Vulnerabilities > CVE-2017-5753 - Information Exposure Through Discrepancy vulnerability in multiple products
Attack vector
LOCAL Attack complexity
HIGH Privileges required
LOW Confidentiality impact
HIGH Integrity impact
NONE Availability impact
NONE Summary
Systems with microprocessors utilizing speculative execution and branch prediction may allow unauthorized disclosure of information to an attacker with local user access via a side-channel analysis.
Vulnerable Configurations
Common Weakness Enumeration (CWE)
Exploit-Db
| description | Multiple CPUs - 'Spectre' Information Disclosure. CVE-2017-5715,CVE-2017-5753. Local exploit for Multiple platform |
| file | exploits/multiple/local/43427.c |
| id | EDB-ID:43427 |
| last seen | 2018-01-24 |
| modified | 2018-01-03 |
| platform | multiple |
| port | |
| published | 2018-01-03 |
| reporter | Exploit-DB |
| source | https://www.exploit-db.com/download/43427/ |
| title | Multiple CPUs - 'Spectre' Information Disclosure |
| type | local |
Nessus
NASL family Windows : Microsoft Bulletins NASL id SMB_NT_MS18_JAN_4056891.NASL description The remote Windows host is missing security update 4056891 or 4057144. It is, therefore, affected by multiple vulnerabilities : - An vulnerability exists within microprocessors utilizing speculative execution and indirect branch prediction, which may allow an attacker with local user access to disclose information via a side-channel analysis. (CVE-2017-5715, CVE-2017-5753, CVE-2017-5754) - An elevation of privilege vulnerability exists when the Windows kernel fails to properly handle objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could run arbitrary code in kernel mode. An attacker could then install programs; view, change, or delete data; or create new accounts with full user rights. (CVE-2018-0744) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists in the way that the scripting engine handles objects in memory in Microsoft Edge. The vulnerability could corrupt memory in such a way that an attacker could execute arbitrary code in the context of the current user. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could gain the same user rights as the current user. (CVE-2018-0758, CVE-2018-0769, CVE-2018-0770, CVE-2018-0776, CVE-2018-0777, CVE-2018-0781) - An elevation of privilege vulnerability exists in the way that the Windows Kernel API enforces permissions. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could impersonate processes, interject cross-process communication, or interrupt system functionality. (CVE-2018-0748, CVE-2018-0751, CVE-2018-0752) - An elevation of privilege vulnerability exists when Microsoft Edge does not properly enforce cross-domain policies, which could allow an attacker to access information from one domain and inject it into another domain. (CVE-2018-0803) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists in Windows Adobe Type Manager Font Driver (ATMFD.dll) when it fails to properly handle objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could potentially read data that was not intended to be disclosed. Note that this vulnerability would not allow an attacker to execute code or to elevate their user rights directly, but it could be used to obtain information that could be used to try to further compromise the affected system. (CVE-2018-0754) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists in the way the scripting engine handles objects in memory in Microsoft browsers. The vulnerability could corrupt memory in such a way that an attacker could execute arbitrary code in the context of the current user. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could gain the same user rights as the current user. (CVE-2018-0762, CVE-2018-0772) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists when Microsoft Edge PDF Reader improperly handles objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could obtain information to further compromise the users system. (CVE-2018-0766) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists when the scripting engine does not properly handle objects in memory in Microsoft Edge. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could obtain information to further compromise the users system. (CVE-2018-0767, CVE-2018-0780) - An elevation of privilege vulnerability exists in the Microsoft Server Message Block (SMB) Server when an attacker with valid credentials attempts to open a specially crafted file over the SMB protocol on the same machine. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could bypass certain security checks in the operating system. (CVE-2018-0749) - A denial of service vulnerability exists in the way that Windows handles objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could cause a target system to stop responding. Note that the denial of service condition would not allow an attacker to execute code or to elevate user privileges. However, the denial of service condition could prevent authorized users from using system resources. The security update addresses the vulnerability by correcting how Windows handles objects in memory. (CVE-2018-0753) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists in the Windows kernel that could allow an attacker to retrieve information that could lead to a Kernel Address Space Layout Randomization (ASLR) bypass. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could retrieve the memory address of a kernel object. (CVE-2018-0745, CVE-2018-0746, CVE-2018-0747) - An elevation of privilege vulnerability exists due to an integer overflow in Windows Subsystem for Linux. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could execute code with elevated permissions. (CVE-2018-0743) last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 105549 published 2018-01-04 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018 Tenable Network Security, Inc. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/105549 title KB4056891: Windows 10 Version 1703 January 2018 Security Update (Meltdown)(Spectre) NASL family SuSE Local Security Checks NASL id SUSE_SU-2018-0609-1.NASL description This update for xen fixes several issues. These security issues were fixed : - CVE-2017-5753, CVE-2017-5715, CVE-2017-5754: Prevent information leaks via side effects of speculative execution, aka last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 107144 published 2018-03-06 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/107144 title SUSE SLES12 Security Update : xen (SUSE-SU-2018:0609-1) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family OracleVM Local Security Checks NASL id ORACLEVM_OVMSA-2018-0224.NASL description The remote OracleVM system is missing necessary patches to address critical security updates : please see Oracle VM Security Advisory OVMSA-2018-0224 for details. last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 110110 published 2018-05-25 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/110110 title OracleVM 3.3 : xen (OVMSA-2018-0224) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family Ubuntu Local Security Checks NASL id UBUNTU_USN-3541-1.NASL description Jann Horn discovered that microprocessors utilizing speculative execution and branch prediction may allow unauthorized memory reads via sidechannel attacks. This flaw is known as Spectre. A local attacker could use this to expose sensitive information, including kernel memory. This update provides mitigations for the i386 (CVE-2017-5753 only), amd64, ppc64el, and s390x architectures. (CVE-2017-5715, CVE-2017-5753) USN-3523-1 mitigated CVE-2017-5754 (Meltdown) for the amd64 architecture in Ubuntu 17.10. This update provides the corresponding mitigations for the ppc64el architecture. Jann Horn discovered that microprocessors utilizing speculative execution and indirect branch prediction may allow unauthorized memory reads via sidechannel attacks. This flaw is known as Meltdown. A local attacker could use this to expose sensitive information, including kernel memory. (CVE-2017-5754). Note that Tenable Network Security has extracted the preceding description block directly from the Ubuntu security advisory. Tenable has attempted to automatically clean and format it as much as possible without introducing additional issues. last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 106270 published 2018-01-23 reporter Ubuntu Security Notice (C) 2018-2019 Canonical, Inc. / NASL script (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/106270 title Ubuntu 17.10 : linux vulnerabilities (USN-3541-1) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family Ubuntu Local Security Checks NASL id UBUNTU_USN-3530-1.NASL description It was discovered that speculative execution performed by modern CPUs could leak information through a timing side-channel attack, and that this could be exploited in web browser JavaScript engines. If a user were tricked in to opening a specially crafted website, an attacker could potentially exploit this to obtain sensitive information from other domains, bypassing same-origin restrictions. (CVE-2017-5753, CVE-2017-5715). Note that Tenable Network Security has extracted the preceding description block directly from the Ubuntu security advisory. Tenable has attempted to automatically clean and format it as much as possible without introducing additional issues. last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 105766 published 2018-01-12 reporter Ubuntu Security Notice (C) 2018-2019 Canonical, Inc. / NASL script (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/105766 title Ubuntu 16.04 LTS / 17.04 / 17.10 : webkit2gtk vulnerabilities (USN-3530-1) (Spectre) NASL family SuSE Local Security Checks NASL id SUSE_SU-2018-0011-1.NASL description The SUSE Linux Enterprise 11 SP4 kernel was updated to receive various security and bugfixes. This update adds mitigations for various side channel attacks against modern CPUs that could disclose content of otherwise unreadable memory (bnc#1068032). - CVE-2017-5753: Local attackers on systems with modern CPUs featuring deep instruction pipelining could use attacker controllable speculative execution over code patterns in the Linux Kernel to leak content from otherwise not readable memory in the same address space, allowing retrieval of passwords, cryptographic keys and other secrets. This problem is mitigated by adding speculative fencing on affected code paths throughout the Linux kernel. This issue is addressed for the x86_64, the IBM Power and IBM zSeries architecture. - CVE-2017-5715: Local attackers on systems with modern CPUs featuring branch prediction could use mispredicted branches to speculatively execute code patterns that in turn could be made to leak other non-readable content in the same address space, an attack similar to CVE-2017-5753. This problem is mitigated by disabling predictive branches, depending on CPU architecture either by firmware updates and/or fixes in the user-kernel privilege boundaries. This is done with help of Linux Kernel fixes on the Intel/AMD x86_64 and IBM zSeries architectures. On x86_64, this requires also updates of the CPU microcode packages, delivered in separate updates. For IBM Power and zSeries the required firmware updates are supplied over regular channels by IBM. As this feature can have a performance impact, it can be disabled using the last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 105575 published 2018-01-04 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/105575 title SUSE SLES11 Security Update : kernel (SUSE-SU-2018:0011-1) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family F5 Networks Local Security Checks NASL id F5_BIGIP_SOL91229003.NASL description The following three side-channel attacks were publicly disclosed on January 3, 2018 : CVE-2017-5715 Spectre-BTB (previously known as Spectre Variant 2) Branch target injection Systems with microprocessors utilizing speculative execution and indirect branch prediction may allow unauthorized disclosure of information to an attacker with local user access via a side-channel analysis. CVE-2017-5753 Spectre-PHT (previously known as Spectre Variant 1) Bounds checking bypass Systems with microprocessors utilizing speculative execution and branch prediction may allow unauthorized disclosure of information to an attacker with local user access via a side-channel analysis. CVE-2017-5754 Meltdown-US (previously known as Meltdown) Rogue data cache load Systems with microprocessors utilizing speculative execution and indirect branch prediction may allow unauthorized disclosure of information to an attacker with local user access via a side-channel analysis of the data cache. Impact F5 continues to investigate the impact of the Spectre and Meltdown vulnerabilities on our products. F5 is focused onproviding patched releases as soon as we have fully tested and verified fixes. F5 will update this article with the most current information as soon as it is confirmed. BIG-IP First and foremost, there is no exposure on BIG-IP products by way ofthe data plane. All exposure is limited to the control plane (also known as the management plane). Furthermore, on the control plane, the vulnerabilities are exploitable only by four authorized, authenticated account roles: Administrator, Resource Administrator, Manager, and iRules Manager. You must be authorized to access the system in one of these roles to even attempt to exploit the vulnerabilities. All three vulnerabilities require an attacker who can provideand runbinary code of their choosing on the BIG-IP platform. These conditions severely restrict the exposure risk of BIG-IP products. For single-tenancy products, such as astandalone BIG-IP appliance, the risk is limited to a local, authorized user using one of the vulnerabilities to read information from memory that they would not normally be able to access, exceeding their privileges. Effectively, the risk in a single-tenancy situation is that a user may be able to access kernel-space memory, instead of being limited to their own user-space. For multi-tenancy environments, such as cloud, VE, and Virtual Clustered Multiprocessing (vCMP), the same local risk applies as with single-tenancy environments local kernel memory access. Additionally, the risk of attacks across guests exists, or attacks against the hypervisor/host. In cloud and VE environments, preventing these new attacks falls on the hypervisor/host platform, outside the scope of F5 last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 118702 published 2018-11-02 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/118702 title F5 Networks BIG-IP : Side-channel processor vulnerabilities (K91229003) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family Windows : Microsoft Bulletins NASL id SMB_NT_MS18_APR_4093112.NASL description The remote Windows host is missing security update 4093112. It is, therefore, affected by multiple vulnerabilities : - An vulnerability exists within microprocessors utilizing speculative execution and indirect branch prediction, which may allow an attacker with local user access to disclose information via a side-channel analysis. (CVE-2017-5715, CVE-2017-5753, CVE-2017-5754) - An elevation of privilege vulnerability exists when Windows improperly handles objects in memory and incorrectly maps kernel memory. (CVE-2018-1009) - A security feature bypass exists when Device Guard incorrectly validates an untrusted file. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could make an unsigned file appear to be signed. Because Device Guard relies on the signature to determine the file is non- malicious, Device Guard could then allow a malicious file to execute. In an attack scenario, an attacker could make an untrusted file appear to be a trusted file. The update addresses the vulnerability by correcting how Device Guard handles untrusted files. (CVE-2018-0966, CVE-2018-1035) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists in the way that the Chakra scripting engine handles objects in memory in Microsoft Edge. The vulnerability could corrupt memory in such a way that an attacker could execute arbitrary code in the context of the current user. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could gain the same user rights as the current user. (CVE-2018-0979, CVE-2018-0980, CVE-2018-0990, CVE-2018-0993, CVE-2018-0994, CVE-2018-0995, CVE-2018-1019) - A denial of service vulnerability exists in the way that Windows SNMP Service handles malformed SNMP traps. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could cause a target system to stop responding. Note that the denial of service condition would not allow an attacker to execute code or to elevate user privileges. However, the denial of service condition could prevent authorized users from using system resources. The security update addresses the vulnerability by correcting how Windows SNMP Service processes SNMP traps. (CVE-2018-0967) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists when the Windows kernel improperly handles objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could obtain information to further compromise the users system. (CVE-2018-0960) - An elevation of privilege vulnerability exists in Windows Adobe Type Manager Font Driver (ATMFD.dll) when it fails to properly handle objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could execute arbitrary code and take control of an affected system. An attacker could then install programs; view, change, or delete data; or create new accounts with full user rights. (CVE-2018-1008) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists when the scripting engine does not properly handle objects in memory in Internet Explorer. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could obtain information to further compromise the users system. (CVE-2018-0987) - A buffer overflow vulnerability exists in the Microsoft JET Database Engine that could allow remote code execution on an affected system. