Security News > 2022 > September > Brazilian Prilex Hackers Resurfaced With Sophisticated Point-of-Sale Malware
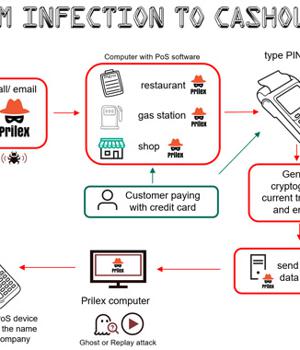
A Brazilian threat actor known as Prilex has resurfaced after a year-long operational hiatus with an advanced and complex malware to steal money by means of fraudulent transactions.
"The Prilex group has shown a high level of knowledge about credit and debit card transactions, and how software used for payment processing works," Kaspersky researchers said.
The cybercrime group emerged on the scene with ATM-focused malware attacks in the South American nation, providing it the ability to break into ATM machines to perform jackpotting - a type of attack aiming to dispense cash illegitimately - and clone thousands of credit cards to steal funds from the targeted bank's customers.
Known to be active since 2014, the operators are also adept at carrying out EMV replay attacks in which traffic from a legitimate EMV-based chip card transaction is captured and replayed to a payment processor like Mastercard, but with the transaction fields modified to include stolen card data.
The method, called GHOST transactions, includes a stealer component that grabs all communications between the PoS software and the PIN pad used for reading the card during the transaction with the goal of obtaining the card information.
While previous versions of Prilex circumvented these security measures by monitoring the ongoing transaction to get the cryptogram and conduct a replay attack using the collected "Signature," the GHOST attack requests for new EMV cryptograms that are put to use to complete the rogue transactions.
News URL
https://thehackernews.com/2022/09/brazilian-prilex-hackers-resurfaced.html
Related news
- Chinese FamousSparrow hackers deploy upgraded malware in attacks (source)
- North Korean Hackers Deploy BeaverTail Malware via 11 Malicious npm Packages (source)
- Chinese Hackers Target Linux Systems Using SNOWLIGHT Malware and VShell Tool (source)
- State-Sponsored Hackers Weaponize ClickFix Tactic in Targeted Malware Campaigns (source)
- Chinese hackers target Russian govt with upgraded RAT malware (source)
- Hackers Abuse Russian Bulletproof Host Proton66 for Global Attacks and Malware Delivery (source)
- Iran-Linked Hackers Target Israel with MURKYTOUR Malware via Fake Job Campaign (source)
- North Korean Hackers Spread Malware via Fake Crypto Firms and Job Interview Lures (source)