkit, open a SOCKS5 proxy, and functions to upload sensitive information back to the C2 server.

With attackers increasingly deploying automated attack methods, default credentials are the most common passwords used by these bad actors, acting in effect as a 'skeleton key' for criminal access. Default credentials providing an entry point for attackers.

Network-attached storage appliance maker QNAP on Monday warned of a recently disclosed Linux vulnerability affecting its devices that could be abused to elevate privileges and gain control of affected systems. "A local privilege escalation vulnerability, also known as 'Dirty Pipe,' has been reported to affect the Linux kernel on QNAP NAS running QTS 5.0.x and QuTS hero h5.0.x," the company said.