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could take control of an affected system. An attacker could then install programs; view, change, or delete data; or create new accounts with full user rights. Users whose accounts are configured to have fewer user rights on the system could be less impacted than users who operate with administrative user rights. (CVE-2018-1003) - An elevation of privilege vulnerability exists in the way that the Windows Kernel handles objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could execute code with elevated permissions. (CVE-2018-0963) - A denial of service vulnerability exists in Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) when an attacker connects to the target system using RDP and sends specially crafted requests. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could cause the RDP service on the target system to stop responding. (CVE-2018-0976) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists in the way that the scripting engine handles objects in memory in Internet Explorer. The vulnerability could corrupt memory in such a way that an attacker could execute arbitrary code in the context of the current user. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could gain the same user rights as the current user. (CVE-2018-0988, CVE-2018-0996, CVE-2018-1001) - A security feature bypass vulnerability exists when Active Directory incorrectly applies Network Isolation settings. (CVE-2018-0890) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists when the Windows font library improperly handles specially crafted embedded fonts. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could take control of the affected system. An attacker could then install programs; view, change, or delete data; or create new accounts with full user rights. (CVE-2018-1010, CVE-2018-1012, CVE-2018-1013, CVE-2018-1015, CVE-2018-1016) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists when Internet Explorer improperly accesses objects in memory. The vulnerability could corrupt memory in such a way that an attacker could execute arbitrary code in the context of the current user. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could gain the same user rights as the current user. (CVE-2018-0870, CVE-2018-0991, CVE-2018-0997, CVE-2018-1018, CVE-2018-1020) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists when Microsoft Edge PDF Reader improperly handles objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could obtain information to further compromise the users system. (CVE-2018-0998) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists in the Windows kernel that could allow an attacker to retrieve information that could lead to a Kernel Address Space Layout Randomization (ASLR) bypass. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could retrieve the memory address of a kernel object. (CVE-2018-0968, CVE-2018-0969, CVE-2018-0970, CVE-2018-0971, CVE-2018-0972, CVE-2018-0973, CVE-2018-0974, CVE-2018-0975) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists when Microsoft Edge improperly handles objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could obtain information to further compromise the users system. (CVE-2018-0892) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists when Windows Hyper-V on a host operating system fails to properly validate input from an authenticated user on a guest operating system. (CVE-2018-0957, CVE-2018-0964) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists in the way that Microsoft browsers access objects in memory. The vulnerability could corrupt memory in a way that could allow an attacker to execute arbitrary code in the context of the current user. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could gain the same user rights as the current user. (CVE-2018-1023) - A denial of service vulnerability exists in the way that Windows handles objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could cause a target system to stop responding. Note that the denial of service condition would not allow an attacker to execute code or to elevate user privileges. However, the denial of service condition could prevent authorized users from using system resources. The security update addresses the vulnerability by correcting how Windows handles objects in memory. (CVE-2018-8116) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists in the way that the VBScript engine handles objects in memory. The vulnerability could corrupt memory in such a way that an attacker could execute arbitrary code in the context of the current user. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could gain the same user rights as the current user. (CVE-2018-1004) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists in the way that the scripting engine handles objects in memory in Internet Explorer. The vulnerability could corrupt memory in such a way that an attacker could provide an attacker with information to further compromise the user last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 108964 published 2018-04-10 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/108964 title KB4093112: Windows 10 Version 1709 and Windows Server Version 1709 April 2018 Security Update (Meltdown)(Spectre) NASL family Red Hat Local Security Checks NASL id REDHAT-RHSA-2018-0512.NASL description An update for kernel is now available for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6. Red Hat Product Security has rated this update as having a security impact of Important. A Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) base score, which gives a detailed severity rating, is available for each vulnerability from the CVE link(s) in the References section. The kernel packages contain the Linux kernel, the core of any Linux operating system. Security Fix(es) : * hw: cpu: speculative execution branch target injection (s390-only) (CVE-2017-5715, Important) * hw: cpu: speculative execution bounds-check bypass (s390 and powerpc) (CVE-2017-5753, Important) * hw: cpu: speculative execution permission faults handling (powerpc-only) (CVE-2017-5754) For more details about the security issue(s), including the impact, a CVSS score, acknowledgments, and other related information, refer to the CVE page(s) listed in the References section. Bug Fixes : * If a fibre channel (FC) switch was powered down and then powered on again, the SCSI device driver stopped permanently the SCSI device last seen 2020-05-19 modified 2018-03-14 plugin id 108329 published 2018-03-14 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2020 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/108329 title RHEL 6 : kernel (RHSA-2018:0512) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family Huawei Local Security Checks NASL id EULEROS_SA-2018-1236.NASL description According to the versions of the kernel packages installed, the EulerOS Virtualization installation on the remote host is affected by the following vulnerabilities : - The recent speculative execution CVEs address three potential attacks across a wide variety of architectures and hardware platforms. - Note: This issue is present in hardware and cannot be fully fixed via software update. The nature of these vulnerabilities and their fixes introduces the possibility of reduced performance on patched systems. The performance impact depends on the hardware and the applications in place. - The first two variants abuse speculative execution to perform bounds-check bypass (CVE-2017-5753), or by utilizing branch target injection (CVE-2017-5715) to cause kernel code at an address under attacker control to execute speculatively. Collectively these are known as last seen 2020-03-19 modified 2018-09-18 plugin id 117545 published 2018-09-18 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2020 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/117545 title EulerOS Virtualization 2.5.0 : kernel (EulerOS-SA-2018-1236) NASL family Windows NASL id NVIDIA_WIN_CVE_2017_5753.NASL description The NVIDIA GPU display driver software on the remote host is missing a security update. It is, therefore, affected by multiple vulnerabilities. last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 105777 published 2018-01-12 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/105777 title NVIDIA Windows GPU Display Driver 384.x / 385.x / 386.x < 386.07 / 390.x < 390.65 Multiple Vulnerabilities (Meltdown)(Spectre) NASL family Red Hat Local Security Checks NASL id REDHAT-RHSA-2018-0045.NASL description An update for rhvm-appliance is now available for RHEV 4.X, RHEV-H, and Agents for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7. Red Hat Product Security has rated this update as having a security impact of Important. A Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) base score, which gives a detailed severity rating, is available for each vulnerability from the CVE link(s) in the References section. The RHV-M Virtual Appliance automates the process of installing and configuring the Red Hat Virtualization Manager. The appliance is available to download as an OVA file from the Customer Portal. Security Fix(es) : An industry-wide issue was found in the way many modern microprocessor designs have implemented speculative execution of instructions (a commonly used performance optimization). There are three primary variants of the issue which differ in the way the speculative execution can be exploited. Note: This issue is present in hardware and cannot be fully fixed via software update. The updated kernel packages provide software mitigation for this hardware issue at a cost of potential performance penalty. Please refer to References section for further information about this issue and the performance impact. Variant CVE-2017-5753 triggers the speculative execution by performing a bounds-check bypass. It relies on the presence of a precisely-defined instruction sequence in the privileged code as well as the fact that memory accesses may cause allocation into the microprocessor last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 105676 published 2018-01-09 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/105676 title RHEL 7 : rhvm-appliance (RHSA-2018:0045) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family PhotonOS Local Security Checks NASL id PHOTONOS_PHSA-2018-1_0-0098_LINUX.NASL description An update of the linux package has been released. last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 121800 published 2019-02-07 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/121800 title Photon OS 1.0: Linux PHSA-2018-1.0-0098 NASL family Fedora Local Security Checks NASL id FEDORA_2018-690989736A.NASL description This update includes improvements to mitigate the effects of Spectre ([CVE-2017-5753](https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-20 17-5753) and [CVE-2017-5715](https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-201 7-5715)) : - Disable SharedArrayBuffers from Web API. - Reduce the precision of “high” resolution time to 1ms. Additional fixes : - Fix API documentation generation with newer gtk-doc. Note that Tenable Network Security has extracted the preceding description block directly from the Fedora update system website. Tenable has attempted to automatically clean and format it as much as possible without introducing additional issues. last seen 2020-06-05 modified 2018-01-19 plugin id 106178 published 2018-01-19 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2020 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/106178 title Fedora 26 : webkitgtk4 (2018-690989736a) (Spectre) NASL family SuSE Local Security Checks NASL id SUSE_SU-2018-0040-1.NASL description The SUSE Linux Enterprise 11 SP3 LTSS kernel was updated to receive various security and bugfixes. This update adds mitigations for various side channel attacks against modern CPUs that could disclose content of otherwise unreadable memory (bnc#1068032). - CVE-2017-5753: Local attackers on systems with modern CPUs featuring deep instruction pipelining could use attacker controllable speculative execution over code patterns in the Linux Kernel to leak content from otherwise not readable memory in the same address space, allowing retrieval of passwords, cryptographic keys and other secrets. This problem is mitigated by adding speculative fencing on affected code paths throughout the Linux kernel. - CVE-2017-5715: Local attackers on systems with modern CPUs featuring branch prediction could use mispredicted branches to speculatively execute code patterns that in turn could be made to leak other non-readable content in the same address space, an attack similar to CVE-2017-5753. This problem is mitigated by disabling predictive branches, depending on CPU architecture either by firmware updates and/or fixes in the user-kernel privilege boundaries. Please contact your CPU / hardware vendor for potential microcode or BIOS updates needed for this fix. As this feature can have a performance impact, it can be disabled using the last seen 2020-06-05 modified 2018-01-09 plugin id 105685 published 2018-01-09 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2020 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/105685 title SUSE SLES11 Security Update : kernel (SUSE-SU-2018:0040-1) (BlueBorne) (KRACK) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family NewStart CGSL Local Security Checks NASL id NEWSTART_CGSL_NS-SA-2019-0143_KERNEL.NASL description The remote NewStart CGSL host, running version MAIN 4.05, has kernel packages installed that are affected by multiple vulnerabilities: - A flaw was found in the Linux kernel last seen 2020-03-18 modified 2019-08-12 plugin id 127408 published 2019-08-12 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2019-2020 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/127408 title NewStart CGSL MAIN 4.05 : kernel Multiple Vulnerabilities (NS-SA-2019-0143) NASL family Huawei Local Security Checks NASL id EULEROS_SA-2018-1002.NASL description According to the versions of the kernel packages installed, the EulerOS installation on the remote host is affected by the following vulnerabilities : - The recent speculative execution CVEs address three potential attacks across a wide variety of architectures and hardware platforms. - Note: This issue is present in hardware and cannot be fully fixed via software update. The nature of these vulnerabilities and their fixes introduces the possibility of reduced performance on patched systems. The performance impact depends on the hardware and the applications in place. - The first two variants abuse speculative execution to perform bounds-check bypass (CVE-2017-5753), or by utilizing branch target injection (CVE-2017-5715) to cause kernel code at an address under attacker control to execute speculatively. Collectively these are known as last seen 2020-05-06 modified 2018-01-09 plugin id 105655 published 2018-01-09 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2020 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/105655 title EulerOS 2.0 SP1 : kernel (EulerOS-SA-2018-1002) NASL family Scientific Linux Local Security Checks NASL id SL_20180313_KERNEL_ON_SL6_X.NASL description Security Fix(es) : - hw: cpu: speculative execution branch target injection (s390-only) (CVE-2017-5715, Important) - hw: cpu: speculative execution bounds-check bypass (s390 and powerpc) (CVE-2017-5753, Important) - hw: cpu: speculative execution permission faults handling (powerpc-only) (CVE-2017-5754) Bug Fixes : - If a fibre channel (FC) switch was powered down and then powered on again, the SCSI device driver stopped permanently the SCSI device last seen 2020-03-18 modified 2018-03-15 plugin id 108364 published 2018-03-15 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2020 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/108364 title Scientific Linux Security Update : kernel on SL6.x i386/x86_64 (20180313) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family Ubuntu Local Security Checks NASL id UBUNTU_USN-3516-1.NASL description It was discovered that speculative execution performed by modern CPUs could leak information through a timing side-channel attack, and that this could be exploited in web browser JavaScript engines. If a user were tricked in to opening a specially crafted website, an attacker could potentially exploit this to obtain sensitive information from other domains, bypassing same-origin restrictions. (CVE-2017-5715, CVE-2017-5753, CVE-2017-5754). Note that Tenable Network Security has extracted the preceding description block directly from the Ubuntu security advisory. Tenable has attempted to automatically clean and format it as much as possible without introducing additional issues. last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 105649 published 2018-01-08 reporter Ubuntu Security Notice (C) 2018-2019 Canonical, Inc. / NASL script (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/105649 title Ubuntu 14.04 LTS / 16.04 LTS / 17.04 / 17.10 : firefox vulnerabilities (USN-3516-1) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family SuSE Local Security Checks NASL id SUSE_SU-2019-0765-1.NASL description The SUSE Linux Enterprise 12 SP4 kernel was updated to receive various security and bugfixes. The following security bugs were fixed : CVE-2018-20669: Missing access control checks in ioctl of gpu/drm/i915 driver were fixed which might have lead to information leaks. (bnc#1122971). CVE-2019-3459, CVE-2019-3460: The Bluetooth stack suffered from two remote information leak vulnerabilities in the code that handles incoming L2cap configuration packets (bsc#1120758). CVE-2019-3819: A flaw was found in the function hid_debug_events_read() in drivers/hid/hid-debug.c file which may enter an infinite loop with certain parameters passed from a userspace. A local privileged user ( last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 123413 published 2019-03-27 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2019-2020 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/123413 title SUSE SLED12 / SLES12 Security Update : kernel (SUSE-SU-2019:0765-1) (Spectre) NASL family Windows : Microsoft Bulletins NASL id SMB_NT_MS18_JAN_4056890.NASL description The remote Windows host is missing security update 4056890 or 4057142. It is, therefore, affected by multiple vulnerabilities : - An vulnerability exists within microprocessors utilizing speculative execution and indirect branch prediction, which may allow an attacker with local user access to disclose information via a side-channel analysis. (CVE-2017-5715, CVE-2017-5753, CVE-2017-5754) - An elevation of privilege vulnerability exists when the Windows kernel fails to properly handle objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could run arbitrary code in kernel mode. An attacker could then install programs; view, change, or delete data; or create new accounts with full user rights. (CVE-2018-0744) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists in the way that the scripting engine handles objects in memory in Microsoft Edge. The vulnerability could corrupt memory in such a way that an attacker could execute arbitrary code in the context of the current user. