Security News
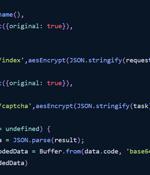
The npm package registry has emerged as the target of yet another highly targeted attack campaign that aims to entice developers into downloading malevolent modules. Software supply chain security firm Phylum told The Hacker News the activity exhibits similar behaviors to that of a previous attack wave uncovered in June, which has since been linked to North Korean threat actors.

The Discord.io custom invite service has temporarily shut down after suffering a data breach exposing the information of 760,000 members. The most sensitive information in the breach is a member's username, email address, billing address, salted and hashed password, and Discord ID. "This information is not private and can be obtained by anyone sharing a server with you. Its inclusion in the breach does mean that other people might be able to link your Discord account to a given email address," Discord.io explained about the leaking of Discord IDs.

The U.S. government released a report after analyzing simple techniques, e.g. SIM swapping, used by the Lapsus$ extortion group to breach dozens of organizations with a strong security posture. The group used SIM swapping to gain access to a target company's internal network and steal confidential information like source code, details about proprietary technology, or business and customer-related documents.

A cyberespionage group named 'MoustachedBouncer' has been observed using adversary-in-the-middle (AitM) attacks at ISPs to hack foreign embassies in Belarus. [...]

Ukraine is warning of a wave of attacks targeting state organizations using 'Merlin,' an open-source post-exploitation and command and control framework. Merlin is a Go-based cross-platform post-exploitation toolkit available for free via GitHub, offering extensive documentation for security professionals to use in red team exercises.

Multiple zero-day vulnerabilities named 'BitForge' in the implementation of widely used cryptographic protocols like GG-18, GG-20, and Lindell 17 affected popular cryptocurrency wallet providers, including Coinbase, ZenGo, Binance, and many more. Today, the analysts publicly disclosed BitForge in the "Small Leaks, Billions Of Dollars: Practical Cryptographic Exploits That Undermine Leading Crypto Wallets" BlackHat presentation, by which time Coinbase and ZenGo have applied fixes to address the problem.

Google has changed the Google Chrome security updates schedule from bi-weekly to weekly to address the growing patch gap problem that allows threat actors extra time to exploit published n-day and...
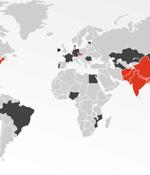
Active since 2019, some of the prominent sectors targeted by the prolific actor encompass academia, aerospace, government, media, telecommunications, and research. A majority of the victims during the period were government organizations.

North Korean state-sponsored hackers have breached Russian missile maker NPO Mashinostroyeniya, according to SentinelLabs researchers. The researchers came across leaked email communication between NPO Mashinostroyeniya's IT staff that contained information about a possible cyber intrusion first detected in May 2022.
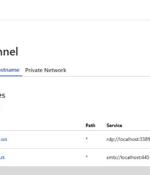
New research has revealed that threat actors are abusing Cloudflare Tunnels to establish covert communication channels from compromised hosts and retain persistent access. "Cloudflared is functionally very similar to ngrok," Nic Finn, a senior threat intelligence analyst at GuidePoint Security, said.