Security News

According to Google, this new version includes 24 security fixes, though none of them are reported as "In-the-wild", which means that there weren't any zero-days patched this time. Suddenly, bug-free code elsewhere in the program behaves as if it were buggy itself, thanks to the flaw in your code that just invalidated what was in memory.

Chrome version 104 accidentally introduced a bug that removes the user requirement to approve clipboard writing events from websites they visit. When the user tries to make a payment and copies the wallet address to the clipboard, the website can write to the clipboard the threat actor's address.
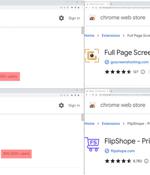
Five imposter extensions for the Google Chrome web browser masquerading as Netflix viewers and others have been found to track users' browsing activity and profit of retail affiliate programs. "The extensions offer various functions such as enabling users to watch Netflix shows together, website coupons, and taking screenshots of a website," McAfee researchers Oliver Devane and Vallabh Chole said.

Threat analysts at McAfee found five Google Chrome extensions that steal track users' browsing activity. Collectively, the extensions have been downloaded more then 1.4 million times.

Google Chrome extension 'Internet Download Manager' installed by more than 200,000 users is adware. Although the extension may install a known and legitimate download manager program, BleepingComputer observed unwanted behavior exhibited by the extension-such as opening links to spammy sites, changing the default browser search engine, and further hounding the user with pop-ups asking them to download more "Patches" and unwanted programs.

Google Chrome extension 'Internet Download Manager' installed by more than 200,000 users is adware. Although the extension may install a known and legitimate download manager program, BleepingComputer observed unwanted behavior exhibited by the extension-such as opening links to spammy sites, changing the default browser search engine, and further hounding the user with pop-ups asking them to download more "Patches" and unwanted programs.

Google has patched the fifth actively exploited zero-day vulnerability discovered in Chrome this year as one in a series of fixes included in a stable channel update released Wednesday. Google credits Ashley Shen and Christian Resell of its Google Threat Analysis Group for reporting the zero-day bug, which could allow for arbitrary code execution, on July 19.

The latest update to Google's Chrome browser is out, bumping the four-part version number to 104.0.5112.101, or to 104.0.5112.102. Chrome will probably update itself, but we always recommend checking anyway.

Google on Tuesday rolled out patches for Chrome browser for desktops to contain an actively exploited high-severity zero-day flaw in the wild. Security researchers Ashley Shen and Christian Resell of Google Threat Analysis Group have been credited with reporting the flaw on July 19, 2022.

Google has released a security update for the Chrome browser that addresses close to a dozen vulnerabilities, including a zero-day flaw that is being exploited in the wild. The security update is currently rolling out for Windows, Mac and Linux.