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could gain the same user rights as the current user. (CVE-2018-0758, CVE-2018-0769, CVE-2018-0770, CVE-2018-0776, CVE-2018-0777, CVE-2018-0781) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists in the Windows kernel that could allow an attacker to retrieve information that could lead to a Kernel Address Space Layout Randomization (ASLR) bypass. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could retrieve the memory address of a kernel object. (CVE-2018-0746, CVE-2018-0747) - An elevation of privilege vulnerability exists when Microsoft Edge does not properly enforce cross-domain policies, which could allow an attacker to access information from one domain and inject it into another domain. (CVE-2018-0803) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists in Windows Adobe Type Manager Font Driver (ATMFD.dll) when it fails to properly handle objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could potentially read data that was not intended to be disclosed. Note that this vulnerability would not allow an attacker to execute code or to elevate their user rights directly, but it could be used to obtain information that could be used to try to further compromise the affected system. (CVE-2018-0754) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists in the way the scripting engine handles objects in memory in Microsoft browsers. The vulnerability could corrupt memory in such a way that an attacker could execute arbitrary code in the context of the current user. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could gain the same user rights as the current user. (CVE-2018-0762, CVE-2018-0772) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists when Microsoft Edge PDF Reader improperly handles objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could obtain information to further compromise the users system. (CVE-2018-0766) - An elevation of privilege vulnerability exists in the way that the Windows Kernel API enforces permissions. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could impersonate processes, interject cross-process communication, or interrupt system functionality. (CVE-2018-0748, CVE-2018-0751, CVE-2018-0752) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists when the scripting engine does not properly handle objects in memory in Microsoft Edge. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could obtain information to further compromise the users system. (CVE-2018-0767, CVE-2018-0780) - An elevation of privilege vulnerability exists in the Microsoft Server Message Block (SMB) Server when an attacker with valid credentials attempts to open a specially crafted file over the SMB protocol on the same machine. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could bypass certain security checks in the operating system. (CVE-2018-0749) - A denial of service vulnerability exists in the way that Windows handles objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could cause a target system to stop responding. Note that the denial of service condition would not allow an attacker to execute code or to elevate user privileges. However, the denial of service condition could prevent authorized users from using system resources. The security update addresses the vulnerability by correcting how Windows handles objects in memory. (CVE-2018-0753) last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 105548 published 2018-01-04 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/105548 title KB4056890: Windows 10 Version 1607 and Windows Server 2016 January 2018 Security Update (Meltdown)(Spectre) NASL family Windows : Microsoft Bulletins NASL id SMB_NT_MS18_MAR_4088877.NASL description The remote Windows host is missing security update 4088880 or cumulative update 4088877. It is, therefore, affected by multiple vulnerabilities : - An vulnerability exists within microprocessors utilizing speculative execution and indirect branch prediction, which may allow an attacker with local user access to disclose information via a side-channel analysis. (CVE-2017-5715, CVE-2017-5753, CVE-2017-5754) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists when Windows Remote Assistance incorrectly processes XML External Entities (XXE). An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could obtain information to further compromise the users system. (CVE-2018-0878) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists when Internet Explorer improperly handles objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could obtain information to further compromise the users system. (CVE-2018-0929) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists when Windows Shell does not properly validate file copy destinations. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could run arbitrary code in the context of the current user. If the current user is logged on with administrative user rights, an attacker could take control of the affected system. An attacker could then install programs; view, change, or delete data; or create new accounts with full user rights. Users whose accounts are configured to have fewer user rights on the system could be less impacted than users who operate with administrative user rights. (CVE-2018-0883) - An elevation of privilege vulnerability exists in Windows when the Microsoft Video Control mishandles objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could run arbitrary code in system mode. An attacker could then install programs; view, change, or delete data; or create new accounts with full user rights. (CVE-2018-0881) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists in the way that the scripting engine handles objects in memory in Internet Explorer. The vulnerability could corrupt memory in such a way that an attacker could execute arbitrary code in the context of the current user. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could gain the same user rights as the current user. (CVE-2018-0889, CVE-2018-0935) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists when the Windows kernel improperly initializes objects in memory. (CVE-2018-0811, CVE-2018-0813, CVE-2018-0814) - A denial of service vulnerability exists when Microsoft Hyper-V Network Switch on a host server fails to properly validate input from a privileged user on a guest operating system. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could cause the host server to crash. (CVE-2018-0885) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists in the Credential Security Support Provider protocol (CredSSP). An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could relay user credentials and use them to execute code on the target system. CredSSP is an authentication provider which processes authentication requests for other applications; any application which depends on CredSSP for authentication may be vulnerable to this type of attack. As an example of how an attacker would exploit this vulnerability against Remote Desktop Protocol, the attacker would need to run a specially crafted application and perform a man-in-the-middle attack against a Remote Desktop Protocol session. An attacker could then install programs; view, change, or delete data; or create new accounts with full user rights. The security update addresses the vulnerability by correcting how Credential Security Support Provider protocol (CredSSP) validates requests during the authentication process. To be fully protected against this vulnerability users must enable Group Policy settings on their systems and update their Remote Desktop clients. The Group Policy settings are disabled by default to prevent connectivity problems and users must follow the instructions documented HERE to be fully protected. (CVE-2018-0886) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists in the Windows kernel that could allow an attacker to retrieve information that could lead to a Kernel Address Space Layout Randomization (ASLR) bypass. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could retrieve the memory address of a kernel object. (CVE-2018-0894, CVE-2018-0895, CVE-2018-0896, CVE-2018-0897, CVE-2018-0898, CVE-2018-0899, CVE-2018-0900, CVE-2018-0901, CVE-2018-0904) - An elevation of privilege vulnerability exists in the Windows Installer when the Windows Installer fails to properly sanitize input leading to an insecure library loading behavior. A locally authenticated attacker could run arbitrary code with elevated system privileges. An attacker could then install programs; view, change, or delete data; or create new accounts with full user rights. The security update addresses the vulnerability by correcting the input sanitization error to preclude unintended elevation. (CVE-2018-0868) - An elevation of privilege vulnerability exists in the way that the Windows Graphics Device Interface (GDI) handles objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could run arbitrary code in kernel mode. An attacker could then install programs; view, change, or delete data; or create new accounts with full user rights. (CVE-2018-0816, CVE-2018-0817) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists when affected Microsoft browsers improperly handle objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could obtain information to further compromise the users system. (CVE-2018-0927) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists when Windows Hyper-V on a host operating system fails to properly validate input from an authenticated user on a guest operating system. (CVE-2018-0888) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists when the scripting engine does not properly handle objects in memory in Microsoft browsers. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could obtain information to further compromise the users system. (CVE-2018-0891) last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 108292 published 2018-03-13 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/108292 title KB4088880: Windows Server 2012 March 2018 Security Update (Meltdown)(Spectre) NASL family SuSE Local Security Checks NASL id OPENSUSE-2018-599.NASL description This update for xen to version 4.10.1 fixes several issues (bsc#1027519). These security issues were fixed : - CVE-2018-3639: Prevent attackers with local user access from extracting information via a side-channel analysis, aka Speculative Store Bypass (SSB), Variant 4 (bsc#1092631). - CVE-2017-5753,CVE-2017-5715,CVE-2017-5754: Improved Spectre v2 mitigations (bsc#1074562). This non-security issue was fixed : - Always call qemus xen-save-devices-state in suspend/resume to fix migration with qcow2 images (bsc#1079730) last seen 2020-06-05 modified 2018-06-11 plugin id 110438 published 2018-06-11 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2020 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/110438 title openSUSE Security Update : xen (openSUSE-2018-599) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family PhotonOS Local Security Checks NASL id PHOTONOS_PHSA-2018-2_0-0011_LINUX.NASL description An update of the linux package has been released. last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 121909 published 2019-02-07 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/121909 title Photon OS 2.0: Linux PHSA-2018-2.0-0011 NASL family Huawei Local Security Checks NASL id EULEROS_SA-2019-1638.NASL description According to the versions of the kernel packages installed, the EulerOS Virtualization installation on the remote host is affected by the following vulnerabilities : - The recent speculative execution CVEs address three potential attacks across a wide variety of architectures and hardware platforms. - Note: This issue is present in hardware and cannot be fully fixed via software update. The nature of these vulnerabilities and their fixes introduces the possibility of reduced performance on patched systems. The performance impact depends on the hardware and the applications in place. - The first two variants abuse speculative execution to perform bounds-check bypass (CVE-2017-5753), or by utilizing branch target injection (CVE-2017-5715) to cause kernel code at an address under attacker control to execute speculatively. Collectively these are known as last seen 2020-03-19 modified 2019-06-07 plugin id 125753 published 2019-06-07 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2019-2020 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/125753 title EulerOS Virtualization 2.5.1 : kernel (EulerOS-SA-2019-1638) NASL family Huawei Local Security Checks NASL id EULEROS_SA-2019-1637.NASL description According to the versions of the kernel packages installed, the EulerOS Virtualization installation on the remote host is affected by the following vulnerabilities : - The recent speculative execution CVEs address three potential attacks across a wide variety of architectures and hardware platforms. - Note: This issue is present in hardware and cannot be fully fixed via software update. The nature of these vulnerabilities and their fixes introduces the possibility of reduced performance on patched systems. The performance impact depends on the hardware and the applications in place. - The first two variants abuse speculative execution to perform bounds-check bypass (CVE-2017-5753), or by utilizing branch target injection (CVE-2017-5715) to cause kernel code at an address under attacker control to execute speculatively. Collectively these are known as last seen 2020-03-19 modified 2019-06-07 plugin id 125752 published 2019-06-07 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2019-2020 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/125752 title EulerOS Virtualization 2.5.2 : kernel (EulerOS-SA-2019-1637) NASL family AIX Local Security Checks NASL id AIX_IJ03030.NASL description Systems with microprocessors utilizing speculative execution and indirect branch prediction may allow unauthorized disclosure of information to an attacker with local user access via a side-channel analysis. last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 106311 published 2018-01-25 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/106311 title AIX 6.1 TL 9 : spectre_meltdown (IJ03030) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family Solaris Local Security Checks NASL id SOLARIS_APR2018_SRU11_3_31_6_0.NASL description This Solaris system is missing necessary patches to address a critical security update : - Vulnerability in the Oracle Communications LSMS component of Oracle Communications Applications (subcomponent: Platform (Kernel)). Supported versions that are affected are 13.1, 13.2 and 13.3. Difficult to exploit vulnerability allows low privileged attacker with logon to the infrastructure where Oracle Communications LSMS executes to compromise Oracle Communications LSMS. While the vulnerability is in Oracle Communications LSMS, attacks may significantly impact additional products. Successful attacks of this vulnerability can result in unauthorized access to critical data or complete access to all Oracle Communications LSMS accessible data. (CVE-2017-5753) last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 109176 published 2018-04-20 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2020 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/109176 title Oracle Solaris Critical Patch Update : apr2018_SRU11_3_31_6_0 (Spectre) NASL family Windows : Microsoft Bulletins NASL id SMB_NT_MS18_FEB_4074592.NASL description The remote Windows host is missing security update 4074592. It is, therefore, affected by multiple vulnerabilities : - An vulnerability exists within microprocessors utilizing speculative execution and indirect branch prediction, which may allow an attacker with local user access to disclose information via a side-channel analysis. (CVE-2017-5715, CVE-2017-5753, CVE-2017-5754) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists in the way that the scripting engine handles objects in memory in Internet Explorer. The vulnerability could corrupt memory in such a way that an attacker could execute arbitrary code in the context of the current user. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could gain the same user rights as the current user. (CVE-2018-0866) - A security feature bypass vulnerability exists in Windows Scripting Host which could allow an attacker to bypass Device Guard. