Security News

Two malicious packages discovered on the npm package registry have been found to leverage GitHub to store Base64-encrypted SSH keys stolen from developer systems on which they were installed. The...

A malicious package uploaded to the npm registry has been found deploying a sophisticated remote access trojan on compromised Windows machines. The package, named "oscompatible," was published on...

Since these 3,000+ packages manage to include every single npm package on the npmjs.com registry as their dependency, npm package authors who have ever published to the npm registry would now be unable to remove their packages at will, because of npm's policy. Everything prevents you from unpublishing your packages.

A blockchain developer shares his ordeal over the holidays when he was approached on LinkedIn by a "Recruiter" for a web development job. The recruiter in question asked the developer to download npm packages from a GitHub repository, and hours later the developer discovered his MetaMask wallet had been emptied.

A new set of 48 malicious npm packages have been discovered in the npm repository with capabilities to deploy a reverse shell on compromised systems. "These packages, deceptively named to appear...

A new deceptive package hidden within the npm package registry has been uncovered deploying an open-source rootkit called r77, marking the first time a rogue package has delivered rootkit...

Nearly three dozen counterfeit packages have been discovered in the npm package repository that are designed to exfiltrate sensitive data from developer systems, according to findings from...

A stream of malicious npm and PyPi packages have been found stealing a wide range of sensitive data from software developers on the platforms. The campaign started on September 12, 2023, and was first discovered by Sonatype, whose analysts unearthed 14 malicious packages on npm.
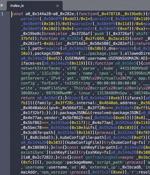
Cybersecurity researchers have discovered a fresh batch of malicious packages in the npm package registry that are designed to exfiltrate Kubernetes configurations and SSH keys from compromised...

My colleague and Sonatype senior software engineer Lex Vorona came across not one but several npm packages that do not strictly follow naming conventions, or have rather striking names. That means, the package itself is called "-" but published under an oddly named scope "!-!" giving it a funky moniker altogether.