Security News

Several distributed denial-of-service botnets have been observed exploiting a critical flaw in Zyxel devices that came to light in April 2023 to gain remote control of vulnerable systems. "Through the capture of exploit traffic, the attacker's IP address was identified, and it was determined that the attacks were occurring in multiple regions, including Central America, North America, East Asia, and South Asia," Fortinet FortiGuard Labs researcher Cara Lin said.
A new malware strain has been found covertly targeting small office/home office routers for more than two years, infiltrating over 70,000 devices and creating a botnet with 40,000 nodes spanning 20 countries. Lumen Black Lotus Labs has dubbed the malware AVrecon, making it the third such strain to focus on SOHO routers after ZuoRAT and HiatusRAT over the past year.

Since at least May 2021, stealthy Linux malware called AVrecon was used to infect over 70,000 Linux-based small office/home office routers to a botnet designed to steal bandwidth and provide a hidden residential proxy service. According to Lumen's Black Lotus Labs threat research team, while the AVrecon remote access trojan compromised over 70,000 devices, only 40,000 were added to the botnet after gaining persistence.

Since at least May 2021, stealthy Linux malware called AVrecon was used to infect over 70,000 Linux-based small office/home office routers to a botnet designed to steal bandwidth and provide a hidden residential proxy service. According to Lumen's Black Lotus Labs threat research team, while the AVrecon remote access trojan compromised over 70,000 devices, only 40,00 were added to the botnet after gaining persistence.
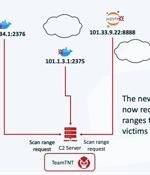
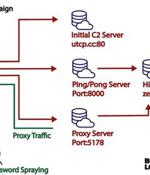
As many as 196 hosts have been infected as part of an aggressive cloud campaign mounted by the TeamTNT group called Silentbob. "The botnet run by TeamTNT has set its sights on Docker and Kubernetes environments, Redis servers, Postgres databases, Hadoop clusters, Tomcat and Nginx servers, Weave Scope, SSH, and Jupyter applications," Aqua security researchers Ofek Itach and Assaf Morag said in a report shared with The Hacker News.

A variant of the Mirai botnet is targeting almost two dozen vulnerabilities aiming to take control of D-Link, Arris, Zyxel, TP-Link, Tenda, Netgear, and MediaTek devices to use them for distributed denial-of-service attacks. In total, the malware targets no less than 22 known seccurity issues in various connected products, which include routers, DVRs, NVRs, WiFi communication dongles, thermal monitoring systems, access control systems, and solar power generation monitors.

A new malware called Condi has been observed exploiting a security vulnerability in TP-Link Archer AX21 Wi-Fi routers to rope the devices into a distributed denial-of-service botnet. "The Telegram channel was started in May 2022, and the threat actor has been monetizing its botnet by providing DDoS-as-a-service and selling the malware source code," security researchers Joie Salvio and Roy Tay said.

A new DDoS-as-a-Service botnet called "Condi" emerged in May 2023, exploiting a vulnerability in TP-Link Archer AX21 Wi-Fi routers to build an army of bots to conduct attacks. Condi aims to enlist new devices to create a powerful DDoS botnet that can be rented to launch attacks on websites and services.

An unknown threat actor is brute-forcing Linux SSH servers to install a wide range of malware, including the Tsunami DDoS bot, ShellBot, log cleaners, privilege escalation tools, and an XMRig coin miner. Network administrators typically use SSH to manage Linux devices remotely, performing tasks such as running commands, changing the configuration, updating software, and troubleshooting problems.

Cybersecurity researchers have discovered previously undocumented payloads associated with a Romanian threat actor named Diicot, revealing its potential for launching distributed denial-of-service attacks. "The Diicot name is significant, as it's also the name of the Romanian organized crime and anti-terrorism policing unit," Cado Security said in a technical report.