Vulnerabilities > CVE-2017-8759 - Unspecified vulnerability in Microsoft .Net Framework
Attack vector
LOCAL Attack complexity
LOW Privileges required
NONE Confidentiality impact
HIGH Integrity impact
HIGH Availability impact
HIGH Summary
Microsoft .NET Framework 2.0, 3.5, 3.5.1, 4.5.2, 4.6, 4.6.1, 4.6.2 and 4.7 allow an attacker to execute code remotely via a malicious document or application, aka ".NET Framework Remote Code Execution Vulnerability."
Vulnerable Configurations
Exploit-Db
| description | Microsoft Windows .NET Framework - Remote Code Execution. CVE-2017-8759. Remote exploit for Windows platform |
| file | exploits/windows/remote/42711.txt |
| id | EDB-ID:42711 |
| last seen | 2017-09-13 |
| modified | 2017-09-13 |
| platform | windows |
| port | |
| published | 2017-09-13 |
| reporter | Exploit-DB |
| source | https://www.exploit-db.com/download/42711/ |
| title | Microsoft Windows .NET Framework - Remote Code Execution |
| type | remote |
Nessus
NASL family Windows : Microsoft Bulletins NASL id SMB_NT_MS17_SEP_4038777.NASL description The remote Windows host is missing security update 4038779 or cumulative update 4038777. It is, therefore, affected by multiple vulnerabilities : - A race condition that could lead to a remote code execution vulnerability exists in NetBT Session Services when NetBT fails to maintain certain sequencing requirements. (CVE-2017-0161) - A spoofing vulnerability exists in Microsoft last seen 2020-05-31 modified 2017-09-12 plugin id 103127 published 2017-09-12 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2017-2020 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/103127 title Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2 September 2017 Security Updates code # # (C) Tenable Network Security, Inc. # # The descriptive text and package checks in this plugin were # extracted from the Microsoft Security Updates API. The text # itself is copyright (C) Microsoft Corporation. # include("compat.inc"); if (description) { script_id(103127); script_version("1.22"); script_set_attribute(attribute:"plugin_modification_date", value:"2020/05/28"); script_cve_id( "CVE-2017-0161", "CVE-2017-8529", "CVE-2017-8628", "CVE-2017-8675", "CVE-2017-8676", "CVE-2017-8677", "CVE-2017-8678", "CVE-2017-8679", "CVE-2017-8680", "CVE-2017-8681", "CVE-2017-8682", "CVE-2017-8683", "CVE-2017-8684", "CVE-2017-8685", "CVE-2017-8687", "CVE-2017-8688", "CVE-2017-8695", "CVE-2017-8696", "CVE-2017-8699", "CVE-2017-8707", "CVE-2017-8708", "CVE-2017-8709", "CVE-2017-8710", "CVE-2017-8719", "CVE-2017-8720", "CVE-2017-8733", "CVE-2017-8736", "CVE-2017-8741", "CVE-2017-8747", "CVE-2017-8748", "CVE-2017-8749", "CVE-2017-8750" ); script_bugtraq_id( 98953, 100720, 100722, 100724, 100727, 100728, 100736, 100737, 100742, 100743, 100744, 100752, 100755, 100756, 100764, 100765, 100766, 100767, 100769, 100770, 100771, 100772, 100773, 100780, 100781, 100782, 100783, 100790, 100791, 100792, 100793, 100803, 100804 ); script_xref(name:"MSKB", value:"4038779"); script_xref(name:"MSFT", value:"MS17-4038779"); script_xref(name:"MSKB", value:"4038777"); script_xref(name:"MSFT", value:"MS17-4038777"); script_name(english:"Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2 September 2017 Security Updates"); script_summary(english:"Checks for rollup."); script_set_attribute(attribute:"synopsis", value: "The remote Windows host is affected by multiple vulnerabilities."); script_set_attribute(attribute:"description", value: "The remote Windows host is missing security update 4038779 or cumulative update 4038777. It is, therefore, affected by multiple vulnerabilities : - A race condition that could lead to a remote code execution vulnerability exists in NetBT Session Services when NetBT fails to maintain certain sequencing requirements. (CVE-2017-0161) - A spoofing vulnerability exists in Microsoft's implementation of the Bluetooth stack. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could perform a man-in-the-middle attack and force a user's computer to unknowingly route traffic through the attacker's computer. The attacker can then monitor and read the traffic before sending it on to the intended recipient. (CVE-2017-8628) - An elevation of privilege vulnerability exists in Windows when the Windows kernel-mode driver fails to properly handle objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could run arbitrary code in kernel mode. An attacker could then install programs; view, change, or delete data; or create new accounts with full user rights. To exploit this vulnerability, an attacker would first have to log on to the system. An attacker could then run a specially crafted application that could exploit the vulnerability and take control of an affected system. The update addresses this vulnerability by correcting how the Windows kernel-mode driver handles objects in memory. (CVE-2017-8675) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists in the way that the Windows Graphics Device Interface (GDI) handles objects in memory, allowing an attacker to retrieve information from a targeted system. By itself, the information disclosure does not allow arbitrary code execution; however, it could allow arbitrary code to be run if the attacker uses it in combination with another vulnerability. (CVE-2017-8676) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists when the Windows font library improperly handles specially crafted embedded fonts. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could take control of the affected system. An attacker could then install programs; view, change, or delete data; or create new accounts with full user rights. (CVE-2017-8682) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists when the Microsoft Windows Graphics Component improperly handles objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could obtain information to further compromise the users system. (CVE-2017-8683) - A information disclosure vulnerability exists when the Windows GDI+ component improperly discloses kernel memory addresses. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could obtain information to further compromise the users system. (CVE-2017-8677, CVE-2017-8680, CVE-2017-8681, CVE-2017-8684, CVE-2017-8685) - An Information disclosure vulnerability exists in Windows kernel that could allow an attacker to retrieve information that could lead to a Kernel Address Space Layout Randomization (KASLR) bypass. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could retrieve the memory address of a kernel object. (CVE-2017-8687) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists in the way that the Windows Graphics Device Interface+ (GDI+) handles objects in memory, allowing an attacker to retrieve information from a targeted system. By itself, the information disclosure does not allow arbitrary code execution; however, it could allow arbitrary code to be run if the attacker uses it in combination with another vulnerability. (CVE-2017-8688) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists when Windows Uniscribe improperly discloses the contents of its memory. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could obtain information to further compromise the users system. There are multiple ways an attacker could exploit the vulnerability, such as by convincing a user to open a specially crafted document or by convincing a user to visit an untrusted webpage. The update addresses the vulnerability by correcting how Windows Uniscribe handles objects in memory. (CVE-2017-8695) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists due to the way Windows Uniscribe handles objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could take control of the affected system. An attacker could then install programs; view, change, or delete data; or create new accounts with full user rights. (CVE-2017-8696) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists when Windows Shell does not properly validate file copy destinations. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could run arbitrary code in the context of the current user. (CVE-2017-8699) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists when Windows Hyper-V on a host operating system fails to properly validate input from an authenticated user on a guest operating system. (CVE-2017-8707) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists when the Windows kernel fails to properly initialize a memory address, allowing an attacker to retrieve information that could lead to a Kernel Address Space Layout Randomization (KASLR) bypass. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could retrieve the base address of the kernel driver from a compromised process. (CVE-2017-8708) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists in the Windows System Information Console when it improperly parses XML input containing a reference to an external entity. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could read arbitrary files via an XML external entity (XXE) declaration. To exploit the vulnerability, an attacker could create a file containing specially crafted XML content and convince an authenticated user to open the file. The update addresses the vulnerability by modifying the way that the Windows System Information Console parses XML input. (CVE-2017-8710) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists when the Windows kernel improperly handles objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could obtain information to further compromise the users system. (CVE-2017-8678, CVE-2017-8679, CVE-2017-8709, CVE-2017-8719) - An elevation of privilege vulnerability exists in Windows when the Win32k component fails to properly handle objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could run arbitrary code in kernel mode. An attacker could then install programs; view, change, or delete data; or create new accounts with full user rights. (CVE-2017-8720) - A spoofing vulnerability exists when Internet Explorer improperly handles specific HTML content. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could trick a user into believing that the user was visiting a legitimate website. The specially crafted website could either spoof content or serve as a pivot to chain an attack with other vulnerabilities in web services. To exploit the vulnerability, the user must either browse to a malicious website or be redirected to it. In an email attack scenario, an attacker could send an email message in an attempt to convince the user to click a link to the malicious website. (CVE-2017-8733) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists in Microsoft browsers due to improper parent domain verification in certain functionality. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could obtain specific information that is used in the parent domain. (CVE-2017-8736) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists in the way that Microsoft browser JavaScript engines render content when handling objects in memory. The vulnerability could corrupt memory in such a way that an attacker could execute arbitrary code in the context of the current user. (CVE-2017-8741, CVE-2017-8748) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists when Internet Explorer improperly accesses objects in memory. The vulnerability could corrupt memory in such a way that an attacker could execute arbitrary code in the context of the current user. (CVE-2017-8747, CVE-2017-8749) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists when Microsoft browsers improperly access objects in memory. The vulnerability could corrupt memory in such a way that an attacker could execute arbitrary code in the context of the current user. (CVE-2017-8750) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists when Microsoft .NET Framework processes untrusted input. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability in software using the .NET framework could take control of an affected system. An attacker could then install programs; view, change, or delete data; or create new accounts with full user rights. (CVE-2017-8759) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists in Microsoft browsers in the scripting engines due to improper handling of objects in memory. An unauthenticated, remote attacker can exploit this, by convincing a user to visit a specially crafted website, to disclose files on a user's computer. (CVE-2017-8529)"); # https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/help/4038779/windows-7-update-kb4038779 script_set_attribute(attribute:"see_also", value:"http://www.nessus.org/u?bf7e8b94"); # https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/help/4038777/windows-7-update-kb4038777 script_set_attribute(attribute:"see_also", value:"http://www.nessus.org/u?1dbb18cc"); script_set_attribute(attribute:"solution", value: "Apply Security Only update KB4038779 or Cumulative update KB4038777 as well as refer to the KB article for additional information."); script_set_cvss_base_vector("CVSS2#AV:N/AC:M/Au:N/C:C/I:C/A:C"); script_set_cvss_temporal_vector("CVSS2#E:H/RL:OF/RC:C"); script_set_cvss3_base_vector("CVSS:3.0/AV:N/AC:L/PR:N/UI:R/S:U/C:H/I:H/A:H"); script_set_cvss3_temporal_vector("CVSS:3.0/E:H/RL:O/RC:C"); script_set_attribute(attribute:"cvss_score_source", value:"CVE-2017-8682"); script_set_attribute(attribute:"exploitability_ease", value:"Exploits are available"); script_set_attribute(attribute:"exploit_available", value:"true"); script_set_attribute(attribute:"exploited_by_malware", value:"true"); script_set_attribute(attribute:"vuln_publication_date", value:"2017/09/12"); script_set_attribute(attribute:"patch_publication_date", value:"2017/09/12"); script_set_attribute(attribute:"plugin_publication_date", value:"2017/09/12"); script_set_attribute(attribute:"plugin_type", value:"local"); script_set_attribute(attribute:"cpe", value:"cpe:/o:microsoft:windows"); script_end_attributes(); script_category(ACT_GATHER_INFO); script_family(english:"Windows : Microsoft Bulletins"); script_copyright(english:"This script is Copyright (C) 2017-2020 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof."); script_dependencies("smb_check_rollup.nasl", "smb_hotfixes.nasl", "ms_bulletin_checks_possible.nasl"); script_require_keys("SMB/MS_Bulletin_Checks/Possible"); script_require_ports(139, 445, "Host/patch_management_checks"); exit(0); } include("global_settings.inc"); include("audit.inc"); include("smb_hotfixes_fcheck.inc"); include("smb_hotfixes.inc"); include("smb_func.inc"); include("smb_reg_query.inc"); include("misc_func.inc"); get_kb_item_or_exit("SMB/MS_Bulletin_Checks/Possible"); bulletin = "MS17-09"; kbs = make_list('4038779', '4038777'); if (get_kb_item("Host/patch_management_checks")) hotfix_check_3rd_party(bulletin:bulletin, kbs:kbs, severity:SECURITY_HOLE); get_kb_item_or_exit("SMB/Registry/Enumerated"); get_kb_item_or_exit("SMB/WindowsVersion", exit_code:1); if (hotfix_check_sp_range(win7:'1') <= 0) audit(AUDIT_OS_SP_NOT_VULN); share = hotfix_get_systemdrive(as_share:TRUE, exit_on_fail:TRUE); if (!is_accessible_share(share:share)) audit(AUDIT_SHARE_FAIL, share); if ( smb_check_rollup( os:"6.1", sp:1, rollup_date:"09_2017", bulletin:bulletin, rollup_kb_list:[4038779, 4038777] ) ) { replace_kb_item(name:'SMB/Missing/'+bulletin, value:TRUE); hotfix_security_hole(); hotfix_check_fversion_end(); exit(0); } else { hotfix_check_fversion_end(); audit(AUDIT_HOST_NOT, hotfix_get_audit_report()); }NASL family Windows : Microsoft Bulletins NASL id SMB_NT_MS17_SEP_4038781.NASL description The remote Windows host is missing security update 4038781. It is, therefore, affected by multiple vulnerabilities : - A remote code execution vulnerability exists when Microsoft Windows PDF Library improperly handles objects in memory. The vulnerability could corrupt memory in a way that enables an attacker to execute arbitrary code in the context of the current user. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could gain the same user rights as the current user. If the current user is logged on with administrative user rights, an attacker could take control of an affected system. An attacker could then install programs; view, change, or delete data; or create new accounts with full user rights. (CVE-2017-8728, CVE-2017-8737) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists when Windows Hyper-V on a host operating system fails to properly validate input from an authenticated user on a guest operating system. (CVE-2017-8706, CVE-2017-8707, CVE-2017-8713) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists when the Microsoft Windows Graphics Component improperly handles objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could obtain information to further compromise the users system. (CVE-2017-8683) - An Information disclosure vulnerability exists in Windows kernel that could allow an attacker to retrieve information that could lead to a Kernel Address Space Layout Randomization (KASLR) bypass. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could retrieve the memory address of a kernel object. (CVE-2017-8687) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists when Microsoft Edge improperly accesses objects in memory. The vulnerability could corrupt memory in such a way that enables an attacker to execute arbitrary code in the context of the current user. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could gain the same user rights as the current user. (CVE-2017-8734) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists in the way that the Windows Graphics Device Interface (GDI) handles objects in memory, allowing an attacker to retrieve information from a targeted system. By itself, the information disclosure does not allow arbitrary code execution; however, it could allow arbitrary code to be run if the attacker uses it in combination with another vulnerability. (CVE-2017-8676) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists in the way that Microsoft browser JavaScript engines render content when handling objects in memory. The vulnerability could corrupt memory in such a way that an attacker could execute arbitrary code in the context of the current user. In a web-based attack scenario, an attacker could host a specially crafted website that is designed to exploit the vulnerability through Microsoft browsers and then convince a user to view the website. An attacker could also embed an ActiveX control marked "safe for initialization" in an application or Microsoft Office document that hosts the related rendering engine. The attacker could also take advantage of compromised websites, and websites that accept or host user-provided content or advertisements. These websites could contain specially crafted content that could exploit the vulnerability. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could gain the same user rights as the current user. (CVE-2017-8741, CVE-2017-8748) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists in the way that the scripting engine handles objects in memory in Microsoft Edge. The vulnerability could corrupt memory in such a way that an attacker could execute arbitrary code in the context of the current user. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could gain the same user rights as the current user. (CVE-2017-8738, CVE-2017-8753, CVE-2017-8756) - A race condition that could lead to a remote code execution vulnerability exists in NetBT Session Services when NetBT fails to maintain certain sequencing requirements. (CVE-2017-0161) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists in the way Microsoft Edge handles objects in memory. The vulnerability could corrupt memory in such a way that an attacker could execute arbitrary code in the context of the current user. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could gain the same user rights as the current user. (CVE-2017-8757) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists when Internet Explorer improperly accesses objects in memory. The vulnerability could corrupt memory in such a way that an attacker could execute arbitrary code in the context of the current user. (CVE-2017-8747, CVE-2017-8749) - An elevation of privilege vulnerability exists in Windows when the Win32k component fails to properly handle objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could run arbitrary code in kernel mode. An attacker could then install programs; view, change, or delete data; or create new accounts with full user rights. (CVE-2017-8720) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists when Windows Uniscribe improperly discloses the contents of its memory. