Security News

An unknown threat actor is leveraging malicious npm packages to target developers with an aim to steal source code and configuration files from victim machines, a sign of how threats lurk consistently in open-source repositories. They have continuously published malicious packages."

More than a dozen malicious packages have been discovered on the npm package repository since the start of August 2023 with capabilities to deploy an open-source information stealer called Luna Token Grabber on systems belonging to Roblox developers. "The malicious packages reproduce code from the legitimate noblox.js package but add malicious, information-stealing functions," software threat researcher Lucija Valentić said in a Tuesday analysis.
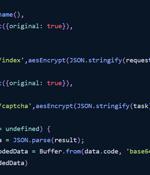
The npm package registry has emerged as the target of yet another highly targeted attack campaign that aims to entice developers into downloading malevolent modules. Software supply chain security firm Phylum told The Hacker News the activity exhibits similar behaviors to that of a previous attack wave uncovered in June, which has since been linked to North Korean threat actors.

Cybersecurity researchers have discovered a new bunch of malicious packages on the npm package registry that are designed to exfiltrate sensitive developer information. Software supply chain firm...

A security researcher and system administrator has developed a tool that can help users check for manifest mismatches in packages from the NPM JavaScript software registry. The problem is with the inconsistent information between a package's manifest data as displayed in the NPM registry and the data present in the 'package.

Manifest confusion occurs there is an inconsistency between a package's manifest information presented on the npm registry and the actual 'package. Json' file in the tarball of the published npm package used when the package is installed.

The npm Public Registry, a database of JavaScript packages, fails to compare npm package manifest data with the archive of files that data describes, creating an opportunity for the installation and execution of malicious files. "The npm Public Registry does not validate manifest information with the contents of the package tarball, relying instead on npm-compatible clients to interpret and enforce validation/consistency," Clarke explains.

Cybersecurity researchers have discovered a new ongoing campaign aimed at the npm ecosystem that leverages a unique execution chain to deliver an unknown payload to targeted systems. "The packages in question seem to be published in pairs, each pair working in unison to fetch additional resources which are subsequently decoded and/or executed," software supply chain security firm Phylum said in a report released last week.

Researchers have discovered multiple npm packages named after NodeJS libraries that even pack a Windows executable that resembles NodeJS but instead drops a sinister trojan. These packages, given their stealthiness and a very low detection rate, had been present on npm for over two months prior to their detection by the researchers.

Researchers have discovered multiple npm packages named after NodeJS libraries that even pack a Windows executable that resembles NodeJS but instead drops a sinister trojan. These packages, given their stealthiness and a very low detection rate, had been present on npm for over two months prior to their detection by the researchers.