Security News

Mozilla is rolling out a forced upgrade for Thunderbird 78.x users, getting everyone aboard version 91, the latest stable release that came out in August. If you were sticking with version 78.x thus far, it's likely that you were doing so for reasons of stability and add-on compatibility.

Mozilla is running a study to test users' responses to changing the default Firefox search engine to Microsoft Bing. Like all browsers, Mozilla Firefox automatically configures a browser to a default search engine for performing searches via the address bar.

Mozilla has launched an experiment where they change the Firefox browser user agent to a three-digit "Firefox/100.0" version to see if it will break websites. The current user agent for Mozilla Firefox version 90 is listed below.


Mozilla has a new privacy-focused data sharing platform that provides users with increased control of their data and also allows them to contribute to a better Internet. Built in collaboration with Princeton University researchers, the new Mozilla Rally allows users to select who they want to share their browsing data with, the browser maker says.

Essentially, FLoC allows marketers to guess users' interests without having to uniquely identify them, thereby eliminating the privacy implications associated with tailored advertising, which currently relies on techniques such as tracking cookies and device fingerprinting that expose users' browsing history across sites to advertisers or ad platforms. FLoC sidesteps the cookie with a new "Cohort" identifier wherein users are bucketed into clusters based on similar browsing behaviors.

Google, Microsoft, Apple, and Mozilla have launched the WebExtensions Community Group to collaborate on standardizing browser extensions to enhance both security and performance. "With multiple browsers adopting a broadly compatible model for extensions in the last few years, the WECG is excited to explore how browser vendors and other interested parties can work together to advance a common browser extension platform," the browser vendors said.

Mozilla advises Firefox users to update to the latest released version to avoid experiencing video streaming issues after Google updates the Widevine digital rights management on May 31. Once Google updates the Widevine private encryption keys and content decryption module on May 31, video streaming services using Google's DRM-protection technology will no longer work with older Firefox versions.

Mozilla Thunderbird spent the last couple of months saving some users' OpenPGP keys in plain text - but that's now been patched, the author of both the bug and the patch fixing it has told The Register. The vulnerability, assessed as "Low" impact by Mozilla, existed in the free open source Thunderbird email client between version 78.8.1 and version 78.10.1 after a crestfallen maintainer realised carefully designed protections were in fact not protecting users' private OpenPGP keys.
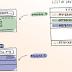
Mozilla has begun rolling out a new security feature for its Firefox browser in nightly and beta channels that aims to protect users against a new class of side-channel attacks from malicious sites. "This fundamental redesign of Firefox's Security architecture extends current security mechanisms by creating operating system process-level boundaries for all sites loaded in Firefox for Desktop," Mozilla said in a statement.