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could obtain information to further compromise the users system. There are multiple ways an attacker could exploit the vulnerability, such as by convincing a user to open a specially crafted document or by convincing a user to visit an untrusted webpage. The update addresses the vulnerability by correcting how Windows Uniscribe handles objects in memory. (CVE-2017-8695) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists when Microsoft Edge improperly handles clipboard events. For an attack to be successful, an attacker must persuade a user to visit a malicious website and leave it open during clipboard activities. The update addresses the vulnerability by changing how Microsoft Edge handles clipboard events in the browser. (CVE-2017-8643) - A spoofing vulnerability exists in Microsoft last seen 2020-05-31 modified 2017-11-03 plugin id 104385 published 2017-11-03 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2017-2020 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/104385 title KB4038781: Windows 10 September 2017 Cumulative Update code # # (C) Tenable Network Security, Inc. # # The descriptive text and package checks in this plugin were # extracted from the Microsoft Security Updates API. The text # itself is copyright (C) Microsoft Corporation. # include("compat.inc"); if (description) { script_id(104385); script_version("1.7"); script_set_attribute(attribute:"plugin_modification_date", value:"2020/05/28"); script_cve_id( "CVE-2017-0161", "CVE-2017-8529", "CVE-2017-8628", "CVE-2017-8643", "CVE-2017-8675", "CVE-2017-8676", "CVE-2017-8677", "CVE-2017-8678", "CVE-2017-8679", "CVE-2017-8681", "CVE-2017-8682", "CVE-2017-8683", "CVE-2017-8687", "CVE-2017-8688", "CVE-2017-8692", "CVE-2017-8695", "CVE-2017-8699", "CVE-2017-8702", "CVE-2017-8706", "CVE-2017-8707", "CVE-2017-8708", "CVE-2017-8709", "CVE-2017-8713", "CVE-2017-8719", "CVE-2017-8720", "CVE-2017-8723", "CVE-2017-8728", "CVE-2017-8733", "CVE-2017-8734", "CVE-2017-8735", "CVE-2017-8736", "CVE-2017-8737", "CVE-2017-8738", "CVE-2017-8741", "CVE-2017-8747", "CVE-2017-8748", "CVE-2017-8749", "CVE-2017-8750", "CVE-2017-8753", "CVE-2017-8754", "CVE-2017-8756", "CVE-2017-8757", "CVE-2017-8759", "CVE-2017-11766" ); script_bugtraq_id( 98953, 100718, 100720, 100721, 100727, 100728, 100729, 100736, 100737, 100738, 100739, 100740, 100742, 100743, 100744, 100747, 100749, 100752, 100755, 100756, 100759, 100762, 100764, 100765, 100766, 100767, 100768, 100769, 100770, 100771, 100772, 100773, 100776, 100779, 100781, 100783, 100785, 100789, 100790, 100791, 100792, 100796, 100803, 100804 ); script_xref(name:"MSKB", value:"4038781"); script_xref(name:"MSFT", value:"MS17-4038781"); script_name(english:"KB4038781: Windows 10 September 2017 Cumulative Update"); script_summary(english:"Checks for rollup."); script_set_attribute(attribute:"synopsis", value: "The remote Windows host is affected by multiple vulnerabilities."); script_set_attribute(attribute:"description", value: "The remote Windows host is missing security update 4038781. It is, therefore, affected by multiple vulnerabilities : - A remote code execution vulnerability exists when Microsoft Windows PDF Library improperly handles objects in memory. The vulnerability could corrupt memory in a way that enables an attacker to execute arbitrary code in the context of the current user. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could gain the same user rights as the current user. If the current user is logged on with administrative user rights, an attacker could take control of an affected system. An attacker could then install programs; view, change, or delete data; or create new accounts with full user rights. (CVE-2017-8728, CVE-2017-8737) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists when Windows Hyper-V on a host operating system fails to properly validate input from an authenticated user on a guest operating system. (CVE-2017-8706, CVE-2017-8707, CVE-2017-8713) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists when the Microsoft Windows Graphics Component improperly handles objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could obtain information to further compromise the users system. (CVE-2017-8683) - An Information disclosure vulnerability exists in Windows kernel that could allow an attacker to retrieve information that could lead to a Kernel Address Space Layout Randomization (KASLR) bypass. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could retrieve the memory address of a kernel object. (CVE-2017-8687) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists when Microsoft Edge improperly accesses objects in memory. The vulnerability could corrupt memory in such a way that enables an attacker to execute arbitrary code in the context of the current user. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could gain the same user rights as the current user. (CVE-2017-8734) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists in the way that the Windows Graphics Device Interface (GDI) handles objects in memory, allowing an attacker to retrieve information from a targeted system. By itself, the information disclosure does not allow arbitrary code execution; however, it could allow arbitrary code to be run if the attacker uses it in combination with another vulnerability. (CVE-2017-8676) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists in the way that Microsoft browser JavaScript engines render content when handling objects in memory. The vulnerability could corrupt memory in such a way that an attacker could execute arbitrary code in the context of the current user. In a web-based attack scenario, an attacker could host a specially crafted website that is designed to exploit the vulnerability through Microsoft browsers and then convince a user to view the website. An attacker could also embed an ActiveX control marked "safe for initialization" in an application or Microsoft Office document that hosts the related rendering engine. The attacker could also take advantage of compromised websites, and websites that accept or host user-provided content or advertisements. These websites could contain specially crafted content that could exploit the vulnerability. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could gain the same user rights as the current user. (CVE-2017-8741, CVE-2017-8748) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists in the way that the scripting engine handles objects in memory in Microsoft Edge. The vulnerability could corrupt memory in such a way that an attacker could execute arbitrary code in the context of the current user. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could gain the same user rights as the current user. (CVE-2017-8738, CVE-2017-8753, CVE-2017-8756) - A race condition that could lead to a remote code execution vulnerability exists in NetBT Session Services when NetBT fails to maintain certain sequencing requirements. (CVE-2017-0161) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists in the way Microsoft Edge handles objects in memory. The vulnerability could corrupt memory in such a way that an attacker could execute arbitrary code in the context of the current user. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could gain the same user rights as the current user. (CVE-2017-8757) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists when Internet Explorer improperly accesses objects in memory. The vulnerability could corrupt memory in such a way that an attacker could execute arbitrary code in the context of the current user. (CVE-2017-8747, CVE-2017-8749) - An elevation of privilege vulnerability exists in Windows when the Win32k component fails to properly handle objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could run arbitrary code in kernel mode. An attacker could then install programs; view, change, or delete data; or create new accounts with full user rights. (CVE-2017-8720) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists when Windows Uniscribe improperly discloses the contents of its memory. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could obtain information to further compromise the users system. There are multiple ways an attacker could exploit the vulnerability, such as by convincing a user to open a specially crafted document or by convincing a user to visit an untrusted webpage. The update addresses the vulnerability by correcting how Windows Uniscribe handles objects in memory. (CVE-2017-8695) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists when Microsoft Edge improperly handles clipboard events. For an attack to be successful, an attacker must persuade a user to visit a malicious website and leave it open during clipboard activities. The update addresses the vulnerability by changing how Microsoft Edge handles clipboard events in the browser. (CVE-2017-8643) - A spoofing vulnerability exists in Microsoft's implementation of the Bluetooth stack. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could perform a man-in-the-middle attack and force a user's computer to unknowingly route traffic through the attacker's computer. The attacker can then monitor and read the traffic before sending it on to the intended recipient. (CVE-2017-8628) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists in Microsoft browsers due to improper parent domain verification in certain functionality. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could obtain specific information that is used in the parent domain. (CVE-2017-8736) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists when the Windows kernel improperly handles objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could obtain information to further compromise the users system. (CVE-2017-8678, CVE-2017-8679, CVE-2017-8709, CVE-2017-8719) - A vulnerability exists when Microsoft Edge improperly accesses objects in memory. The vulnerability could corrupt memory in such a way that an attacker could execute arbitrary code in the context of the current user. (CVE-2017-11766) - A security feature bypass exists in Microsoft Edge when the Edge Content Security Policy (CSP) fails to properly validate certain specially crafted documents. An attacker who exploited the bypass could trick a user into loading a page containing malicious content. (CVE-2017-8723, CVE-2017-8754) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists when Microsoft .NET Framework processes untrusted input. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability in software using the .NET framework could take control of an affected system. An attacker could then install programs; view, change, or delete data; or create new accounts with full user rights. Users whose accounts are configured to have fewer user rights on the system could be less impacted than users who operate with administrative user rights. (CVE-2017-8759) - A information disclosure vulnerability exists when the Windows GDI+ component improperly discloses kernel memory addresses. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could obtain information to further compromise the users system. (CVE-2017-8677, CVE-2017-8681) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists in the way that the Windows Graphics Device Interface (GDI) handles objects in memory, allowing an attacker to retrieve information from a targeted system. By itself, the information disclosure does not allow arbitrary code execution; however, it could allow arbitrary code to be run if the attacker uses it in combination with another vulnerability. (CVE-2017-8688) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists due to the way Windows Uniscribe handles objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could take control of the affected system. An attacker could then install programs; view, change, or delete data; or create new accounts with full user rights. (CVE-2017-8692) - An elevation of privilege vulnerability exists in Windows when the Windows kernel-mode driver fails to properly handle objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could run arbitrary code in kernel mode. An attacker could then install programs; view, change, or delete data; or create new accounts with full user rights. (CVE-2017-8675) - A spoofing vulnerability exists when Microsoft Edge does not properly parse HTTP content. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could trick a user by redirecting the user to a specially crafted website. The specially crafted website could either spoof content or serve as a pivot to chain an attack with other vulnerabilities in web services. (CVE-2017-8735) - A spoofing vulnerability exists when Internet Explorer improperly handles specific HTML content. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could trick a user into believing that the user was visiting a legitimate website. The specially crafted website could either spoof content or serve as a pivot to chain an attack with other vulnerabilities in web services. (CVE-2017-8733) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists when Microsoft browsers improperly access objects in memory. The vulnerability could corrupt memory in such a way that an attacker could execute arbitrary code in the context of the current user. (CVE-2017-8750) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists when the Windows kernel fails to properly initialize a memory address, allowing an attacker to retrieve information that could lead to a Kernel Address Space Layout Randomization (KASLR) bypass. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could retrieve the base address of the kernel driver from a compromised process. (CVE-2017-8708) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists when the Windows font library improperly handles specially crafted embedded fonts. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could take control of the affected system. An attacker could then install programs; view, change, or delete data; or create new accounts with full user rights. (CVE-2017-8682) - An elevation of privilege vulnerability exists in Windows Error Reporting (WER) when WER handles and executes files. The vulnerability could allow elevation of privilege if an attacker can successfully exploit it. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could gain greater access to sensitive information and system functionality. (CVE-2017-8702) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists when Windows Shell does not properly validate file copy destinations. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could run arbitrary code in the context of the current user. If the current user is logged on with administrative user rights, an attacker could take control of the affected system. An attacker could then install programs; view, change, or delete data; or create new accounts with full user rights. Users whose accounts are configured to have fewer user rights on the system could be less impacted than users who operate with administrative user rights. (CVE-2017-8699) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists in Microsoft browsers in the scripting engines due to improper handling of objects in memory. An unauthenticated, remote attacker can exploit this, by convincing a user to visit a specially crafted website, to disclose files on a user's computer. (CVE-2017-8529)"); # https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/help/4038781/windows-10-update-kb4038781 script_set_attribute(attribute:"see_also", value:"http://www.nessus.org/u?7c29dee1"); script_set_attribute(attribute:"solution", value: "Apply security update KB4038781."); script_set_cvss_base_vector("CVSS2#AV:N/AC:M/Au:N/C:C/I:C/A:C"); script_set_cvss_temporal_vector("CVSS2#E:H/RL:OF/RC:C"); script_set_cvss3_base_vector("CVSS:3.0/AV:L/AC:L/PR:N/UI:R/S:U/C:H/I:H/A:H"); script_set_cvss3_temporal_vector("CVSS:3.0/E:H/RL:O/RC:C"); script_set_attribute(attribute:"cvss_score_source", value:"CVE-2017-8759"); script_set_attribute(attribute:"exploitability_ease", value:"Exploits are available"); script_set_attribute(attribute:"exploit_available", value:"true"); script_set_attribute(attribute:"exploit_framework_core", value:"true"); script_set_attribute(attribute:"exploited_by_malware", value:"true"); script_set_attribute(attribute:"exploit_framework_canvas", value:"true"); script_set_attribute(attribute:"canvas_package", value:'CANVAS'); script_set_attribute(attribute:"vuln_publication_date", value:"2017/09/12"); script_set_attribute(attribute:"patch_publication_date", value:"2017/09/12"); script_set_attribute(attribute:"plugin_publication_date", value:"2017/11/03"); script_set_attribute(attribute:"plugin_type", value:"local"); script_set_attribute(attribute:"cpe", value:"cpe:/o:microsoft:windows"); script_end_attributes(); script_category(ACT_GATHER_INFO); script_family(english:"Windows : Microsoft Bulletins"); script_copyright(english:"This script is Copyright (C) 2017-2020 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof."); script_dependencies("smb_check_rollup.nasl", "smb_hotfixes.nasl", "ms_bulletin_checks_possible.nasl"); script_require_keys("SMB/MS_Bulletin_Checks/Possible"); script_require_ports(139, 445, "Host/patch_management_checks"); exit(0); } include("audit.inc"); include("smb_hotfixes_fcheck.inc"); include("smb_hotfixes.inc"); include("smb_func.inc"); include("misc_func.inc"); get_kb_item_or_exit("SMB/MS_Bulletin_Checks/Possible"); bulletin = "MS17-09"; kbs = make_list('4038781'); if (get_kb_item("Host/patch_management_checks")) hotfix_check_3rd_party(bulletin:bulletin, kbs:kbs, severity:SECURITY_HOLE); get_kb_item_or_exit("SMB/Registry/Enumerated"); get_kb_item_or_exit("SMB/WindowsVersion", exit_code:1); os_name = get_kb_item_or_exit("SMB/ProductName"); if (hotfix_check_sp_range(win10:'0') <= 0) audit(AUDIT_OS_SP_NOT_VULN); if("LTSB" >!< os_name) audit(AUDIT_OS_NOT, "Windows 10 version 1507 LTSB"); share = hotfix_get_systemdrive(as_share:TRUE, exit_on_fail:TRUE); if (!is_accessible_share(share:share)) audit(AUDIT_SHARE_FAIL, share); if ( smb_check_rollup(os:"10", sp:0, os_build:"10240", rollup_date:"09_2017", bulletin:bulletin, rollup_kb_list:[4038781]) ) { replace_kb_item(name:'SMB/Missing/'+bulletin, value:TRUE); hotfix_security_hole(); hotfix_check_fversion_end(); exit(0); } else { hotfix_check_fversion_end(); audit(AUDIT_HOST_NOT, hotfix_get_audit_report()); }NASL family Windows : Microsoft Bulletins NASL id SMB_NT_MS17_SEP_4038783.NASL description The remote Windows host is missing security update 4038783. It is, therefore, affected by multiple vulnerabilities : - A race condition that could lead to a remote code execution vulnerability exists in NetBT Session Services when NetBT fails to maintain certain sequencing requirements. (CVE-2017-0161) - A vulnerability exists when Microsoft Edge improperly accesses objects in memory. The vulnerability could corrupt memory in such a way that an attacker could execute arbitrary code in the context of the current user. (CVE-2017-11766) - A spoofing vulnerability exists in Microsoft last seen 2020-05-31 modified 2017-09-12 plugin id 103129 published 2017-09-12 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2017-2020 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/103129 title KB4038783: Windows 10 Version 1511 September 2017 Cumulative Update code # # (C) Tenable Network Security, Inc. # # The descriptive text and package checks in this plugin were # extracted from the Microsoft Security Updates API. The text # itself is copyright (C) Microsoft Corporation. # include("compat.inc"); if (description) { script_id(103129); script_version("1.9"); script_set_attribute(attribute:"plugin_modification_date", value:"2020/05/28"); script_cve_id( "CVE-2017-0161", "CVE-2017-8529", "CVE-2017-8628", "CVE-2017-8643", "CVE-2017-8660", "CVE-2017-8675", "CVE-2017-8676", "CVE-2017-8677", "CVE-2017-8678", "CVE-2017-8679", "CVE-2017-8681", "CVE-2017-8682", "CVE-2017-8683", "CVE-2017-8687", "CVE-2017-8688", "CVE-2017-8692", "CVE-2017-8695", "CVE-2017-8699", "CVE-2017-8702", "CVE-2017-8706", "CVE-2017-8707", "CVE-2017-8708", "CVE-2017-8709", "CVE-2017-8713", "CVE-2017-8719", "CVE-2017-8720", "CVE-2017-8723", "CVE-2017-8728", "CVE-2017-8733", "CVE-2017-8734", "CVE-2017-8735", "CVE-2017-8736", "CVE-2017-8737", "CVE-2017-8738", "CVE-2017-8741", "CVE-2017-8747", "CVE-2017-8748", "CVE-2017-8749", "CVE-2017-8750", "CVE-2017-8752", "CVE-2017-8753", "CVE-2017-8754", "CVE-2017-8755", "CVE-2017-8756", "CVE-2017-8757", "CVE-2017-8759", "CVE-2017-11766" ); script_xref(name:"MSKB", value:"4038783"); script_xref(name:"MSFT", value:"MS17-4038783"); script_name(english:"KB4038783: Windows 10 Version 1511 September 2017 Cumulative Update"); script_summary(english:"Checks for rollup."); script_set_attribute(attribute:"synopsis", value: "The remote Windows host is affected by multiple vulnerabilities."); script_set_attribute(attribute:"description", value: "The remote Windows host is missing security update 4038783. It is, therefore, affected by multiple vulnerabilities : - A race condition that could lead to a remote code execution vulnerability exists in NetBT Session Services when NetBT fails to maintain certain sequencing requirements. (CVE-2017-0161) - A vulnerability exists when Microsoft Edge improperly accesses objects in memory. The vulnerability could corrupt memory in such a way that an attacker could execute arbitrary code in the context of the current user. (CVE-2017-11766) - A spoofing vulnerability exists in Microsoft's implementation of the Bluetooth stack. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could perform a man-in-the-middle attack and force a user's computer to unknowingly route traffic through the attacker's computer. The attacker can then monitor and read the traffic before sending it on to the intended recipient. (CVE-2017-8628) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists when Microsoft Edge improperly handles clipboard events. For an attack to be successful, an attacker must persuade a user to visit a malicious website and leave it open during clipboard activities. The update addresses the vulnerability by changing how Microsoft Edge handles clipboard events in the browser. (CVE-2017-8643) - An elevation of privilege vulnerability exists in Windows when the Windows kernel-mode driver fails to properly handle objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could run arbitrary code in kernel mode. An attacker could then install programs; view, change, or delete data; or create new accounts with full user rights. To exploit this vulnerability, an attacker would first have to log on to the system. An attacker could then run a specially crafted application that could exploit the vulnerability and take control of an affected system. The update addresses this vulnerability by correcting how the Windows kernel-mode driver handles objects in memory. (CVE-2017-8675) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists in the way that the Windows Graphics Device Interface (GDI) handles objects in memory, allowing an attacker to retrieve information from a targeted system. By itself, the information disclosure does not allow arbitrary code execution; however, it could allow arbitrary code to be run if the attacker uses it in combination with another vulnerability. (CVE-2017-8676) - A information disclosure vulnerability exists when the Windows GDI+ component improperly discloses kernel memory addresses. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could obtain information to further compromise the users system. (CVE-2017-8677, CVE-2017-8681) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists when the Windows font library improperly handles specially crafted embedded fonts. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could take control of the affected system. An attacker could then install programs; view, change, or delete data; or create new accounts with full user rights.(CVE-2017-8682) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists when the Microsoft Windows Graphics Component improperly handles objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could obtain information to further compromise the users system. (CVE-2017-8683) - An Information disclosure vulnerability exists in Windows kernel that could allow an attacker to retrieve information that could lead to a Kernel Address Space Layout Randomization (KASLR) bypass. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could retrieve the memory address of a kernel object. (CVE-2017-8687) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists in the way that the Windows Graphics Device Interface+ (GDI+) handles objects in memory, allowing an attacker to retrieve information from a targeted system. (CVE-2017-8688) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists due to the way Windows Uniscribe handles objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could take control of the affected system. An attacker could then install programs; view, change, or delete data; or create new accounts with full user rights. (CVE-2017-8692) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists when Windows Uniscribe improperly discloses the contents of its memory. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could obtain information to further compromise the users system. (CVE-2017-8695) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists when Windows Shell does not properly validate file copy destinations. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could run arbitrary code in the context of the current user. (CVE-2017-8699) - An elevation of privilege vulnerability exists in Windows Error Reporting (WER) when WER handles and executes files. The vulnerability could allow elevation of privilege if an attacker can successfully exploit it. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could gain greater access to sensitive information and system functionality. (CVE-2017-8702) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists when Windows Hyper-V on a host operating system fails to properly validate input from an authenticated user on a guest operating system. (CVE-2017-8706, CVE-2017-8707) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists when the Windows kernel fails to properly initialize a memory address, allowing an attacker to retrieve information that could lead to a Kernel Address Space Layout Randomization (KASLR) bypass. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could retrieve the base address of the kernel driver from a compromised process. (CVE-2017-8708) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists when Windows Hyper-V on a host operating system fails to properly validate input from an authenticated user on a guest operating system. (CVE-2017-8706, CVE-2017-8707, CVE-2017-8713) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists when the Windows kernel improperly handles objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could obtain information to further compromise the users system.(CVE-2017-8678, CVE-2017-8679, CVE-2017-8709, CVE-2017-8719) - An elevation of privilege vulnerability exists in Windows when the Win32k component fails to properly handle objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could run arbitrary code in kernel mode. An attacker could then install programs; view, change, or delete data; or create new accounts with full user rights.(CVE-2017-8720) - A spoofing vulnerability exists when Internet Explorer improperly handles specific HTML content. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could trick a user into believing that the user was visiting a legitimate website. The specially crafted website could either spoof content or serve as a pivot to chain an attack with other vulnerabilities in web services. (CVE-2017-8733) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists when Microsoft Edge improperly accesses objects in memory. The vulnerability could corrupt memory in such a way that enables an attacker to execute arbitrary code in the context of the current user. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could gain the same user rights as the current user.(CVE-2017-8734) - A spoofing vulnerability exists when Microsoft Edge does not properly parse HTTP content. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could trick a user by redirecting the user to a specially crafted website. The specially crafted website could either spoof content or serve as a pivot to chain an attack with other vulnerabilities in web services. (CVE-2017-8735) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists in Microsoft browsers due to improper parent domain verification in certain functionality. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could obtain specific information that is used in the parent domain. (CVE-2017-8736) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists when Microsoft Windows PDF Library improperly handles objects in memory. The vulnerability could corrupt memory in a way that enables an attacker to execute arbitrary code in the context of the current user. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could gain the same user rights as the current user. (CVE-2017-8728, CVE-2017-8737) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists in the way that Microsoft browser JavaScript engines render content when handling objects in memory. The vulnerability could corrupt memory in such a way that an attacker could execute arbitrary code in the context of the current user. (CVE-2017-8660, CVE-2017-8741, CVE-2017-8748) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists when Internet Explorer improperly accesses objects in memory. The vulnerability could corrupt memory in such a way that an attacker could execute arbitrary code in the context of the current user. (CVE-2017-8747, CVE-2017-8749) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists when Microsoft browsers improperly access objects in memory. The vulnerability could corrupt memory in such a way that an attacker could execute arbitrary code in the context of the current user. (CVE-2017-8750) - A security feature bypass exists in Microsoft Edge when the Edge Content Security Policy (CSP) fails to properly validate certain specially crafted documents. An attacker who exploited the bypass could trick a user into loading a page containing malicious content. (CVE-2017-8723, CVE-2017-8754) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists in the way that the scripting engine handles objects in memory in Microsoft Edge. The vulnerability could corrupt memory in such a way that an attacker could execute arbitrary code in the context of the current user. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could gain the same user rights as the current user. (CVE-2017-8738, CVE-2017-8752, CVE-2017-8753, CVE-2017-8755, CVE-2017-8756) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists in the way Microsoft Edge handles objects in memory. The vulnerability could corrupt memory in such a way that an attacker could execute arbitrary code in the context of the current user. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could gain the same user rights as the current user. (CVE-2017-8757) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists when Microsoft .NET Framework processes untrusted input. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability in software using the .NET framework could take control of an affected system. An attacker could then install programs; view, change, or delete data; or create new accounts with full user rights. (CVE-2017-8759) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists in Microsoft browsers in the scripting engines due to improper handling of objects in memory. An unauthenticated, remote attacker can exploit this, by convincing a user to visit a specially crafted website, to disclose files on a user's computer. (CVE-2017-8529)"); # https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/help/4038783/windows-10-update-kb4038783 script_set_attribute(attribute:"see_also", value:"http://www.nessus.org/u?15cd901b"); script_set_attribute(attribute:"solution", value: "Apply security update KB4038783."); script_set_cvss_base_vector("CVSS2#AV:N/AC:M/Au:N/C:C/I:C/A:C"); script_set_cvss_temporal_vector("CVSS2#E:H/RL:OF/RC:C"); script_set_cvss3_base_vector("CVSS:3.0/AV:L/AC:L/PR:N/UI:R/S:U/C:H/I:H/A:H"); script_set_cvss3_temporal_vector("CVSS:3.0/E:H/RL:O/RC:C"); script_set_attribute(attribute:"cvss_score_source", value:"CVE-2017-8759"); script_set_attribute(attribute:"exploitability_ease", value:"Exploits are available"); script_set_attribute(attribute:"exploit_available", value:"true"); script_set_attribute(attribute:"exploit_framework_core", value:"true"); script_set_attribute(attribute:"exploited_by_malware", value:"true"); script_set_attribute(attribute:"exploit_framework_canvas", value:"true"); script_set_attribute(attribute:"canvas_package", value:'CANVAS'); script_set_attribute(attribute:"vuln_publication_date", value:"2017/09/12"); script_set_attribute(attribute:"patch_publication_date", value:"2017/09/12"); script_set_attribute(attribute:"plugin_publication_date", value:"2017/09/12"); script_set_attribute(attribute:"plugin_type", value:"local"); script_set_attribute(attribute:"cpe", value:"cpe:/o:microsoft:windows"); script_end_attributes(); script_category(ACT_GATHER_INFO); script_family(english:"Windows : Microsoft Bulletins"); script_copyright(english:"This script is Copyright (C) 2017-2020 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof."); script_dependencies("smb_check_rollup.nasl", "smb_hotfixes.nasl", "ms_bulletin_checks_possible.nasl"); script_require_keys("SMB/MS_Bulletin_Checks/Possible"); script_require_ports(139, 445, "Host/patch_management_checks"); exit(0); } include("audit.inc"); include("smb_hotfixes_fcheck.inc"); include("smb_hotfixes.inc"); include("smb_func.inc"); include("misc_func.inc"); get_kb_item_or_exit("SMB/MS_Bulletin_Checks/Possible"); bulletin = "MS17-09"; kbs = make_list('4038783'); if (get_kb_item("Host/patch_management_checks")) hotfix_check_3rd_party(bulletin:bulletin, kbs:kbs, severity:SECURITY_HOLE); get_kb_item_or_exit("SMB/Registry/Enumerated"); get_kb_item_or_exit("SMB/WindowsVersion", exit_code:1); if (hotfix_check_sp_range(win10:'0') <= 0) audit(AUDIT_OS_SP_NOT_VULN); share = hotfix_get_systemdrive(as_share:TRUE, exit_on_fail:TRUE); if (!is_accessible_share(share:share)) audit(AUDIT_SHARE_FAIL, share); if ( smb_check_rollup(os:"10", sp:0, os_build:"10586", rollup_date:"09_2017", bulletin:bulletin, rollup_kb_list:[4038783]) ) { replace_kb_item(name:'SMB/Missing/'+bulletin, value:TRUE); hotfix_security_hole(); hotfix_check_fversion_end(); exit(0); } else { hotfix_check_fversion_end(); audit(AUDIT_HOST_NOT, hotfix_get_audit_report()); }NASL family Windows : Microsoft Bulletins NASL id SMB_NT_MS17_SEP_4038788.NASL description The remote Windows host is missing security update 4038788. It is, therefore, affected by multiple vulnerabilities : - A race condition that could lead to a remote code execution vulnerability exists in NetBT Session Services when NetBT fails to maintain certain sequencing requirements. (CVE-2017-0161) - A vulnerability exists when Microsoft Edge improperly accesses objects in memory. The vulnerability could corrupt memory in such a way that an attacker could execute arbitrary code in the context of the current user. (CVE-2017-11766) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists when Microsoft Edge does not properly handle objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could obtain information to further compromise the user last seen 2020-05-31 modified 2017-09-12 plugin id 103130 published 2017-09-12 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2017-2020 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/103130 title KB4038788: Windows 10 Version 1703 September 2017 Cumulative Update NASL family Windows : Microsoft Bulletins NASL id SMB_NT_MS17_SEP_4038792.NASL description The remote Windows host is missing security update 4038793 or cumulative update 4038792. It is, therefore, affected by multiple vulnerabilities : - A race condition that could lead to a remote code execution vulnerability exists in NetBT Session Services when NetBT fails to maintain certain sequencing requirements. (CVE-2017-0161) - A spoofing vulnerability exists in Microsoft last seen 2020-05-31 modified 2017-09-12 plugin id 103131 published 2017-09-12 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2017-2020 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/103131 title Windows 8.1 and Windows Server 2012 R2 September 2017 Security Updates NASL family Windows : Microsoft Bulletins NASL id SMB_NT_MS17_SEP_4038799.NASL description The remote Windows host is missing security update 4038786 or cumulative update 4038799. It is, therefore, affected by multiple vulnerabilities : - A race condition that could lead to a remote code execution vulnerability exists in NetBT Session Services when NetBT fails to maintain certain sequencing requirements. (CVE-2017-0161) - An elevation of privilege vulnerability exists in Windows when the Windows kernel-mode driver fails to properly handle objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could run arbitrary code in kernel mode. An attacker could then install programs; view, change, or delete data; or create new accounts with full user rights. (CVE-2017-8675) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists in the way that the Windows Graphics Device Interface (GDI) handles objects in memory, allowing an attacker to retrieve information from a targeted system. By itself, the information disclosure does not allow arbitrary code execution; however, it could allow arbitrary code to be run if the attacker uses it in combination with another vulnerability. (CVE-2017-8676) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists when the Windows font library improperly handles specially crafted embedded fonts. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could take control of the affected system. An attacker could then install programs; view, change, or delete data; or create new accounts with full user rights. (CVE-2017-8682) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists when the Microsoft Windows Graphics Component improperly handles objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could obtain information to further compromise the users system. (CVE-2017-8683) - A information disclosure vulnerability exists when the Windows GDI+ component improperly discloses kernel memory addresses. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could obtain information to further compromise the users system. (CVE-2017-8677, CVE-2017-8680, CVE-2017-8681, CVE-2017-8684) - A memory corruption vulnerability exists in the Windows Server DHCP service when an attacker sends specially crafted packets to a DHCP failover server. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could either run arbitrary code on the DHCP failover server or cause the DHCP service to become nonresponsive. To exploit the vulnerability, an attacker could send a specially crafted packet to a DHCP server. However, the DHCP server must be set to failover mode for the attack to succeed. The security update addresses the vulnerability by correcting how DHCP failover servers handle network packets. (CVE-2017-8686) - An Information disclosure vulnerability exists in Windows kernel that could allow an attacker to retrieve information that could lead to a Kernel Address Space Layout Randomization (KASLR) bypass. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could retrieve the memory address of a kernel object. (CVE-2017-8687) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists in the way that the Windows Graphics Device Interface+ (GDI+) handles objects in memory, allowing an attacker to retrieve information from a targeted system. By itself, the information disclosure does not allow arbitrary code execution; however, it could allow arbitrary code to be run if the attacker uses it in combination with another vulnerability. (CVE-2017-8688) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists due to the way Windows Uniscribe handles objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could take control of the affected system. An attacker could then install programs; view, change, or delete data; or create new accounts with full user rights. (CVE-2017-8692) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists when Windows Uniscribe improperly discloses the contents of its memory. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could obtain information to further compromise the users system. There are multiple ways an attacker could exploit the vulnerability, such as by convincing a user to open a specially crafted document or by convincing a user to visit an untrusted webpage. The update addresses the vulnerability by correcting how Windows Uniscribe handles objects in memory. (CVE-2017-8695) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists when Windows Shell does not properly validate file copy destinations. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could run arbitrary code in the context of the current user. (CVE-2017-8699) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists when the Windows kernel fails to properly initialize a memory address, allowing an attacker to retrieve information that could lead to a Kernel Address Space Layout Randomization (KASLR) bypass. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could retrieve the base address of the kernel driver from a compromised process. (CVE-2017-8708) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists when Windows Hyper-V on a host operating system fails to properly validate input from an authenticated user on a guest operating system. (CVE-2017-8713) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists in the VM Host Agent Service of Remote Desktop Virtual Host role when it fails to properly validate input from an authenticated user on a guest operating system. To exploit the vulnerability, an attacker could issue a specially crafted certificate on the guest operating system that could cause the VM host agent service on the host operating system to execute arbitrary code. The Remote Desktop Virtual Host role is not enabled by default. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could execute arbitrary code on the host operating system. The security update addresses the vulnerability by correcting how VM host agent service validates guest operating system user input. (CVE-2017-8714) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists when the Windows kernel improperly handles objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could obtain information to further compromise the users system. (CVE-2017-8678, CVE-2017-8679, CVE-2017-8709, CVE-2017-8719) - An elevation of privilege vulnerability exists in Windows when the Win32k component fails to properly handle objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could run arbitrary code in kernel mode. An attacker could then install programs; view, change, or delete data; or create new accounts with full user rights. (CVE-2017-8720) - A spoofing vulnerability exists when Internet Explorer improperly handles specific HTML content. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could trick a user into believing that the user was visiting a legitimate website. The specially crafted website could either spoof content or serve as a pivot to chain an attack with other vulnerabilities in web services. To exploit the vulnerability, the user must either browse to a malicious website or be redirected to it. In an email attack scenario, an attacker could send an email message in an attempt to convince the user to click a link to the malicious website. (CVE-2017-8733) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists when Microsoft Windows PDF Library improperly handles objects in memory. The vulnerability could corrupt memory in a way that enables an attacker to execute arbitrary code in the context of the current user. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could gain the same user rights as the current user. (CVE-2017-8728, CVE-2017-8737) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists in the way that Microsoft browser JavaScript engines render content when handling objects in memory. The vulnerability could corrupt memory in such a way that an attacker could execute arbitrary code in the context of the current user. (CVE-2017-8741) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists when Internet Explorer improperly accesses objects in memory. The vulnerability could corrupt memory in such a way that an attacker could execute arbitrary code in the context of the current user. (CVE-2017-8747) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists when Internet Explorer improperly accesses objects in memory. The vulnerability could corrupt memory in such a way that an attacker could execute arbitrary code in the context of the current user. (CVE-2017-8747, CVE-2017-8749) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists when Microsoft .NET Framework processes untrusted input. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability in software using the .NET framework could take control of an affected system. An attacker could then install programs; view, change, or delete data; or create new accounts with full user rights. (CVE-2017-8759) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists in Microsoft browsers in the scripting engines due to improper handling of objects in memory. An unauthenticated, remote attacker can exploit this, by convincing a user to visit a specially crafted website, to disclose files on a user last seen 2020-05-31 modified 2017-09-12 plugin id 103132 published 2017-09-12 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2017-2020 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/103132 title Windows Server 2012 September 2017 Security Updates NASL family Windows : Microsoft Bulletins NASL id SMB_NT_MS17_SEP_4038782.NASL description The remote Windows host is missing security update 4038782. It is, therefore, affected by multiple vulnerabilities : - A race condition that could lead to a remote code execution vulnerability exists in NetBT Session Services when NetBT fails to maintain certain sequencing requirements. (CVE-2017-0161) - A vulnerability exists when Microsoft Edge improperly accesses objects in memory. The vulnerability could corrupt memory in such a way that an attacker could execute arbitrary code in the context of the current user. (CVE-2017-11766) - A spoofing vulnerability exists in Microsoft last seen 2020-05-31 modified 2017-09-12 plugin id 103128 published 2017-09-12 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2017-2020 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/103128 title KB4038782: Windows 10 Version 1607 and Windows Server 2016 September 2017 Cumulative Update NASL family Windows : Microsoft Bulletins NASL id SMB_NT_MS17_SEP_WIN2008.NASL description The remote Windows host is missing multiple security updates released on 2017/09/12. It is, therefore, affected by multiple vulnerabilities : - An information disclosure vulnerability exists when Windows Hyper-V on a host operating system fails to properly validate input from an authenticated user on a guest operating system. To exploit the vulnerability, an attacker on a guest operating system could run a specially crafted application that could cause the Hyper-V host operating system to disclose memory information. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could gain access to information on the Hyper-V host operating system. The security update addresses the vulnerability by correcting how Hyper-V validates guest operating system user input. (CVE-2017-8707) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists in the Windows System Information Console when it improperly parses XML input containing a reference to an external entity. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could read arbitrary files via an XML external entity (XXE) declaration. To exploit the vulnerability, an attacker could create a file containing specially crafted XML content and convince an authenticated user to open the file. The update addresses the vulnerability by modifying the way that the Windows System Information Console parses XML input. (CVE-2017-8710) - An Information disclosure vulnerability exists in Windows kernel that could allow an attacker to retrieve information that could lead to a Kernel Address Space Layout Randomization (KASLR) bypass. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could retrieve the memory address of a kernel object. To exploit this vulnerability, an attacker would have to log on to an affected system and run a specially crafted application. The security update addresses the vulnerability by correcting how the Windows kernel handles memory addresses. (CVE-2017-8687) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists when the Microsoft Windows Graphics Component improperly handles objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could obtain information to further compromise the users system. To exploit this vulnerability, an attacker would have to log on to an affected system and run a specially crafted application. The vulnerability would not allow an attacker to execute code or to elevate user rights directly, but it could be used to obtain information that could be used to try to further compromise the affected system. The update addresses the vulnerability by correcting the way in which the Windows Graphics Component handles objects in memory. (CVE-2017-8683) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists when the Windows font library improperly handles specially crafted embedded fonts. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could take control of the affected system. An attacker could then install programs; view, change, or delete data; or create new accounts with full user rights. Users whose accounts are configured to have fewer user rights on the system could be less impacted than users who operate with administrative user rights. There are multiple ways an attacker could exploit this vulnerability. In a web- based attack scenario, an attacker could host a specially crafted website that is designed to exploit this vulnerability and then convince a user to view the website. An attacker would have no way to force users to view the attacker-controlled content. Instead, an attacker would have to convince users to take action, typically by getting them to click a link in an email message or in an Instant Messenger message that takes users to the attacker last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 103140 published 2017-09-12 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2017-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/103140 title Windows 2008 September 2017 Multiple Security Updates NASL family Windows : Microsoft Bulletins NASL id SMB_NT_MS17_SEP_4041083.NASL description The .NET Framework installation on the remote host is missing a security update. It is, therefore, affected by the following vulnerability: - A remote code execution vulnerability exists when Microsoft .NET Framework processes untrusted input. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability in software using the .NET framework could take control of an affected system. An attacker could then install programs; view, change, or delete data; or create new accounts with full user rights. Users whose accounts are configured to have fewer user rights on the system could be less impacted than users who operate with administrative user rights. (CVE-2017-8759) last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 103137 published 2017-09-12 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2017-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/103137 title Security and Quality Rollup for .NET Framework (Sep 2017)
Packetstorm
| data source | https://packetstormsecurity.com/files/download/144148/cve-2017-8759_toolkit.py.txt |
| id | PACKETSTORM:144148 |
| last seen | 2017-09-15 |
| published | 2017-09-14 |
| reporter | bhdresh |
| source | https://packetstormsecurity.com/files/144148/Microsoft-.NET-Framework-Remote-Code-Execution.html |
| title | Microsoft .NET Framework Remote Code Execution |
Seebug
| bulletinFamily | exploit |
| description | FireEye recently detected a malicious Microsoft Office RTF document that leveraged CVE-2017-8759, a SOAP WSDL parser code injection vulnerability. This vulnerability allows a malicious actor to inject arbitrary code during the parsing of SOAP WSDL definition contents. FireEye analyzed a Microsoft Word document where attackers used the arbitrary code injection to download and execute a Visual Basic script that contained PowerShell commands. FireEye shared the details of the vulnerability with Microsoft and has been coordinating public disclosure timed with the release of a patch to address the vulnerability and security guidance, which can be found here. FireEye email, endpoint and network products detected the malicious documents. ### Vulnerability Used to Target Russian Speakers The malicious document, “Проект.doc” (MD5: fe5c4d6bb78e170abf5cf3741868ea4c), might have been used to target a Russian speaker. Upon successful exploitation of CVE-2017-8759, the document downloads multiple components (details follow), and eventually launches a FINSPY payload (MD5: a7b990d5f57b244dd17e9a937a41e7f5). FINSPY malware, also reported as FinFisher or WingBird, is available for purchase as part of a “lawful intercept” capability. Based on this and previous use of FINSPY, we assess with moderate confidence that this malicious document was used by a nation-state to target a Russian-speaking entity for cyber espionage purposes. Additional detections by FireEye’s Dynamic Threat Intelligence system indicates that related activity, though potentially for a different client, might have occurred as early as July 2017. ### CVE-2017-8759 WSDL Parser Code Injection A code injection vulnerability exists in the WSDL parser module within the PrintClientProxy method (http://referencesource.microsoft.com/ - System.Runtime.Remoting/metadata/wsdlparser.cs,6111). The IsValidUrl does not perform correct validation if provided data that contains a CRLF sequence. This allows an attacker to inject and execute arbitrary code. A portion of the vulnerable code is shown in Figure 1. 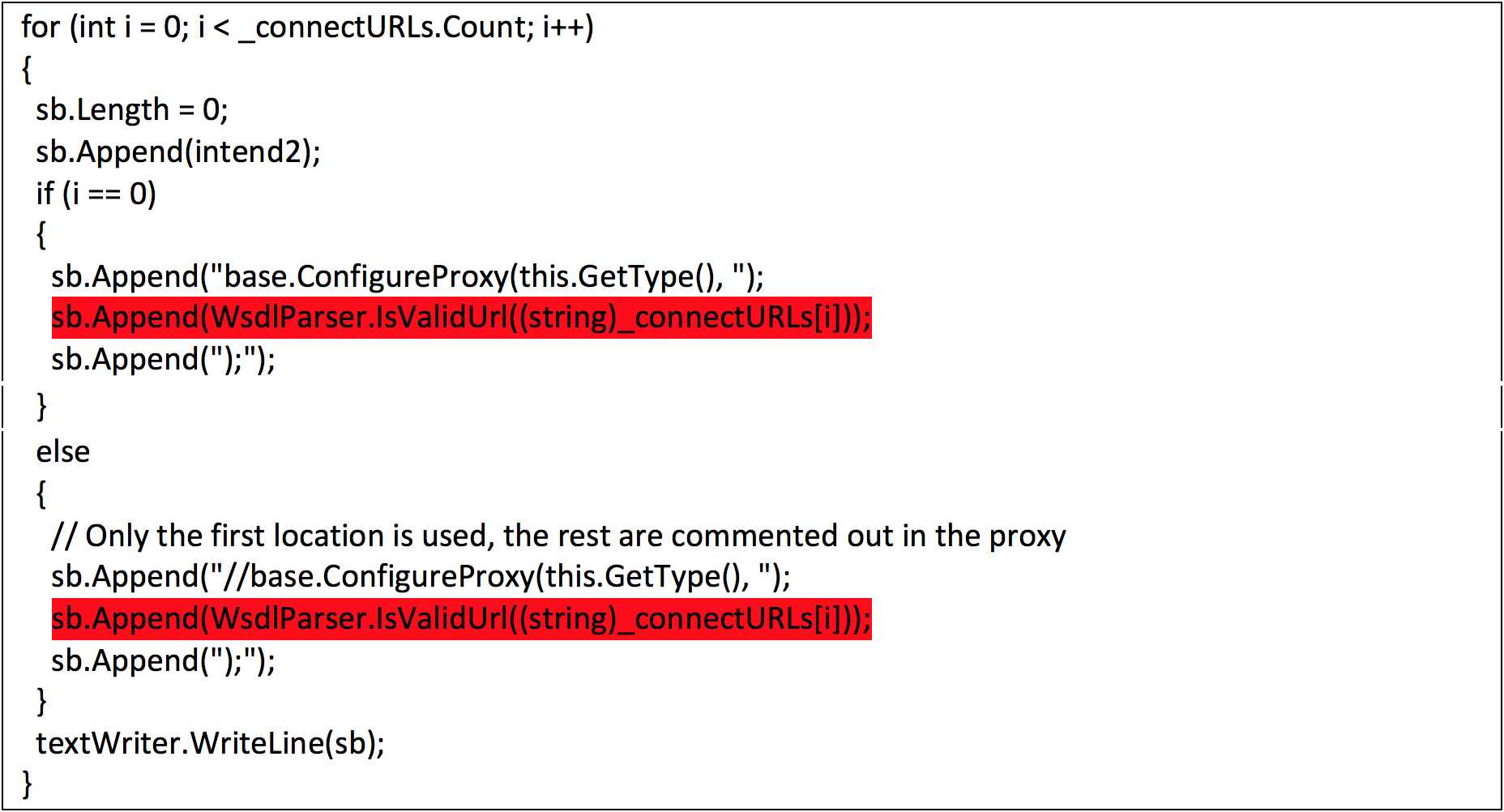 Figure 1: Vulnerable WSDL Parser When multiple address definitions are provided in a SOAP response, the code inserts the “//base.ConfigureProxy(this.GetType(),” string after the first address, commenting out the remaining addresses. However, if a CRLF sequence is in the additional addresses, the code following the CRLF will not be commented out. Figure 2 shows that due to lack validation of CRLF, a System.Diagnostics.Process.Start method call is injected. The generated code will be compiled by csc.exe of .NET framework, and loaded by the Office executables as a DLL. 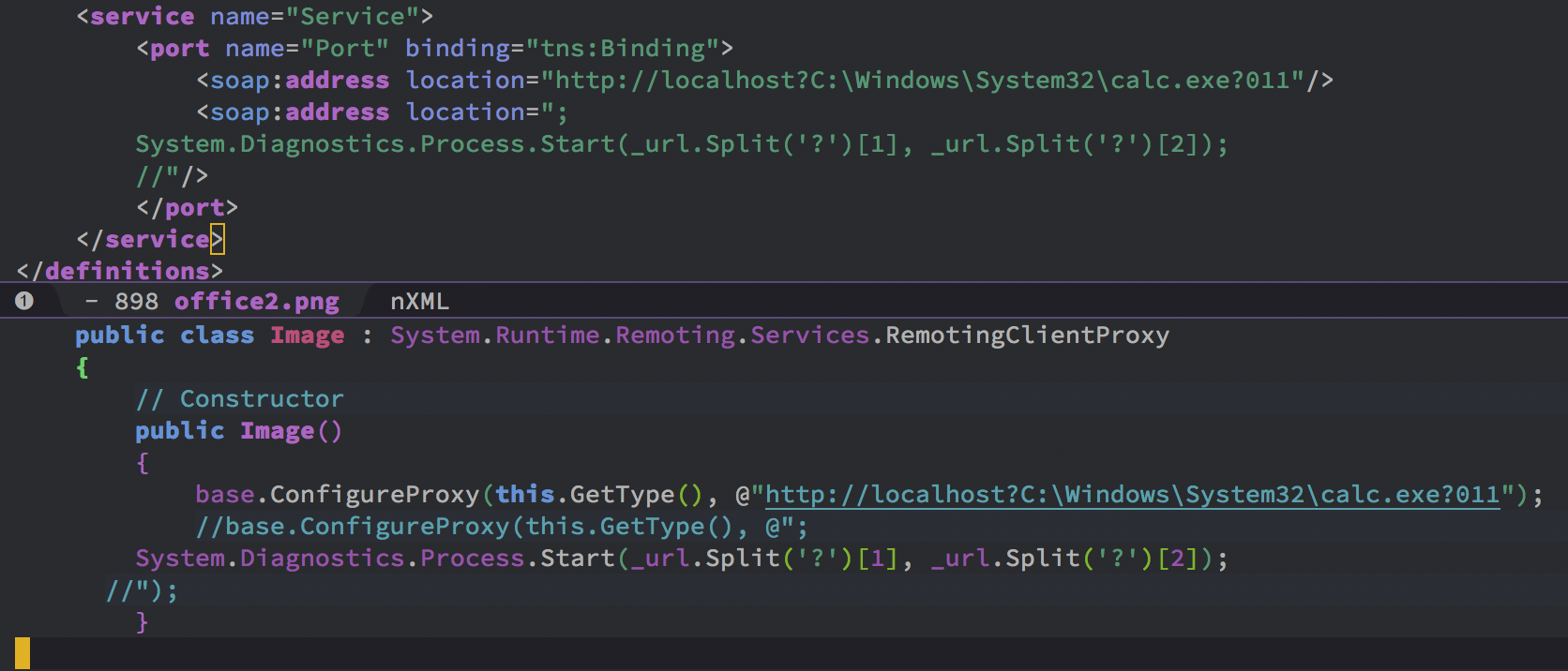 Figure 2: SOAP definition VS Generated code ### The In-the-Wild Attacks The attacks that FireEye observed in the wild leveraged a Rich Text Format (RTF) document, similar to the CVE-2017-0199 documents we previously reported on. The malicious sampled contained an embedded SOAP monikers to facilitate exploitation (Figure 3). 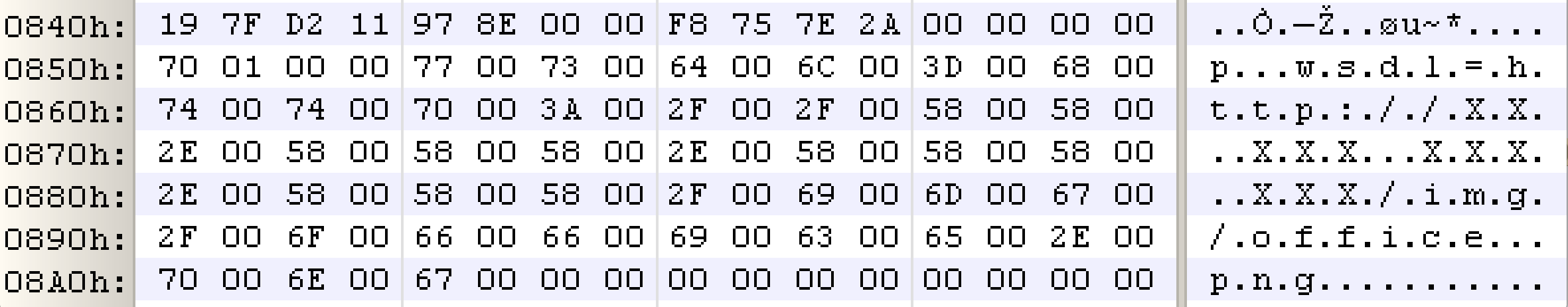 Figure 3: SOAP Moniker The payload retrieves the malicious SOAP WSDL definition from an attacker-controlled server. The WSDL parser, implemented in System.Runtime.Remoting.ni.dll of .NET framework, parses the content and generates a .cs source code at the working directory. The csc.exe of .NET framework then compiles the generated source code into a library, namely http[url path].dll. Microsoft Office then loads the library, completing the exploitation stage. Figure 4 shows an example library loaded as a result of exploitation. 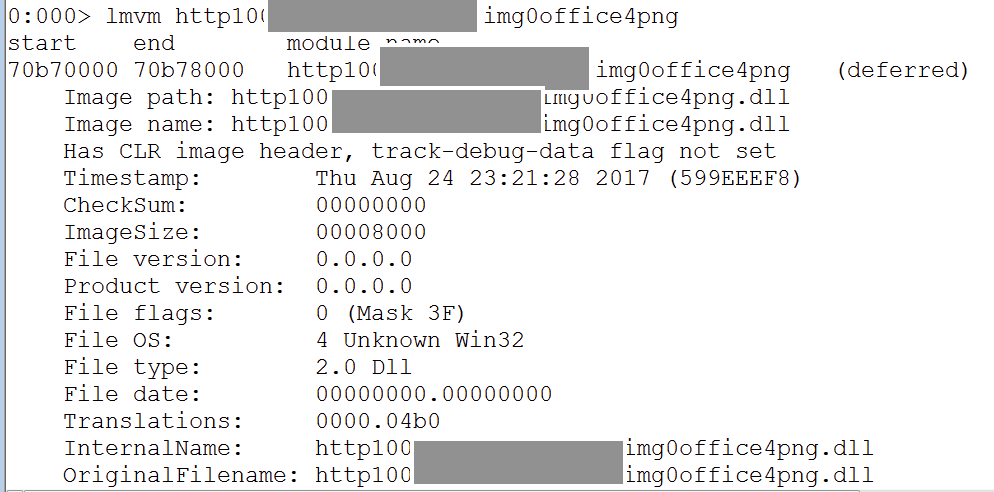 Figure 4: DLL loaded Upon successful exploitation, the injected code creates a new process and leverages mshta.exe to retrieve a HTA script named “word.db” from the same server. The HTA script removes the source code, compiled DLL and the PDB files from disk and then downloads and executes the FINSPY malware named “left.jpg,” which in spite of the .jpg extension and “image/jpeg” content-type, is actually an executable. Figure 5 shows the details of the PCAP of this malware transfer. 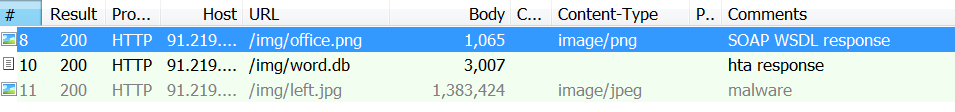 Figure 5: Live requests The malware will be placed at %appdata%\Microsoft\Windows\OfficeUpdte-KB[ 6 random numbers ].exe. Figure 6 shows the process create chain under Process Monitor. 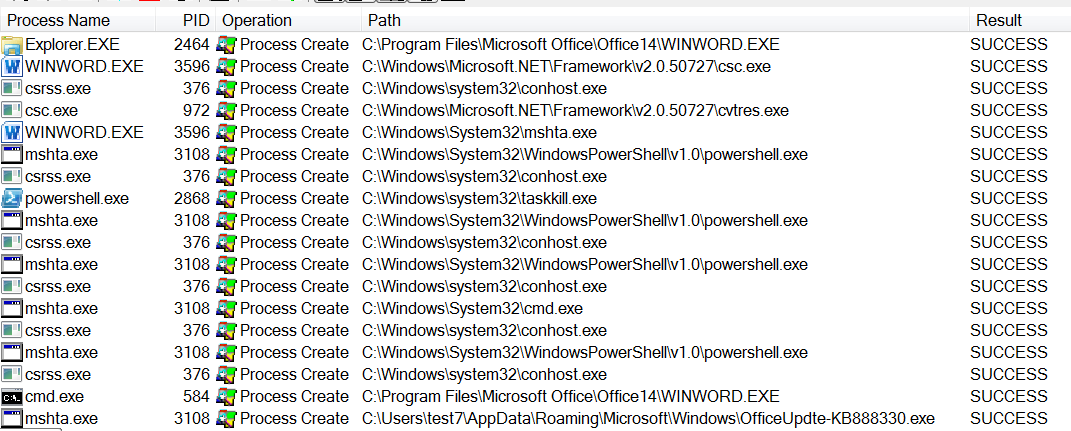 Figure 6: Process Created Chain ### The Malware The “left.jpg” (md5: a7b990d5f57b244dd17e9a937a41e7f5) is a variant of FINSPY. It leverages heavily obfuscated code that employs a built-in virtual machine – among other anti-analysis techniques – to make reversing more difficult. As likely another unique anti-analysis technique, it parses its own full path and searches for the string representation of its own MD5 hash. Many resources, such as analysis tools and sandboxes, rename files/samples to their MD5 hash in order to ensure unique filenames. This variant runs with a mutex of "WininetStartupMutex0". ### Conclusion CVE-2017-8759 is the second zero-day vulnerability used to distribute FINSPY uncovered by FireEye in 2017. These exposures demonstrate the significant resources available to “lawful intercept” companies and their customers. Furthermore, FINSPY has been sold to multiple clients, suggesting the vulnerability was being used against other targets. It is possible that CVE-2017-8759 was being used by additional actors. While we have not found evidence of this, the zero day being used to distribute FINSPY in April 2017, CVE-2017-0199 was simultaneously being used by a financially motivated actor. If the actors behind FINSPY obtained this vulnerability from the same source used previously, it is possible that source sold it to additional actors. |
| id | SSV:96484 |
| last seen | 2017-11-19 |
| modified | 2017-09-14 |
| published | 2017-09-14 |
| reporter | Root |
| source | https://www.seebug.org/vuldb/ssvid-96484 |
| title | FireEye Uncovers CVE-2017-8759: Zero-Day Used in the Wild to Distribute FINSPY |
The Hacker News
id THN:5AD427A8B33BDFD2EE553727C6CE4EE0 last seen 2018-01-27 modified 2017-10-16 published 2017-10-16 reporter Mohit Kumar source https://thehackernews.com/2017/10/flash-player-zero-day.html title Hackers Use New Flash Zero-Day Exploit to Distribute FinFisher Spyware id THN:C21D17F1D92C12B031AB9C761BBD004A last seen 2018-01-27 modified 2018-01-17 published 2018-01-17 reporter Mohit Kumar source https://thehackernews.com/2018/01/microsoft-office-malware.html title Hackers Exploiting Three Microsoft Office Flaws to Spread Zyklon Malware id THN:5133F80C8A11FE7678A971A326DDA682 last seen 2018-01-27 modified 2017-09-13 published 2017-09-13 reporter Mohit Kumar source https://thehackernews.com/2017/09/windows-zero-day-spyware.html title Immediately Patch Windows 0-Day Flaw That's Being Used to Spread Spyware
References
- http://www.securityfocus.com/bid/100742
- http://www.securityfocus.com/bid/100742
- http://www.securitytracker.com/id/1039324
- http://www.securitytracker.com/id/1039324
- https://github.com/bhdresh/CVE-2017-8759
- https://github.com/bhdresh/CVE-2017-8759
- https://github.com/GitHubAssessments/CVE_Assessments_01_2020
- https://github.com/GitHubAssessments/CVE_Assessments_01_2020
- https://github.com/nccgroup/CVE-2017-8759
- https://github.com/nccgroup/CVE-2017-8759
- https://portal.msrc.microsoft.com/en-US/security-guidance/advisory/CVE-2017-8759
- https://portal.msrc.microsoft.com/en-US/security-guidance/advisory/CVE-2017-8759
- https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/42711/
- https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/42711/