Security News > 2021 > September > Microsoft Warns of Cross-Account Takeover Bug in Azure Container Instances
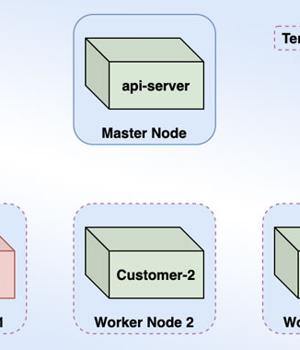
Microsoft on Wednesday said it remediated a vulnerability in its Azure Container Instances services that could have been exploited by a malicious actor "To access other customers' information" in what the researcher described as the "First cross-account container takeover in the public cloud."
Azure Container Instances is a managed service that allows users to run Docker containers directly in a serverless cloud environment, without requiring the use of virtual machines, clusters, or orchestrators.
Palo Alto Networks' Unit 42 threat intelligence team dubbed the vulnerability "Azurescape," referring to how an attacker can leverage the cross-tenant technique to escape their rogue ACI container, escalate privileges over a multitenant Kubernetes cluster, and take control of impacted containers by executing malicious code.
Breaking out of the container, the researchers said, was made possible due to an outdated container runtime used in ACI, thereby making it possible to exploit CVE-2019-5736 to escape the container and get code execution with elevated privileges on the underlying host.
Microsoft said it notified select customers with containers running on the same Kubernetes cluster as that of the malicious container created by Palo Alto Networks to demonstrate the attack.
The disclosure is the second Azure-related flaw to come to light in a span of two weeks, the first one being a critical Cosmos database flaw that could have been potentially exploited to grant any Azure user full admin access to other customers' database instances without any authorization.
News URL
http://feedproxy.google.com/~r/TheHackersNews/~3/TbU9jkAaJlY/microsoft-warns-of-cross-account.html
Related Vulnerability
| DATE | CVE | VULNERABILITY TITLE | RISK |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2019-02-11 | CVE-2019-5736 | OS Command Injection vulnerability in multiple products runc through 1.0-rc6, as used in Docker before 18.09.2 and other products, allows attackers to overwrite the host runc binary (and consequently obtain host root access) by leveraging the ability to execute a command as root within one of these types of containers: (1) a new container with an attacker-controlled image, or (2) an existing container, to which the attacker previously had write access, that can be attached with docker exec. local low complexity docker linuxfoundation redhat google linuxcontainers hp netapp apache opensuse d2iq fedoraproject canonical microfocus CWE-78 | 8.6 |