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could circumvent a User Mode Code Integrity (UMCI) policy on the machine. (CVE-2018-0827) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists when the Windows kernel improperly handles objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could obtain information to further compromise the users system. (CVE-2018-0757, CVE-2018-0829, CVE-2018-0830) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists when Microsoft Edge improperly handles objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could obtain information to further compromise the users system. (CVE-2018-0763, CVE-2018-0839) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists when VBScript improperly discloses the contents of its memory, which could provide an attacker with information to further compromise the users computer or data. (CVE-2018-0847) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists in StructuredQuery when the software fails to properly handle objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could run arbitrary code in the context of the current user. If the current user is logged on with administrative user rights, an attacker could take control of the affected system. An attacker could then install programs; view, change, or delete data; or create new accounts with full user rights. (CVE-2018-0825) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists in the way that the scripting engine handles objects in memory in Microsoft Edge. The vulnerability could corrupt memory in such a way that an attacker could execute arbitrary code in the context of the current user. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could gain the same user rights as the current user. (CVE-2018-0834, CVE-2018-0835, CVE-2018-0836, CVE-2018-0837, CVE-2018-0838, CVE-2018-0856, CVE-2018-0857, CVE-2018-0859, CVE-2018-0860, CVE-2018-0861) - An elevation of privilege vulnerability exists when NTFS improperly handles objects. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could run processes in an elevated context. (CVE-2018-0822) - An elevation of privilege vulnerability exists when AppContainer improperly implements constrained impersonation. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could run processes in an elevated context. (CVE-2018-0821) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists when Windows improperly handles objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited these vulnerabilities could take control of an affected system. (CVE-2018-0842) - An elevation of privilege vulnerability exists when the Windows Common Log File System (CLFS) driver improperly handles objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could run processes in an elevated context. (CVE-2018-0844, CVE-2018-0846) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists in the Windows kernel that could allow an attacker to retrieve information that could lead to a Kernel Address Space Layout Randomization (ASLR) bypass. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could retrieve the memory address of a kernel object. (CVE-2018-0832) - An elevation of privilege vulnerability exists when the Windows kernel fails to properly handle objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could run arbitrary code in kernel mode. An attacker could then install programs; view, change, or delete data; or create new accounts with full user rights. (CVE-2018-0809) - An elevation of privilege vulnerability exists in the way that the Windows Kernel handles objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could execute code with elevated permissions. (CVE-2018-0742, CVE-2018-0756, CVE-2018-0820, CVE-2018-0831) - A security feature bypass vulnerability exists when Microsoft Edge improperly handles requests of different origins. The vulnerability allows Microsoft Edge to bypass Same-Origin Policy (SOP) restrictions, and to allow requests that should otherwise be ignored. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could force the browser to send data that would otherwise be restricted. (CVE-2018-0771) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists in the way the scripting engine handles objects in memory in Microsoft browsers. The vulnerability could corrupt memory in such a way that an attacker could execute arbitrary code in the context of the current user. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could gain the same user rights as the current user. (CVE-2018-0840) - An elevation of privilege vulnerability exists when Storage Services improperly handles objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could run processes in an elevated context. (CVE-2018-0826) last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 106798 published 2018-02-13 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/106798 title KB4074592: Windows 10 Version 1703 February 2018 Security Update (Meltdown)(Spectre) NASL family Windows : Microsoft Bulletins NASL id SMB_NT_MS18_FEB_4074591.NASL description The remote Windows host is missing security update 4074591. It is, therefore, affected by multiple vulnerabilities : - An vulnerability exists within microprocessors utilizing speculative execution and indirect branch prediction, which may allow an attacker with local user access to disclose information via a side-channel analysis. (CVE-2017-5715, CVE-2017-5753, CVE-2017-5754) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists in the way that the scripting engine handles objects in memory in Internet Explorer. The vulnerability could corrupt memory in such a way that an attacker could execute arbitrary code in the context of the current user. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could gain the same user rights as the current user. (CVE-2018-0866) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists when the Windows kernel improperly handles objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could obtain information to further compromise the users system. (CVE-2018-0757, CVE-2018-0829, CVE-2018-0830) - An elevation of privilege vulnerability exists in the way that the Windows Kernel handles objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could execute code with elevated permissions. (CVE-2018-0742, CVE-2018-0756, CVE-2018-0820) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists when VBScript improperly discloses the contents of its memory, which could provide an attacker with information to further compromise the users computer or data. (CVE-2018-0847) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists in StructuredQuery when the software fails to properly handle objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could run arbitrary code in the context of the current user. If the current user is logged on with administrative user rights, an attacker could take control of the affected system. An attacker could then install programs; view, change, or delete data; or create new accounts with full user rights. (CVE-2018-0825) - An elevation of privilege vulnerability exists when Storage Services improperly handles objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could run processes in an elevated context. (CVE-2018-0826) - An elevation of privilege vulnerability exists when NTFS improperly handles objects. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could run processes in an elevated context. (CVE-2018-0822) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists in the way that the scripting engine handles objects in memory in Microsoft Edge. The vulnerability could corrupt memory in such a way that an attacker could execute arbitrary code in the context of the current user. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could gain the same user rights as the current user. (CVE-2018-0834, CVE-2018-0835, CVE-2018-0837, CVE-2018-0838, CVE-2018-0857, CVE-2018-0859, CVE-2018-0860) - An elevation of privilege vulnerability exists when AppContainer improperly implements constrained impersonation. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could run processes in an elevated context. (CVE-2018-0821) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists when Windows improperly handles objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited these vulnerabilities could take control of an affected system. (CVE-2018-0842) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists in the way the scripting engine handles objects in memory in Microsoft browsers. The vulnerability could corrupt memory in such a way that an attacker could execute arbitrary code in the context of the current user. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could gain the same user rights as the current user. (CVE-2018-0840) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists in the Windows kernel that could allow an attacker to retrieve information that could lead to a Kernel Address Space Layout Randomization (ASLR) bypass. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could retrieve the memory address of a kernel object. (CVE-2018-0832) - An elevation of privilege vulnerability exists when the Windows Common Log File System (CLFS) driver improperly handles objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could run processes in an elevated context. (CVE-2018-0844, CVE-2018-0846) last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 106797 published 2018-02-13 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/106797 title KB4074591: Windows 10 Version 1511 February 2018 Security Update (Meltdown)(Spectre) NASL family Windows : Microsoft Bulletins NASL id SMB_NT_MS18_JAN_4056888.NASL description The remote Windows host is missing security update 4056888 or 4075200. It is, therefore, affected by multiple vulnerabilities : - An vulnerability exists within microprocessors utilizing speculative execution and indirect branch prediction, which may allow an attacker with local user access to disclose information via a side-channel analysis. (CVE-2017-5715, CVE-2017-5753, CVE-2017-5754) - An elevation of privilege vulnerability exists when the Windows kernel fails to properly handle objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could run arbitrary code in kernel mode. An attacker could then install programs; view, change, or delete data; or create new accounts with full user rights. (CVE-2018-0744) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists in the way that the scripting engine handles objects in memory in Microsoft Edge. The vulnerability could corrupt memory in such a way that an attacker could execute arbitrary code in the context of the current user. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could gain the same user rights as the current user. (CVE-2018-0758, CVE-2018-0769, CVE-2018-0770, CVE-2018-0776, CVE-2018-0777, CVE-2018-0781) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists in the Windows kernel that could allow an attacker to retrieve information that could lead to a Kernel Address Space Layout Randomization (ASLR) bypass. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could retrieve the memory address of a kernel object. (CVE-2018-0746, CVE-2018-0747) - An elevation of privilege vulnerability exists when Microsoft Edge does not properly enforce cross-domain policies, which could allow an attacker to access information from one domain and inject it into another domain. (CVE-2018-0803) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists in Windows Adobe Type Manager Font Driver (ATMFD.dll) when it fails to properly handle objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could potentially read data that was not intended to be disclosed. Note that this vulnerability would not allow an attacker to execute code or to elevate their user rights directly, but it could be used to obtain information that could be used to try to further compromise the affected system. (CVE-2018-0754) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists in the way the scripting engine handles objects in memory in Microsoft browsers. The vulnerability could corrupt memory in such a way that an attacker could execute arbitrary code in the context of the current user. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could gain the same user rights as the current user. (CVE-2018-0762, CVE-2018-0772) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists when Microsoft Edge PDF Reader improperly handles objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could obtain information to further compromise the users system. (CVE-2018-0766) - An elevation of privilege vulnerability exists in the way that the Windows Kernel API enforces permissions. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could impersonate processes, interject cross-process communication, or interrupt system functionality. (CVE-2018-0748, CVE-2018-0751, CVE-2018-0752) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists when the scripting engine does not properly handle objects in memory in Microsoft Edge. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could obtain information to further compromise the users system. (CVE-2018-0767, CVE-2018-0780) - An elevation of privilege vulnerability exists in the Microsoft Server Message Block (SMB) Server when an attacker with valid credentials attempts to open a specially crafted file over the SMB protocol on the same machine. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could bypass certain security checks in the operating system. (CVE-2018-0749) - A denial of service vulnerability exists in the way that Windows handles objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could cause a target system to stop responding. Note that the denial of service condition would not allow an attacker to execute code or to elevate user privileges. However, the denial of service condition could prevent authorized users from using system resources. The security update addresses the vulnerability by correcting how Windows handles objects in memory. (CVE-2018-0753) last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 105547 published 2018-01-04 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/105547 title KB4056888: Windows 10 Version 1511 January 2018 Security Update (Meltdown)(Spectre) NASL family Amazon Linux Local Security Checks NASL id ALA_ALAS-2018-956.NASL description Kernel address information leak in drivers/acpi/sbshc.c:acpi_smbus_hc_add() function potentially allowing KASLR bypass The acpi_smbus_hc_add function in drivers/acpi/sbshc.c in the Linux kernel, through 4.14.15, allows local users to obtain sensitive address information by reading dmesg data from an SBS HC printk call.(CVE-2018-5750) Improper sorting of GIDs in nfsd can lead to incorrect permissions being applied Linux kernel contains a Incorrect Access Control vulnerability in NFS server (nfsd) that can result in remote users reading or writing files they should not be able to via NFS. This attack appear to be exploitable via NFS server must export a filesystem with the last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 106933 published 2018-02-22 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/106933 title Amazon Linux AMI : kernel (ALAS-2018-956) (Dirty COW) (Spectre) NASL family Misc. NASL id CITRIX_XENSERVER_CTX231390.NASL description The version of Citrix XenServer running on the remote host is missing a security hotfix. It is, therefore, affected by multiple vulnerabilities. last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 105617 published 2018-01-05 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/105617 title Citrix XenServer Multiple Vulnerabilities (CTX231390) (Meltdown)(Spectre) NASL family Ubuntu Local Security Checks NASL id UBUNTU_USN-3597-1.NASL description USNS 3541-1 and 3523-1 provided mitigations for Spectre and Meltdown (CVE-2017-5715, CVE-2017-5753, CVE-2017-5754) for the i386, amd64, and ppc64el architectures in Ubuntu 17.10. This update provides the corresponding mitigations for the arm64 architecture. Original advisory details : Jann Horn discovered that microprocessors utilizing speculative execution and indirect branch prediction may allow unauthorized memory reads via sidechannel attacks. This flaw is known as Meltdown. A local attacker could use this to expose sensitive information, including kernel memory. (CVE-2017-5754) Jann Horn discovered that microprocessors utilizing speculative execution and branch prediction may allow unauthorized memory reads via sidechannel attacks. This flaw is known as Spectre. A local attacker could use this to expose sensitive information, including kernel memory. (CVE-2017-5715, CVE-2017-5753). Note that Tenable Network Security has extracted the preceding description block directly from the Ubuntu security advisory. Tenable has attempted to automatically clean and format it as much as possible without introducing additional issues. last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 108371 published 2018-03-15 reporter Ubuntu Security Notice (C) 2018-2019 Canonical, Inc. / NASL script (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/108371 title Ubuntu 17.10 : linux, linux-raspi2 vulnerabilities (USN-3597-1) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family Red Hat Local Security Checks NASL id REDHAT-RHSA-2018-0017.NASL description An update for kernel is now available for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6.6 Advanced Update Support and Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6.6 Telco Extended Update Support. Red Hat Product Security has rated this update as having a security impact of Important. A Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) base score, which gives a detailed severity rating, is available for each vulnerability from the CVE link(s) in the References section. The kernel packages contain the Linux kernel, the core of any Linux operating system. Security Fix(es) : An industry-wide issue was found in the way many modern microprocessor designs have implemented speculative execution of instructions (a commonly used performance optimization). There are three primary variants of the issue which differ in the way the speculative execution can be exploited. Note: This issue is present in hardware and cannot be fully fixed via software update. The updated kernel packages provide software mitigation for this hardware issue at a cost of potential performance penalty. Please refer to References section for further information about this issue and the performance impact. In this update mitigations for x86-64 architecture are provided. Variant CVE-2017-5753 triggers the speculative execution by performing a bounds-check bypass. It relies on the presence of a precisely-defined instruction sequence in the privileged code as well as the fact that memory accesses may cause