Security News

Google has won a lawsuit filed against two Russian nationals in connection with the operation of a botnet called Glupteba, the company said last week. The defendants' move to press sanctions against Google was denied.

Google sued Dmitry Starovikov and Alexander Filippov - along with 15 other John and Jane Does - in December 2021, saying in the original complaint [PDF] that the botnet "Is distinguished from conventional botnets in its technical sophistication: unlike other botnets, the Glupteba botnet leverages blockchain technology to protect itself from disruption." Judge Cote said in her opinion and order [PDF] that the Defendants had "Attempted to negotiate a discovery plan in bad faith, requesting an exchange of electronic devices" - although they knew they could not provide the devices they said they had. According to the judge, the defendants and their lawyer told Google that pertinent discovery information was held by their former employer Valtron LLC,, a limited liability company based in Moscow.

A Ukrainian national who has been wanted by the U.S for over a decade has been arrested by Swiss authorities for his role in a notorious cybercriminal ring that stole millions of dollars from victims' bank accounts using malware called Zeus. According to court documents released by the U.S. Depart of Justice in 2014, Penchukov and eight other members of the cybercriminal group infected "Thousands of business computers" with Zeus, which is capable of stealing passwords, account numbers, and other information relevant to log into online banking accounts.

The Emotet malware-delivery botnet is back after a short hiatus, quickly ramping up the number of malicious emails it's sending and sporting additional capabilities, including changes to its binary and delivering a new version of the IcedID malware dropper. The various changes after almost four months of silence also could indicate a change of management for Emotet, which has been run by the threat group TA542 and in April was ranked as the top malware threat - affecting six percent of companies worldwide.
The Keksec threat actor has been linked to a previously undocumented malware strain, which has been observed in the wild masquerading as an extension for Chromium-based web browsers to enslave compromised machines into a botnet. Called Cloud9 by security firm Zimperium, the malicious browser add-on comes with a wide range of features that enables it to siphon cookies, log keystrokes, inject arbitrary JavaScript code, mine crypto, and even enlist the host to carry out DDoS attacks.

The Emotet malware operation is again spamming malicious emails after almost a four-month "Vacation" that saw little activity from the notorious cybercrime operation. Emotet is a malware infection distributed through phishing campaigns containing malicious Excel or Word documents.

The Emotet malware operation is again spamming malicious emails after almost a five-month "Vacation" that saw little activity from the notorious cybercrime operation.Emotet is a malware infection distributed through phishing campaigns containing malicious Excel or Word documents.

The threat actor behind the Fodcha distributed denial-of-service botnet has resurfaced with new capabilities, researchers reveal. Fodcha first came to light earlier this April, with the malware propagating through known vulnerabilities in Android and IoT devices as well as weak Telnet or SSH passwords.

A new version of the Fodcha DDoS botnet has emerged, featuring ransom demands injected into packets and new features to evade detection of its infrastructure. The most notable improvement in this botnet version is the delivery of ransom demands directly within DDoS packets used against victims' networks.
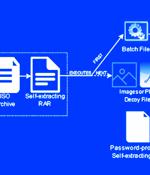
The notorious Emotet botnet has been linked to a new wave of malspam campaigns that take advantage of password-protected archive files to drop CoinMiner and Quasar RAT on compromised systems. In an attack chain detected by Trustwave SpiderLabs researchers, an invoice-themed ZIP file lure was found to contain a nested self-extracting archive, the first archive acting as a conduit to launch the second.