Security News
Google has officially begun its rollout of Privacy Sandbox in the Chrome web browser to a majority of its users, nearly four months after it announced the plans. "We believe it is vital to both improve privacy and preserve access to information, whether it's news, a how-to-guide, or a fun video," Anthony Chavez, vice president of Privacy Sandbox initiatives at Google, said.

The Chaes malware has returned as a new, more advanced variant that includes a custom implementation of the Google DevTools protocol for direct access to the victim's browser functions, allowing it to steal data using WebSockets. A new feature that stands out is Chaes' use of the Chrome DevTools Protocol to steal data from the web browser, including the real-time modification of web pages, execution of JavaScript code, debugging, network request management, memory management, cookie and cache management, and more.

Google is testing a new feature in the Chrome browser that will warn users when an installed extension has been removed from the Chrome Web Store, usually indicative of it being malware. The problem is that these extensions are churned out quickly, with the developers releasing new ones just as Google removes old ones from the Chrome Web Store.
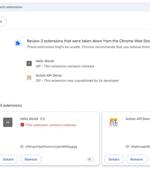
Google has announced plans to add a new feature in the upcoming version of its Chrome web browser to alert users when an extension they have installed has been removed from the Chrome Web Store. The feature, set for release alongside Chrome 117, allows users to be notified when an add-on has been unpublished by a developer, taken down for violating Chrome Web Store policy, or marked as malware.

The Chocolate Factory is doing so because some day, many very bright people believe, quantum computers will be able to break at least some legacy encryption schemes. Google in 2019 said it had conducted an experiment that demonstrated quantum supremacy - the idea that a quantum computer could outperform a classical one.

Google is set to improve Chrome by introducing a new "Link Preview" feature. Link Preview allows users to view a small popup web page preview simply by clicking or hovering over a hyperlink.

Google's Chrome 115 has a new feature that allows users to use Windows Mica material, a design element that enhances user personalization. Mica is a distinctive design feature that doesn't just stay opaque but fuses with the user's desktop theme and wallpaper.

Malwarebytes confirmed today that the Windows 11 22H2 KB5027231 cumulative update released this Patch Tuesday breaks Google Chrome on its customers' systems. The company published a support article today confirming the Malwarebytes conflict with Google Chrome after installing the June 2023 Patch Tuesday updates on Windows 11 systems.

Google Chrome is getting new security-enhancing features for the built-in Password Manager, making it easier for users to manage their passwords and stay safe from account hijacking attacks. The Chrome Password Manager is an integrated part of Google's services that can manage and autofill credentials on the Chrome browser and other Google software products, syncing the login information across all apps used by the same Google Account.
In September 2023, Google Chrome will stop showing the lock icon when a site loads over HTTPS, partly due to the now ubiquitous use of the protocol. "We redesigned the lock icon in 2016 after our research showed that many users misunderstood what the icon conveyed. Despite our best efforts, our research in 2021 showed that only 11% of study participants correctly understood the precise meaning of the lock icon," the team explained.