allocation into the microprocessor last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 105533 published 2018-01-04 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/105533 title RHEL 6 : kernel (RHSA-2018:0017) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family Red Hat Local Security Checks NASL id REDHAT-RHSA-2018-0016.NASL description An update for kernel-rt is now available for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7. Red Hat Product Security has rated this update as having a security impact of Important. A Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) base score, which gives a detailed severity rating, is available for each vulnerability from the CVE link(s) in the References section. The kernel-rt packages provide the Real Time Linux Kernel, which enables fine-tuning for systems with extremely high determinism requirements. Security Fix(es) : An industry-wide issue was found in the way many modern microprocessor designs have implemented speculative execution of instructions (a commonly used performance optimization). There are three primary variants of the issue which differ in the way the speculative execution can be exploited. Note: This issue is present in hardware and cannot be fully fixed via software update. The updated kernel packages provide software mitigation for this hardware issue at a cost of potential performance penalty. Please refer to References section for further information about this issue and the performance impact. In this update mitigations for x86-64 architecture are provided. Variant CVE-2017-5753 triggers the speculative execution by performing a bounds-check bypass. It relies on the presence of a precisely-defined instruction sequence in the privileged code as well as the fact that memory accesses may cause allocation into the microprocessor last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 105532 published 2018-01-04 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/105532 title RHEL 7 : kernel-rt (RHSA-2018:0016) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family Debian Local Security Checks NASL id DEBIAN_DLA-1369.NASL description Several vulnerabilities have been discovered in the Linux kernel that may lead to a privilege escalation, denial of service or information leaks. CVE-2017-0861 Robb Glasser reported a potential use-after-free in the ALSA (sound) PCM core. We believe this was not possible in practice. CVE-2017-5715 Multiple researchers have discovered a vulnerability in various processors supporting speculative execution, enabling an attacker controlling an unprivileged process to read memory from arbitrary addresses, including from the kernel and all other processes running on the system. This specific attack has been named Spectre variant 2 (branch target injection) and is mitigated for the x86 architecture (amd64 and i386) by using the last seen 2020-03-17 modified 2018-05-03 plugin id 109531 published 2018-05-03 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2020 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/109531 title Debian DLA-1369-1 : linux security update (Spectre) NASL family NewStart CGSL Local Security Checks NASL id NEWSTART_CGSL_NS-SA-2019-0007_KERNEL.NASL description The remote NewStart CGSL host, running version MAIN 5.04, has kernel packages installed that are affected by multiple vulnerabilities: - It was found that the timer functionality in the Linux kernel ALSA subsystem is prone to a race condition between read and ioctl system call handlers, resulting in an uninitialized memory disclosure to user space. A local user could use this flaw to read information belonging to other users. (CVE-2017-1000380) - An industry-wide issue was found in the way many modern microprocessor designs have implemented speculative execution of instructions (a commonly used performance optimization). There are three primary variants of the issue which differ in the way the speculative execution can be exploited. Variant CVE-2017-5715 triggers the speculative execution by utilizing branch target injection. It relies on the presence of a precisely- defined instruction sequence in the privileged code as well as the fact that memory accesses may cause allocation into the microprocessor last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 127152 published 2019-08-12 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/127152 title NewStart CGSL MAIN 5.04 : kernel Multiple Vulnerabilities (NS-SA-2019-0007) NASL family FreeBSD Local Security Checks NASL id FREEBSD_PKG_1CE95BC7327811E8B52700012E582166.NASL description The WebKit team reports many vulnerabilities. Please reference the CVE/URL list for details. last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 108703 published 2018-03-29 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/108703 title FreeBSD : webkit2-gtk3 -- multiple vulnerabilities (1ce95bc7-3278-11e8-b527-00012e582166) (Spectre) NASL family Windows NASL id VMWARE_PLAYER_WIN_VMSA_2017_0021.NASL description The version of VMware Player installed on the remote Windows host is 12.x prior to 12.5.8. It is, therefore, affected by multiple vulnerabilities that can allow code execution in a virtual machine via the authenticated VNC session as well as cause information disclosure from one virtual machine to another virtual machine on the same host. last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 105555 published 2018-01-04 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/105555 title VMware Player 12.x < 12.5.8 Multiple Vulnerabilities (VMSA-2017-0021) (VMSA-2018-0002) (Spectre) NASL family Windows : Microsoft Bulletins NASL id SMB_NT_MS18_FEB_4074590.NASL description The remote Windows host is missing security update 4074590. It is, therefore, affected by multiple vulnerabilities : - An vulnerability exists within microprocessors utilizing speculative execution and indirect branch prediction, which may allow an attacker with local user access to disclose information via a side-channel analysis. (CVE-2017-5715, CVE-2017-5753, CVE-2017-5754) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists in the way that the scripting engine handles objects in memory in Internet Explorer. The vulnerability could corrupt memory in such a way that an attacker could execute arbitrary code in the context of the current user. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could gain the same user rights as the current user. (CVE-2018-0866) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists when the Windows kernel improperly handles objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could obtain information to further compromise the users system. (CVE-2018-0757, CVE-2018-0829, CVE-2018-0830) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists when Windows improperly handles objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited these vulnerabilities could take control of an affected system. (CVE-2018-0842) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists in StructuredQuery when the software fails to properly handle objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could run arbitrary code in the context of the current user. If the current user is logged on with administrative user rights, an attacker could take control of the affected system. An attacker could then install programs; view, change, or delete data; or create new accounts with full user rights. (CVE-2018-0825) - An elevation of privilege vulnerability exists when Storage Services improperly handles objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could run processes in an elevated context. (CVE-2018-0826) - An elevation of privilege vulnerability exists when NTFS improperly handles objects. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could run processes in an elevated context. (CVE-2018-0822) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists in the way that the scripting engine handles objects in memory in Microsoft Edge. The vulnerability could corrupt memory in such a way that an attacker could execute arbitrary code in the context of the current user. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could gain the same user rights as the current user. (CVE-2018-0834, CVE-2018-0835, CVE-2018-0837, CVE-2018-0838, CVE-2018-0857, CVE-2018-0859, CVE-2018-0860, CVE-2018-0861) - An elevation of privilege vulnerability exists when AppContainer improperly implements constrained impersonation. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could run processes in an elevated context. (CVE-2018-0821) - An elevation of privilege vulnerability exists in Microsoft Windows when the MultiPoint management account password is improperly secured. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could run arbitrary code with elevated privileges. (CVE-2018-0828) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists in the way the scripting engine handles objects in memory in Microsoft browsers. The vulnerability could corrupt memory in such a way that an attacker could execute arbitrary code in the context of the current user. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could gain the same user rights as the current user. (CVE-2018-0840) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists in the Windows kernel that could allow an attacker to retrieve information that could lead to a Kernel Address Space Layout Randomization (ASLR) bypass. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could retrieve the memory address of a kernel object. (CVE-2018-0832) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists when VBScript improperly discloses the contents of its memory, which could provide an attacker with information to further compromise the users computer or data. (CVE-2018-0847) - An elevation of privilege vulnerability exists when the Windows Common Log File System (CLFS) driver improperly handles objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could run processes in an elevated context. (CVE-2018-0844, CVE-2018-0846) - A security feature bypass vulnerability exists when Microsoft Edge improperly handles requests of different origins. The vulnerability allows Microsoft Edge to bypass Same-Origin Policy (SOP) restrictions, and to allow requests that should otherwise be ignored. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could force the browser to send data that would otherwise be restricted. (CVE-2018-0771) - An elevation of privilege vulnerability exists in the way that the Windows Kernel handles objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could execute code with elevated permissions. (CVE-2018-0742, CVE-2018-0756, CVE-2018-0820, CVE-2018-0831) last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 106796 published 2018-02-13 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/106796 title KB4074590: Windows 10 Version 1607 and Windows Server 2016 February 2018 Security Update (Meltdown)(Spectre) NASL family OracleVM Local Security Checks NASL id ORACLEVM_OVMSA-2018-0007.NASL description The remote OracleVM system is missing necessary patches to address critical security updates : - x86/ibrs: Remove last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 105761 published 2018-01-12 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/105761 title OracleVM 3.4 : Unbreakable / etc (OVMSA-2018-0007) (Spectre) NASL family OracleVM Local Security Checks NASL id ORACLEVM_OVMSA-2018-0029.NASL description The remote OracleVM system is missing necessary patches to address critical security updates : please see Oracle VM Security Advisory OVMSA-2018-0029 for details. last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 108864 published 2018-04-06 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/108864 title OracleVM 3.2 : xen (OVMSA-2018-0029) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family Debian Local Security Checks NASL id DEBIAN_DLA-1423.NASL description Linux 4.9 has been packaged for Debian 8 as linux-4.9. This provides a supported upgrade path for systems that currently use kernel packages from the last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 111165 published 2018-07-20 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/111165 title Debian DLA-1423-1 : linux-4.9 new package (Spectre) NASL family Debian Local Security Checks NASL id DEBIAN_DSA-4120.NASL description Several vulnerabilities have been discovered in the Linux kernel that may lead to a privilege escalation, denial of service or information leaks. - CVE-2017-5715 Multiple researchers have discovered a vulnerability in various processors supporting speculative execution, enabling an attacker controlling an unprivileged process to read memory from arbitrary addresses, including from the kernel and all other processes running on the system. This specific attack has been named Spectre variant 2 (branch target injection) and is mitigated in the Linux kernel for the Intel x86-64 architecture by using the last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 106955 published 2018-02-23 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/106955 title Debian DSA-4120-1 : linux - security update (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family CentOS Local Security Checks NASL id CENTOS_RHSA-2018-0512.NASL description An update for kernel is now available for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6. Red Hat Product Security has rated this update as having a security impact of Important. A Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) base score, which gives a detailed severity rating, is available for each vulnerability from the CVE link(s) in the References section. The kernel packages contain the Linux kernel, the core of any Linux operating system. Security Fix(es) : * hw: cpu: speculative execution branch target injection (s390-only) (CVE-2017-5715, Important) * hw: cpu: speculative execution bounds-check bypass (s390 and powerpc) (CVE-2017-5753, Important) * hw: cpu: speculative execution permission faults handling (powerpc-only) (CVE-2017-5754) For more details about the security issue(s), including the impact, a CVSS score, acknowledgments, and other related information, refer to the CVE page(s) listed in the References section. Bug Fixes : * If a fibre channel (FC) switch was powered down and then powered on again, the SCSI device driver stopped permanently the SCSI device last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 108341 published 2018-03-15 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/108341 title CentOS 6 : kernel (CESA-2018:0512) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family Ubuntu Local Security Checks NASL id UBUNTU_USN-3521-1.NASL description Jann Horn discovered that microprocessors utilizing speculative execution and branch prediction may allow unauthorized memory reads via sidechannel attacks. This flaw is known as Spectre. A local attacker could use this to expose sensitive information, including kernel memory. This update provides mitigations to address the issue, along with compatibility fixes for the corresponding Linux kernel updates. Note that Tenable Network Security has extracted the preceding description block directly from the Ubuntu security advisory. Tenable has attempted to automatically clean and format it as much as possible without introducing additional issues. last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 105723 published 2018-01-10 reporter Ubuntu Security Notice (C) 2018-2019 Canonical, Inc. / NASL script (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/105723 title Ubuntu 14.04 LTS / 16.04 LTS / 17.04 / 17.10 : nvidia-graphics-drivers-384 vulnerability (USN-3521-1) (Spectre) NASL family SuSE Local Security Checks NASL id SUSE_SU-2018-1603-1.NASL description This update for xen fixes several issues. These security issues were fixed : - CVE-2018-3639: Prevent attackers with local user access from extracting information via a side-channel analysis, aka Speculative Store Bypass (SSB), Variant 4 (bsc#1092631). - CVE-2017-5753,CVE-2017-5715,CVE-2017-5754: Improved Spectre v2 mitigations (bsc#1074562). bsc#1027519 Note that Tenable Network Security has extracted the preceding description block directly from the SUSE security advisory. Tenable has attempted to automatically clean and format it as much as possible without introducing additional issues. last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 110444 published 2018-06-11 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/110444 title SUSE SLES11 Security Update : xen (SUSE-SU-2018:1603-1) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family SuSE Local Security Checks NASL id SUSE_SU-2018-1699-2.NASL description This update for xen fixes several issues. This feature was added : Added support for qemu monitor command These security issues were fixed: CVE-2018-3639: Prevent attackers with local user access from extracting information via a side-channel analysis, aka Speculative Store Bypass (SSB), Variant 4 (bsc#1092631). CVE-2017-5753,CVE-2017-5715,CVE-2017-5754: Improved Spectre v2 mitigations (bsc#1074562). The update package also includes non-security fixes. See advisory for details. Note that Tenable Network Security has extracted the preceding description block directly from the SUSE security advisory. Tenable has attempted to automatically clean and format it as much as possible without introducing additional issues. last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 118266 published 2018-10-22 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/118266 title SUSE SLES12 Security Update : xen (SUSE-SU-2018:1699-2) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family Oracle Linux Local Security Checks NASL id ORACLELINUX_ELSA-2018-0008.NASL description From Red Hat Security Advisory 2018:0008 : An update for kernel is now available for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6. Red Hat Product Security has rated this update as having a security impact of Important. A Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) base score, which gives a detailed severity