Security News > 2023 > July > Cybercriminals Exploiting WooCommerce Payments Plugin Flaw to Hijack Websites
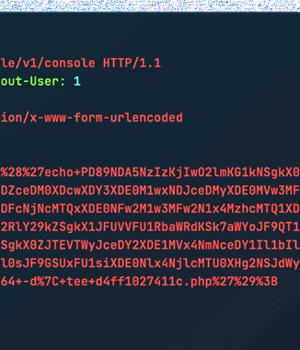
Threat actors are actively exploiting a recently disclosed critical security flaw in the WooCommerce Payments WordPress plugin as part of a massive targeted campaign.
"Large-scale attacks against the vulnerability, assigned CVE-2023-28121, began on Thursday, July 14, 2023 and continued over the weekend, peaking at 1.3 million attacks against 157,000 sites on Saturday, July 16, 2023," Wordfence security researcher Ram Gall said in a Monday post.
Versions 4.8.0 through 5.6.1 of WooCommerce Payments are vulnerable.
Patches for the bug were released by WooCommerce back in March 2023, with WordPress issuing auto-updates to sites using affected versions of the software.
"Threat actors appear to be exploiting CVE-2023-29298 in conjunction with a secondary vulnerability," Rapid7 security researcher Caitlin Condon said.
The additional flaw appears to be CVE-2023-38203, a deserialization flaw that was addressed in an out-of-band update released on July 14.
News URL
https://thehackernews.com/2023/07/cybercriminals-exploiting-woocommerce.html
Related Vulnerability
| DATE | CVE | VULNERABILITY TITLE | RISK |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2023-07-20 | CVE-2023-38203 | Unspecified vulnerability in Adobe Coldfusion 2018/2021/2023 Adobe ColdFusion versions 2018u17 (and earlier), 2021u7 (and earlier) and 2023u1 (and earlier) are affected by a Deserialization of Untrusted Data vulnerability that could result in Arbitrary code execution. | 0.0 |
| 2023-07-12 | CVE-2023-29298 | Unspecified vulnerability in Adobe Coldfusion 2018/2021/2023 Adobe ColdFusion versions 2018u16 (and earlier), 2021u6 (and earlier) and 2023.0.0.330468 (and earlier) are affected by an Improper Access Control vulnerability that could result in a Security feature bypass. | 7.5 |
| 2023-04-12 | CVE-2023-28121 | Improper Authentication vulnerability in Automattic Woocommerce Payments and Woopayments An issue in WooCommerce Payments plugin for WordPress (versions 5.6.1 and lower) allows an unauthenticated attacker to send requests on behalf of an elevated user, like administrator. | 9.8 |