rating, is available for each vulnerability from the CVE link(s) in the References section. [Updated 23rd January 2019] The text has been updated to correct the list of architectures addressed by the CVE-2017-5753 mitigation. No changes have been made to the packages. The kernel packages contain the Linux kernel, the core of any Linux operating system. Security Fix(es) : An industry-wide issue was found in the way many modern microprocessor designs have implemented speculative execution of instructions (a commonly used performance optimization). There are three primary variants of the issue which differ in the way the speculative execution can be exploited. Note: This issue is present in hardware and cannot be fully fixed via software update. The updated kernel packages provide software mitigation for this hardware issue at a cost of potential performance penalty. Please refer to References section for further information about this issue and the performance impact. In this update, mitigations for x86 (CVE-2017-5753) and x86-64 (CVE-2017-5753, CVE-2017-5715, and CVE-2017-5754) architectures are provided. Variant CVE-2017-5753 triggers the speculative execution by performing a bounds-check bypass. It relies on the presence of a precisely-defined instruction sequence in the privileged code as well as the fact that memory accesses may cause allocation into the microprocessor last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 105599 published 2018-01-05 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/105599 title Oracle Linux 6 : kernel (ELSA-2018-0008) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family SuSE Local Security Checks NASL id SUSE_SU-2018-0069-1.NASL description The SUSE Linux Enterprise 11 SP4 kernel was updated to receive various security and bugfixes. This update is only provided as a fix update for IBM Z platform. - CVE-2017-5753 / last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 105765 published 2018-01-12 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/105765 title SUSE SLES12 Security Update : kernel (SUSE-SU-2018:0069-1) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family SuSE Local Security Checks NASL id SUSE_SU-2018-2528-1.NASL description This update for xen fixes the following issues: These security issue were fixed : - CVE-2018-3646: Systems with microprocessors utilizing speculative execution and address translations may have allowed unauthorized disclosure of information residing in the L1 data cache to an attacker with local user access with guest OS privilege via a terminal page fault and a side-channel analysis (bsc#1091107, bsc#1027519). - CVE-2018-12617: An integer overflow that could cause a segmentation fault in qmp_guest_file_read() with g_malloc() in qemu-guest-agent was fixed (bsc#1098744) - CVE-2018-3665: System software utilizing Lazy FP state restore technique on systems using Intel Core-based microprocessors may potentially allow a local process to infer data from another process through a speculative execution side channel. (bsc#1095242) - CVE-2018-3639: Systems with microprocessors utilizing speculative execution and speculative execution of memory reads before the addresses of all prior memory writes are known may allow unauthorized disclosure of information to an attacker with local user access via a side-channel analysis, aka Speculative Store Bypass (SSB), Variant 4. (bsc#1092631) - CVE-2017-5715: Systems with microprocessors utilizing speculative execution and indirect branch prediction may allow unauthorized disclosure of information to an attacker with local user access via a side-channel analysis. (bsc#1074562) - CVE-2017-5753: Systems with microprocessors utilizing speculative execution and branch prediction may allow unauthorized disclosure of information to an attacker with local user access via a side-channel analysis. (bsc#1074562) - CVE-2017-5754: Systems with microprocessors utilizing speculative execution and indirect branch prediction may allow unauthorized disclosure of information to an attacker with local user access via a side-channel analysis of the data cache. (bsc#1074562) - CVE-2018-12891: Certain PV MMU operations may take a long time to process. For that reason Xen explicitly checks for the need to preempt the current vCPU at certain points. A few rarely taken code paths did bypass such checks. By suitably enforcing the conditions through its own page table contents, a malicious guest may cause such bypasses to be used for an unbounded number of iterations. A malicious or buggy PV guest may cause a Denial of Service (DoS) affecting the entire host. Specifically, it may prevent use of a physical CPU for an indeterminate period of time. (bsc#1097521) - CVE-2018-12893: One of the fixes in XSA-260 added some safety checks to help prevent Xen livelocking with debug exceptions. Unfortunately, due to an oversight, at least one of these safety checks can be triggered by a guest. A malicious PV guest can crash Xen, leading to a Denial of Service. Only x86 PV guests can exploit the vulnerability. x86 HVM and PVH guests cannot exploit the vulnerability. An attacker needs to be able to control hardware debugging facilities to exploit the vulnerability, but such permissions are typically available to unprivileged users. (bsc#1097522) - CVE-2018-11806: m_cat in slirp/mbuf.c in Qemu has a heap-based buffer overflow via incoming fragmented datagrams. (bsc#1096224) - CVE-2018-10982: An issue was discovered in Xen allowed x86 HVM guest OS users to cause a denial of service (unexpectedly high interrupt number, array overrun, and hypervisor crash) or possibly gain hypervisor privileges by setting up an HPET timer to deliver interrupts in IO-APIC mode, aka vHPET interrupt injection. (bsc#1090822) - CVE-2018-10981: An issue was discovered in Xen that allowed x86 HVM guest OS users to cause a denial of service (host OS infinite loop) in situations where a QEMU device model attempts to make invalid transitions between states of a request. (bsc#1090823) Following bugs were fixed : - After updating to kernel 3.0.101-0.47.106.32-xen system crashes in check_bugs() (bsc#1097206) - bsc#1079730 - in xen-kmp, unplug emulated devices after migration This is required since xen-4.10 and/or qemu-2.10 because the state of unplug is not propagated from one dom0 to another. Without this unplug qemu last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 112147 published 2018-08-28 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/112147 title SUSE SLES11 Security Update : xen (SUSE-SU-2018:2528-1) (Foreshadow) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family AIX Local Security Checks NASL id AIX_IJ03035.NASL description Systems with microprocessors utilizing speculative execution and indirect branch prediction may allow unauthorized disclosure of information to an attacker with local user access via a side-channel analysis. last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 106315 published 2018-01-25 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/106315 title AIX 7.2 TL 1 : spectre_meltdown (IJ03035) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family Ubuntu Local Security Checks NASL id UBUNTU_USN-3541-2.NASL description USN-3541-1 addressed vulnerabilities in the Linux kernel for Ubuntu 17.10. This update provides the corresponding updates for the Linux Hardware Enablement (HWE) kernel from Ubuntu 17.10 for Ubuntu 16.04 LTS. Jann Horn discovered that microprocessors utilizing speculative execution and branch prediction may allow unauthorized memory reads via sidechannel attacks. This flaw is known as Spectre. A local attacker could use this to expose sensitive information, including kernel memory. This update provides mitigations for the i386 (CVE-2017-5753 only), amd64, ppc64el, and s390x architectures. (CVE-2017-5715, CVE-2017-5753) USN-3523-2 mitigated CVE-2017-5754 (Meltdown) for the amd64 architecture in the Linux Hardware Enablement (HWE) kernel from Ubuntu 17.10 for Ubuntu 16.04 LTS. This update provides the corresponding mitigations for the ppc64el architecture. Jann Horn discovered that microprocessors utilizing speculative execution and indirect branch prediction may allow unauthorized memory reads via sidechannel attacks. This flaw is known as Meltdown. A local attacker could use this to expose sensitive information, including kernel memory. (CVE-2017-5754). Note that Tenable Network Security has extracted the preceding description block directly from the Ubuntu security advisory. Tenable has attempted to automatically clean and format it as much as possible without introducing additional issues. last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 106271 published 2018-01-23 reporter Ubuntu Security Notice (C) 2018-2019 Canonical, Inc. / NASL script (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/106271 title Ubuntu 16.04 LTS : linux-hwe, linux-azure, linux-gcp, linux-oem vulnerabilities (USN-3541-2) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family Windows : Microsoft Bulletins NASL id SMB_NT_MS18_JAN_4056897.NASL description The remote Windows host is missing security update 4056897 or cumulative update 4056894. It is, therefore, affected by multiple vulnerabilities : - An vulnerability exists within microprocessors utilizing speculative execution and indirect branch prediction, which may allow an attacker with local user access to disclose information via a side-channel analysis. (CVE-2017-5715, CVE-2017-5753, CVE-2017-5754) - An elevation of privilege vulnerability exists in Windows Adobe Type Manager Font Driver (ATMFD.dll) when it fails to properly handle objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could execute arbitrary code and take control of an affected system. An attacker could then install programs; view, change, or delete data; or create new accounts with full user rights. (CVE-2018-0788) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists in Windows Adobe Type Manager Font Driver (ATMFD.dll) when it fails to properly handle objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could potentially read data that was not intended to be disclosed. Note that this vulnerability would not allow an attacker to execute code or to elevate their user rights directly, but it could be used to obtain information that could be used to try to further compromise the affected system. (CVE-2018-0754) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists in the way the scripting engine handles objects in memory in Microsoft browsers. The vulnerability could corrupt memory in such a way that an attacker could execute arbitrary code in the context of the current user. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could gain the same user rights as the current user. (CVE-2018-0762, CVE-2018-0772) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists in the way that the Color Management Module (ICM32.dll) handles objects in memory. This vulnerability allows an attacker to retrieve information to bypass usermode ASLR (Address Space Layout Randomization) on a targeted system. By itself, the information disclosure does not allow arbitrary code execution; however, it could allow arbitrary code to be run if the attacker uses it in combination with another vulnerability. (CVE-2018-0741) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists in the Windows kernel that could allow an attacker to retrieve information that could lead to a Kernel Address Space Layout Randomization (ASLR) bypass. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could retrieve the memory address of a kernel object. (CVE-2018-0747) - An elevation of privilege vulnerability exists in the Microsoft Server Message Block (SMB) Server when an attacker with valid credentials attempts to open a specially crafted file over the SMB protocol on the same machine. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could bypass certain security checks in the operating system. (CVE-2018-0749) - An elevation of privilege vulnerability exists in the way that the Windows Kernel API enforces permissions. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could impersonate processes, interject cross-process communication, or interrupt system functionality. (CVE-2018-0748) - A Win32k information disclosure vulnerability exists when the Windows GDI component improperly discloses kernel memory addresses. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could obtain information to further compromise the users system. (CVE-2018-0750) last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 105552 published 2018-01-04 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/105552 title KB4056897: Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2 January 2018 Security Update (Meltdown)(Spectre) NASL family SuSE Local Security Checks NASL id SUSE_SU-2018-0678-1.NASL description This update for xen fixes several issues. These security issues were fixed : - CVE-2017-5753, CVE-2017-5715, CVE-2017-5754: Prevent information leaks via side effects of speculative execution, aka last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 108369 published 2018-03-15 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/108369 title SUSE SLES11 Security Update : xen (SUSE-SU-2018:0678-1) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family Windows : Microsoft Bulletins NASL id SMB_NT_MS18_JAN_4056892.NASL description The remote Windows host is missing security update 4056892 or 4073291. It is, therefore, affected by multiple vulnerabilities : - An vulnerability exists within microprocessors utilizing speculative execution and indirect branch prediction, which may allow an attacker with local user access to disclose information via a side-channel analysis. (CVE-2017-5715, CVE-2017-5753, CVE-2017-5754) - An elevation of privilege vulnerability exists when the Windows kernel fails to properly handle objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could run arbitrary code in kernel mode. An attacker could then install programs; view, change, or delete data; or create new accounts with full user rights. (CVE-2018-0744) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists when the scripting engine does not properly handle objects in memory in Microsoft Edge. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could obtain information to further compromise the users system. (CVE-2018-0767, CVE-2018-0780, CVE-2018-0800) - An elevation of privilege vulnerability exists when Microsoft Edge does not properly enforce cross-domain policies, which could allow an attacker to access information from one domain and inject it into another domain. (CVE-2018-0803) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists in Windows Adobe Type Manager Font Driver (ATMFD.dll) when it fails to properly handle objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could potentially read data that was not intended to be disclosed. Note that this vulnerability would not allow an attacker to execute code or to elevate their user rights directly, but it could be used to obtain information that could be used to try to further compromise the affected system. (CVE-2018-0754) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists in the way the scripting engine handles objects in memory in Microsoft browsers. The vulnerability could corrupt memory in such a way that an attacker could execute arbitrary code in the context of the current user. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could gain the same user rights as the current user. (CVE-2018-0762, CVE-2018-0772) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists when Microsoft Edge PDF Reader improperly handles objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could obtain information to further compromise the users system. (CVE-2018-0766) - An elevation of privilege vulnerability exists in the way that the Windows Kernel API enforces permissions. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could impersonate processes, interject cross-process communication, or interrupt system functionality. (CVE-2018-0748, CVE-2018-0751, CVE-2018-0752) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists in the way that the scripting engine handles objects in memory in Microsoft Edge. The vulnerability could corrupt memory in such a way that an attacker could execute arbitrary code in the context of the current user. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could gain the same user rights as the current user. (CVE-2018-0758, CVE-2018-0768, CVE-2018-0769, CVE-2018-0770, CVE-2018-0773, CVE-2018-0774, CVE-2018-0775, CVE-2018-0776, CVE-2018-0777, CVE-2018-0778, CVE-2018-0781) - An elevation of privilege vulnerability exists in the Microsoft Server Message Block (SMB) Server when an attacker with valid credentials attempts to open a specially crafted file over the SMB protocol on the same machine. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could bypass certain security checks in the operating system. (CVE-2018-0749) - A denial of service vulnerability exists in the way that Windows handles objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could cause a target system to stop responding. Note that the denial of service condition would not allow an attacker to execute code or to elevate user privileges. However, the denial of service condition could prevent authorized users from using system resources. The security update addresses the vulnerability by correcting how Windows handles objects in memory. (CVE-2018-0753) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists in the Windows kernel that could allow an attacker to retrieve information that could lead to a Kernel Address Space Layout Randomization (ASLR) bypass. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could retrieve the memory address of a kernel object. (CVE-2018-0745, CVE-2018-0746, CVE-2018-0747) - An elevation of privilege vulnerability exists due to an integer overflow in Windows Subsystem for Linux. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could execute code with elevated permissions. (CVE-2018-0743) last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 105550 published 2018-01-04 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/105550 title KB4056892: Windows 10 Version 1709 and Windows Server Version 1709 January 2018 Security Update (Meltdown)(Spectre) NASL family Huawei Local Security Checks NASL id EULEROS_SA-2019-1515.NASL description According to the versions of the kernel packages installed, the EulerOS Virtualization installation on the remote host is affected by the following vulnerabilities : - A flaw was found where the kernel truncated the value used to indicate the size of a buffer which it would later become zero using an untruncated value. This can corrupt memory outside of the original allocation.(CVE-2017-9725) - An industry-wide issue was found in the way many modern microprocessor designs have implemented speculative execution of instructions (a commonly used performance optimization). There are three primary variants of the issue which differ in the way the speculative execution can be exploited. Variant CVE-2017-5753 triggers the speculative execution by performing a bounds-check bypass. It relies on the presence of a precisely-defined instruction sequence in the privileged code as well as the fact that memory accesses may cause allocation into the microprocessor last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 124836 published 2019-05-13 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/124836 title EulerOS Virtualization 3.0.1.0 : kernel (EulerOS-SA-2019-1515) NASL family Oracle Linux Local Security Checks NASL id ORACLELINUX_ELSA-2018-4004.NASL description Description of changes: [4.1.12-112.14.5.el7uek] - x86/ibrs: Remove last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 105759 published 2018-01-12 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/105759 title Oracle Linux 6 / 7 : Unbreakable Enterprise kernel (ELSA-2018-4004) (Spectre) NASL family Red Hat Local Security Checks NASL id REDHAT-RHSA-2018-0011.NASL description An update for kernel is now available for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6.7 Extended Update Support. Red Hat Product Security has rated this update as having a security impact of Important. A Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) base score, which gives a detailed severity rating, is available for each vulnerability from the CVE link(s) in the References section. [Updated 23rd January 2019] The text has been updated to correct the list of architectures addressed by the CVE-2017-5753 mitigation. No changes have been made to the packages. The kernel packages contain the Linux kernel, the core of any Linux operating system. Security Fix(es) : An industry-wide issue was found in the way many modern microprocessor designs have implemented speculative execution of instructions (a commonly used performance optimization). There are three primary variants of the issue which differ in the way the speculative execution can be exploited. Note: This issue is present in hardware and cannot be fully fixed via software update. The updated kernel packages provide software mitigation for this hardware issue at a cost of potential performance penalty. Please refer to References section for further information about this issue and the performance impact. In this update, mitigations for x86 (CVE-2017-5753) and x86-64 (CVE-2017-5753, CVE-2017-5715, and CVE-2017-5754) architectures are provided. Variant CVE-2017-5753 triggers the speculative execution by performing a bounds-check bypass. It relies on the presence of a precisely-defined instruction sequence in the privileged code as well as the fact that memory accesses may cause allocation into the microprocessor last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 105527 published 2018-01-04 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/105527 title RHEL 6 : kernel (RHSA-2018:0011) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family Oracle Linux Local Security Checks NASL id ORACLELINUX_ELSA-2018-4109.NASL description The remote Oracle Linux host is missing a security update for the Unbreakable Enterprise kernel package(s). last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 109829 published 2018-05-16 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/109829 title Oracle Linux 6 / 7 : Unbreakable Enterprise kernel (ELSA-2018-4109) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family SuSE Local Security Checks NASL id SUSE_SU-2019-1550-1.NASL description The SUSE Linux Enterprise 15 SP1 kernel was updated to receive various security and bugfixes. The following security bugs were fixed : CVE-2019-12819: The function __mdiobus_register() called put_device(), which triggered a fixed_mdio_bus_init use-after-free. This would cause a denial of service. (bsc#1138291) CVE-2019-12818: The nfc_llcp_build_tlv function in net/nfc/llcp_commands.c may return NULL. If the caller does not check for this, it will trigger a NULL pointer dereference. This will cause denial of service. This used to affect nfc_llcp_build_gb in net/nfc/llcp_core.c. (bsc#1138293) CVE-2019-11477: A sequence of SACKs may have been crafted such that one can trigger an integer overflow, leading to a kernel panic. CVE-2019-11478: It was possible to send a crafted sequence of SACKs which will fragment the TCP retransmission queue. An attacker may have been able to further exploit the fragmented queue to cause an expensive linked-list walk for subsequent SACKs received for that same TCP connection. CVE-2019-11479: An attacker could force the Linux kernel to segment its responses into multiple TCP segments. This would drastically increased the bandwidth required to deliver the same amount of data. Further, it would consume additional resources such as CPU and NIC processing power. CVE-2019-3846: A flaw that allowed an attacker to corrupt memory and possibly escalate privileges was found in the mwifiex kernel module while connecting to a malicious wireless network. (bsc#1136424) CVE-2019-10124: An issue was discovered in the hwpoison implementation in mm/memory-failure.c in the Linux kernel. When soft_offline_in_use_page() runs on a thp tail page after pmd is split, an attacker could cause a denial of service (bsc#1130699, CVE-2019-10124). CVE-2019-12382: An issue was discovered in drm_load_edid_firmware in drivers/gpu/drm/drm_edid_load.c in the Linux kernel There was an unchecked kstrdup of fwstr, which might allow an attacker to cause a denial of service (NULL pointer dereference and system crash). (bsc#1136586) CVE-2019-11487: The Linux kernel allowed page reference count overflow, with resultant use-after-free issues, if about 140 GiB of RAM exists. This is related to fs/fuse/dev.c, fs/pipe.c, fs/splice.c, include/linux/mm.h, include/linux/pipe_fs_i.h, kernel/trace/trace.c, mm/gup.c, and mm/hugetlb.c. It could occur with FUSE requests. (bbsc#1133190) CVE-2019-5489: The mincore() implementation in mm/mincore.c in the Linux kernel allowed local attackers to observe page cache access patterns of other processes on the same system, potentially allowing sniffing of secret information. (Fixing this affects the output of the fincore program.) Limited remote exploitation may be possible, as demonstrated by latency differences in accessing public files from an Apache HTTP Server. (bsc#1120843) CVE-2019-11833: fs/ext4/extents.c in the Linux kernel did not zero out the unused memory region in the extent tree block, which might allow local users to obtain sensitive information by reading uninitialized data in the filesystem. (bsc#1135281) CVE-2019-11091: Microarchitectural Data Sampling Uncacheable Memory (MDSUM): Uncacheable memory on some microprocessors utilizing speculative execution may have allowed an authenticated user to potentially enable information disclosure via a side channel with local access. A list of impacted products can be found here : https://www.intel.com/content/dam/www/public/us/en/documents/corporate -info rmation/SA00233-microcode-update-guidance_05132019. (bsc##1111331) CVE-2018-7191: In the tun subsystem in the Linux kernel, dev_get_valid_name was not called before register_netdevice. This allowed local users to cause a denial of service (NULL pointer dereference and panic) via an ioctl(TUNSETIFF) call with a dev name containing a / character. (bsc#1135603) CVE-2018-12126 CVE-2018-12127 CVE-2018-12130: Microarchitectural Store Buffer Data Sampling (MSBDS): Stored buffers on some microprocessors utilizing speculative execution which may have allowed an authenticated user to potentially enable information disclosure via a side channel with local access. A list of impacted products can be found here : https://www.intel.com/content/dam/www/public/us/en/documents/corporate -info rmation/SA00233-microcode-update-guidance_05132019. (bsc#1103186) CVE-2019-11085: Insufficient input validation in Kernel Mode Driver in Intel(R) i915 Graphics for Linux may have allowed an authenticated user to potentially enable escalation of privilege via local access. (bsc#1135278) CVE-2019-11815: An issue was discovered in rds_tcp_kill_sock in net/rds/tcp.c in the Linux kernel There was a race condition leading to a use-after-free, related to net namespace cleanup. (bsc#1135278) CVE-2019-11884: The do_hidp_sock_ioctl function in net/bluetooth/hidp/sock.c in the Linux kernel allowed a local user to obtain potentially sensitive information from kernel stack memory via a hidPCONNADD command, because a name field may not end with a last seen 2020-05-12 modified 2019-06-19 plugin id 126045 published 2019-06-19 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2019-2020 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/126045 title SUSE SLED15 / SLES15 Security Update : kernel (SUSE-SU-2019:1550-1) (MDSUM/RIDL) (MFBDS/RIDL/ZombieLoad) (MLPDS/RIDL) (MSBDS/Fallout) (SACK Panic) (SACK Slowness) (Spectre) NASL family SuSE Local Security Checks NASL id SUSE_SU-2018-0638-1.NASL description This update for xen fixes several issues. This new feature was included : - add script and sysv service to watch for vcpu online/offline events in a HVM domU These security issues were fixed : - CVE-2017-5753, CVE-2017-5715, CVE-2017-5754: Prevent information leaks via side effects of speculative execution, aka last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 107254 published 2018-03-09 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/107254 title SUSE SLES11 Security Update : xen (SUSE-SU-2018:0638-1) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family SuSE Local Security Checks NASL id SUSE_SU-2018-1376-1.NASL description The SUSE Linux Enterprise 11 SP3 LTSS kernel was updated to receive various security and bugfixes. The following security bugs were fixed : - CVE-2018-3639: Information leaks using last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 110041 published 2018-05-23 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/110041 title SUSE SLES11 Security Update : kernel (SUSE-SU-2018:1376-1) (Spectre) NASL family AIX Local Security Checks NASL id AIX_IJ03034.NASL description Systems with microprocessors utilizing speculative execution and indirect branch prediction may allow unauthorized disclosure of information to an attacker with local user access via a side-channel analysis. last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 106314 published 2018-01-25 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/106314 title AIX 7.2 TL 0 : spectre_meltdown (IJ03034) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family AIX Local Security Checks NASL id AIX_IJ03029.NASL description Systems with microprocessors utilizing speculative execution and indirect branch prediction may allow unauthorized disclosure of information to an attacker with local user access via a side-channel analysis. last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 106310 published 2018-01-25 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/106310 title AIX 5.3 TL 12 : spectre_meltdown (IJ03029) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family Ubuntu Local Security Checks NASL id UBUNTU_USN-3540-1.NASL description Jann Horn discovered that microprocessors utilizing speculative execution and branch prediction may allow unauthorized memory reads via sidechannel attacks. This flaw is known as Spectre. A local attacker could use this to expose sensitive information, including kernel memory. This update provides mitigations for the i386 (CVE-2017-5753 only), amd64, ppc64el, and s390x architectures. (CVE-2017-5715, CVE-2017-5753) USN-3522-1 mitigated CVE-2017-5754 (Meltdown) for the amd64 architecture in Ubuntu 16.04 LTS. This update provides the corresponding mitigations for the ppc64el architecture. Original advisory details : Jann Horn discovered that microprocessors utilizing speculative execution and indirect branch prediction may allow unauthorized memory reads via sidechannel attacks. This flaw is known as Meltdown. A local attacker could use this to expose sensitive information, including kernel memory. (CVE-2017-5754). Note that Tenable Network Security has extracted the preceding description block directly from the Ubuntu security advisory. Tenable has attempted to automatically clean and format it as much as possible without introducing additional issues. last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 106268 published 2018-01-23 reporter Ubuntu Security Notice (C) 2018-2019 Canonical, Inc. / NASL script (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/106268 title Ubuntu 16.04 LTS : linux, linux-aws, linux-euclid vulnerabilities (USN-3540-1) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family Windows NASL id VMWARE_WORKSTATION_WIN_VMSA_2017_0021.NASL description The version of VMware Workstation installed on the remote Windows host is 12.x prior to 12.5.8. It is, therefore, affected by multiple vulnerabilities that can allow code execution in a virtual machine via the authenticated VNC session as well as cause information disclosure from one virtual machine to another virtual machine on the same host. last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 105487 published 2017-12-29 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2017-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/105487 title VMware Workstation 12.x < 12.5.8 Multiple Vulnerabilities (VMSA-2017-0021) (VMSA-2018-0002) (Spectre) NASL family Oracle Linux Local Security Checks NASL id ORACLELINUX_ELSA-2018-4020.NASL description Description of changes: [2.6.39-400.298.2.el6uek] - x86: Use PRED_CMD MSR when ibpb is enabled (Konrad Rzeszutek Wilk) [Orabug: 27369777] {CVE-2017-5715} {CVE-2017-5753} - x86/spec: Don last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 106328 published 2018-01-25 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/106328 title Oracle Linux 6 : Unbreakable Enterprise kernel (ELSA-2018-4020) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family Red Hat Local Security Checks NASL id REDHAT-RHSA-2018-0010.NASL description An update for kernel is now available for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.2 Advanced Update Support, Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.2 Telco Extended Update Support, and Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.2 Update Services for SAP Solutions. Red Hat Product Security has rated this update as having a security impact of Important. A Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) base score, which gives a detailed severity rating, is available for each vulnerability from the CVE link(s) in the References section. The kernel packages contain the Linux kernel, the core of any Linux operating system. Security Fix(es) : An industry-wide issue was found in the way many modern microprocessor designs have implemented speculative execution of instructions (a commonly used performance optimization). There are three primary variants of the issue which differ in the way the speculative execution can be exploited. Note: This issue is present in hardware and cannot be fully fixed via software update. The updated kernel packages provide software mitigation for this hardware issue at a cost of potential performance penalty. Please refer to References section for further information about this issue and the performance impact. In this update mitigations for x86-64 architecture are provided. Variant CVE-2017-5753 triggers the speculative execution by performing a bounds-check bypass. It relies on the presence of a precisely-defined instruction sequence in the privileged code as well as the fact that memory accesses may cause allocation into the microprocessor last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 105526 published 2018-01-04 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/105526 title RHEL 7 : kernel (RHSA-2018:0010) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family Red Hat Local Security Checks NASL id REDHAT-RHSA-2018-0044.NASL description An update for redhat-virtualization-host is now available for RHEV 3.X Hypervisor and Agents for RHEL-7. Red Hat Product Security has rated this update as having a security impact of Important. A Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) base score, which gives a detailed severity rating, is available for each vulnerability from the CVE link(s) in the References section. The ovirt-node-ng packages provide the Red Hat Virtualization Host. These packages include redhat-release-virtualization-host, ovirt-node, and rhev-hypervisor. Red Hat Virtualization Hosts (RHVH) are installed using a special build of Red Hat Enterprise Linux with only the packages required to host virtual machines. RHVH features a Cockpit user interface for monitoring the host last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 105675 published 2018-01-09 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/105675 title RHEL 7 : redhat-virtualization-host (RHSA-2018:0044) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family Red Hat Local Security Checks NASL id REDHAT-RHSA-2018-0496.NASL description An update for kernel is now available for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6.7 Extended Update Support. Red Hat Product Security has rated this update as having a security impact of Important. A Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) base score, which gives a detailed severity rating, is available for each vulnerability from the CVE link(s) in the References section. The kernel packages contain the Linux kernel, the core of any Linux operating system. Security Fix(es) : * hw: cpu: speculative execution branch target injection (s390-only) (CVE-2017-5715, Important) * hw: cpu: speculative execution bounds-check bypass (s390 and powerpc) (CVE-2017-5753, Important) * hw: cpu: speculative execution permission faults handling (powerpc-only) (CVE-2017-5754) For more details about the security issue(s), including the impact, a CVSS score, acknowledgments, and other related information, refer to the CVE page(s) listed in the References section. Bug Fix(es) : * If an NFSv3 client mounted a subdirectory of an exported file system, a directory entry to the mount hosting the export was incorrectly held even after clearing the cache. Consequently, attempts to unmount the subdirectory with the umount command failed with the EBUSY error. With this update, the underlying source code has been fixed, and the unmount operation now succeeds as expected in the described situation. (BZ#1538587) * The Return Trampoline (Retpoline) mechanism mitigates the branch target injection, also known as the Spectre variant 2 vulnerability. With this update, Retpoline has been implemented into the Red Hat Enterprise Linux kernel. (BZ#1543023) last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 108326 published 2018-03-14 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/108326 title RHEL 6 : kernel (RHSA-2018:0496) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family SuSE Local Security Checks NASL id OPENSUSE-2018-169.NASL description This update for xen fixes several issues. These security issues were fixed : - CVE-2017-5753, CVE-2017-5715, CVE-2017-5754: Prevent information leaks via side effects of speculative execution, aka last seen 2020-06-05 modified 2018-02-16 plugin id 106864 published 2018-02-16 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2020 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/106864 title openSUSE Security Update : xen (openSUSE-2018-169) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family Ubuntu Local Security Checks NASL id UBUNTU_USN-3542-1.NASL description Jann Horn discovered that microprocessors utilizing speculative execution and branch prediction may allow unauthorized memory reads via sidechannel attacks. This flaw is known as Spectre. A local attacker could use this to expose sensitive information, including kernel memory. This update provides mitigations for the i386 (CVE-2017-5753 only) and amd64 architectures. Note that Tenable Network Security has extracted the preceding description block directly from the Ubuntu security advisory. Tenable has attempted to automatically clean and format it as much as possible without introducing additional issues. last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 106272 published 2018-01-23 reporter Ubuntu Security Notice (C) 2018-2019 Canonical, Inc. / NASL script (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/106272 title Ubuntu 14.04 LTS : linux vulnerabilities (USN-3542-1) (Spectre) NASL family SuSE Local Security Checks NASL id SUSE_SU-2018-1658-1.NASL description This update for xen fixes several issues. These security issues were fixed : - CVE-2018-3639: Prevent attackers with local user access from extracting information via a side-channel analysis, aka Speculative Store Bypass (SSB), Variant 4 (bsc#1092631). - CVE-2017-5753,CVE-2017-5715,CVE-2017-5754: Improved Spectre v2 mitigations (bsc#1074562). Note that Tenable Network Security has extracted the preceding description block directly from the SUSE security advisory. Tenable has attempted to automatically clean and format it as much as possible without introducing additional issues. last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 110509 published 2018-06-13 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/110509 title SUSE SLES12 Security Update : xen (SUSE-SU-2018:1658-1) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family SuSE Local Security Checks NASL id OPENSUSE-2019-418.NASL description This update for xen to version 4.10.1 fixes several issues (bsc#1027519). These security issues were fixed : - CVE-2018-3639: Prevent attackers with local user access from extracting information via a side-channel analysis, aka Speculative Store Bypass (SSB), Variant 4 (bsc#1092631). - CVE-2017-5753,CVE-2017-5715,CVE-2017-5754: Improved Spectre v2 mitigations (bsc#1074562). This non-security issue was fixed : - Always call qemus xen-save-devices-state in suspend/resume to fix migration with qcow2 images (bsc#1079730) last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 123180 published 2019-03-27 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2019-2020 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/123180 title openSUSE Security Update : xen (openSUSE-2019-418) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family SuSE Local Security Checks NASL id SUSE_SU-2018-1699-1.NASL description This update for xen fixes several issues. This feature was added : - Added support for qemu monitor command These security issues were fixed : - CVE-2018-3639: Prevent attackers with local user access from extracting information via a side-channel analysis, aka Speculative Store Bypass (SSB), Variant 4 (bsc#1092631). - CVE-2017-5753,CVE-2017-5715,CVE-2017-5754: Improved Spectre v2 mitigations (bsc#1074562). The update package also includes non-security fixes. See advisory for details. Note that Tenable Network Security has extracted the preceding description block directly from the SUSE security advisory. Tenable has attempted to automatically clean and format it as much as possible without introducing additional issues. last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 110596 published 2018-06-18 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/110596 title SUSE SLES12 Security Update : xen (SUSE-SU-2018:1699-1) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family MacOS X Local Security Checks NASL id MACOSX_FUSION_VMSA_2017_0021.NASL description The version of VMware Fusion installed on the remote macOS or Mac OS X host is 8.x prior to 8.5.9. It is, therefore, affected by multiple vulnerabilities that can allow code execution in a virtual machine via the authenticated VNC session as well as cause information disclosure from one virtual machine to another virtual machine on the same host. last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 105485 published 2017-12-29 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2017-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/105485 title VMware Fusion 8.x < 8.5.9 Multiple Vulnerabilities (VMSA-2017-0021) (VMSA-2018-0002) (Spectre) (macOS) NASL family OracleVM Local Security Checks NASL id ORACLEVM_OVMSA-2018-0218.NASL description The remote OracleVM system is missing necessary patches to address critical security updates : please see Oracle VM Security Advisory OVMSA-2018-0218 for details. last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 109987 published 2018-05-23 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/109987 title OracleVM 3.4 : xen (OVMSA-2018-0218) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family SuSE Local Security Checks NASL id SUSE_SU-2018-0179-1.NASL description This update for wireshark to version 2.2.12 fixes the following issues : - CVE-2018-5334: IxVeriWave file could crash (bsc#1075737) - CVE-2018-5335: WCP dissector could crash (bsc#1075738) - CVE-2018-5336: Multiple dissector crashes (bsc#1075739) - CVE-2017-17935: Incorrect handling of last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 106293 published 2018-01-24 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/106293 title SUSE SLES11 Security Update : wireshark (SUSE-SU-2018:0179-1) (Spectre) NASL family OracleVM Local Security Checks NASL id ORACLEVM_OVMSA-2018-0016.NASL description The remote OracleVM system is missing necessary patches to address critical security updates : - x86: Add another set of MSR accessor functions (Borislav Petkov) [Orabug: 27444923] (CVE-2017-5753) - userns: prevent speculative execution (Elena Reshetova) [Orabug: 27444923] (CVE-2017-5753) - udf: prevent speculative execution (Elena Reshetova) [Orabug: 27444923] (CVE-2017-5753) - fs: prevent speculative execution (Elena Reshetova) [Orabug: 27444923] (CVE-2017-5753) - qla2xxx: prevent speculative execution (Elena Reshetova) [Orabug: 27444923] (CVE-2017-5753) - p54: prevent speculative execution (Elena Reshetova) [Orabug: 27444923] (CVE-2017-5753) - carl9170: prevent speculative execution (Elena Reshetova) [Orabug: 27444923] (CVE-2017-5753) - uvcvideo: prevent speculative execution (Elena Reshetova) [Orabug: 27444923] (CVE-2017-5753) - locking/barriers: introduce new observable speculation barrier (Elena Reshetova) [Orabug: 27444923] (CVE-2017-5753) - x86/cpu/AMD: Remove now unused definition of MFENCE_RDTSC feature (Elena Reshetova) [Orabug: 27444923] (CVE-2017-5753) - x86/cpu/AMD: Make the LFENCE instruction serialized (Elena Reshetova) [Orabug: 27444923] (CVE-2017-5753) - x86/rsb: add comment specifying why we skip STUFF_RSB (Ankur Arora) [Orabug: 27451658] (CVE-2017-5715) - x86/rsb: make STUFF_RSB jmp labels more robust (Ankur Arora) [Orabug: 27451658] (CVE-2017-5715) - x86/spec: Also print IBRS if IBPB is disabled. (Konrad Rzeszutek Wilk) (CVE-2017-5715) - x86/spectre: Drop the warning about ibrs being obsolete. (Konrad Rzeszutek Wilk) (CVE-2017-5715) - Add set_ibrs_disabled and set_ibpb_disabled (Konrad Rzeszutek Wilk) [Orabug: 27376697] (CVE-2017-5715) - x86/spec: Don last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 106524 published 2018-01-31 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/106524 title OracleVM 3.3 : Unbreakable / etc (OVMSA-2018-0016) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family Oracle Linux Local Security Checks NASL id ORACLELINUX_ELSA-2018-4022.NASL description Description of changes: kernel-uek [3.8.13-118.20.2.el7uek] - x86: Add another set of MSR accessor functions (Borislav Petkov) [Orabug: 27444923] {CVE-2017-5753} - userns: prevent speculative execution (Elena Reshetova) [Orabug: 27444923] {CVE-2017-5753} - udf: prevent speculative execution (Elena Reshetova) [Orabug: 27444923] {CVE-2017-5753} - fs: prevent speculative execution (Elena Reshetova) [Orabug: 27444923] {CVE-2017-5753} - qla2xxx: prevent speculative execution (Elena Reshetova) [Orabug: 27444923] {CVE-2017-5753} - p54: prevent speculative execution (Elena Reshetova) [Orabug: 27444923] {CVE-2017-5753} - carl9170: prevent speculative execution (Elena Reshetova) [Orabug: 27444923] {CVE-2017-5753} - uvcvideo: prevent speculative execution (Elena Reshetova) [Orabug: 27444923] {CVE-2017-5753} - locking/barriers: introduce new observable speculation barrier (Elena Reshetova) [Orabug: 27444923] {CVE-2017-5753} - x86/cpu/AMD: Remove now unused definition of MFENCE_RDTSC feature (Elena Reshetova) [Orabug: 27444923] {CVE-2017-5753} - x86/cpu/AMD: Make the LFENCE instruction serialized (Elena Reshetova) [Orabug: 27444923] {CVE-2017-5753} - x86/rsb: add comment specifying why we skip STUFF_RSB (Ankur Arora) [Orabug: 27451658] {CVE-2017-5715} - x86/rsb: make STUFF_RSB jmp labels more robust (Ankur Arora) [Orabug: 27451658] {CVE-2017-5715} - x86/spec: Also print IBRS if IBPB is disabled. (Konrad Rzeszutek Wilk) {CVE-2017-5715} - x86/spectre: Drop the warning about ibrs being obsolete. (Konrad Rzeszutek Wilk) {CVE-2017-5715} - Add set_ibrs_disabled and set_ibpb_disabled (Konrad Rzeszutek Wilk) [Orabug: 27376697] {CVE-2017-5715} - x86/spec: Don last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 106468 published 2018-01-30 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/106468 title Oracle Linux 6 / 7 : Unbreakable Enterprise kernel (ELSA-2018-4022) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family Red Hat Local Security Checks NASL id REDHAT-RHSA-2018-0008.NASL description An update for kernel is now available for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6. Red Hat Product Security has rated this update as having a security impact of Important. A Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) base score, which gives a detailed severity rating, is available for each vulnerability from the CVE link(s) in the References section. [Updated 23rd January 2019] The text has been updated to correct the list of architectures addressed by the CVE-2017-5753 mitigation. No changes have been made to the packages. The kernel packages contain the Linux kernel, the core of any Linux operating system. Security Fix(es) : An industry-wide issue was found in the way many modern microprocessor designs have implemented speculative execution of instructions (a commonly used performance optimization). There are three primary variants of the issue which differ in the way the speculative execution can be exploited. Note: This issue is present in hardware and cannot be fully fixed via software update. The updated kernel packages provide software mitigation for this hardware issue at a cost of potential performance penalty. Please refer to References section for further information about this issue and the performance impact. In this update, mitigations for x86 (CVE-2017-5753) and x86-64 (CVE-2017-5753, CVE-2017-5715, and CVE-2017-5754) architectures are provided. Variant CVE-2017-5753 triggers the speculative execution by performing a bounds-check bypass. It relies on the presence of a precisely-defined instruction sequence in the privileged code as well as the fact that memory accesses may cause allocation into the microprocessor last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 105524 published 2018-01-04 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/105524 title RHEL 6 : kernel (RHSA-2018:0008) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family OracleVM Local Security Checks NASL id ORACLEVM_OVMSA-2018-0035.NASL description The remote OracleVM system is missing necessary patches to address critical security updates : please see Oracle VM Security Advisory OVMSA-2018-0035 for details. last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 109158 published 2018-04-19 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/109158 title OracleVM 3.4 : Unbreakable / etc (OVMSA-2018-0035) (Dirty COW) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family Debian Local Security Checks NASL id DEBIAN_DLA-1731.NASL description The linux update issued as DLA-1731-1 caused a regression in the vmxnet3 (VMware virtual network adapter) driver. This update corrects that regression, and an earlier regression in the CIFS network filesystem implementation introduced in DLA-1422-1. For reference the original advisory text follows. Several vulnerabilities have been discovered in the Linux kernel that may lead to a privilege escalation, denial of service or information leaks. CVE-2016-10741 A race condition was discovered in XFS that would result in a crash (BUG). A local user permitted to write to an XFS volume could use this for denial of service. CVE-2017-5753 Further instances of code that was vulnerable to Spectre variant 1 (bounds-check bypass) have been mitigated. CVE-2017-13305 A memory over-read was discovered in the keys subsystem last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 123420 published 2019-03-28 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2019-2020 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/123420 title Debian DLA-1731-2 : linux regression update (Spectre) NASL family Scientific Linux Local Security Checks NASL id SL_20180103_KERNEL_ON_SL7_X.NASL description Security Fix(es) : An industry-wide issue was found in the way many modern microprocessor designs have implemented speculative execution of instructions (a commonly used performance optimization). There are three primary variants of the issue which differ in the way the speculative execution can be exploited. Note: This issue is present in hardware and cannot be fully fixed via software update. The updated kernel packages provide software mitigation for this hardware issue at a cost of potential performance penalty. The performance impact of these patches may vary considerably based on workload and hardware configuration. In this update mitigations for x86-64 architecture are provided. Variant CVE-2017-5753 triggers the speculative execution by performing a bounds-check bypass. It relies on the presence of a precisely-defined instruction sequence in the privileged code as well as the fact that memory accesses may cause allocation into the microprocessor last seen 2020-03-18 modified 2018-01-04 plugin id 105535 published 2018-01-04 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2020 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/105535 title Scientific Linux Security Update : kernel on SL7.x x86_64 (20180103) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family OracleVM Local Security Checks NASL id ORACLEVM_OVMSA-2018-0015.NASL description The remote OracleVM system is missing necessary patches to address critical security updates : please see Oracle VM Security Advisory OVMSA-2018-0015 for details. last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 106469 published 2018-01-30 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/106469 title OracleVM 3.4 : Unbreakable / etc (OVMSA-2018-0015) (BlueBorne) (Meltdown) (Spectre) (Stack Clash) NASL family Windows NASL id MOZILLA_FIREFOX_57_0_4.NASL description The version of Mozilla Firefox installed on the remote Windows host is prior to 57.0.4. It is, therefore, vulnerable to a speculative execution side-channel attack. Code from a malicious web page could read data from other web sites or private data from the browser itself. last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 105616 published 2018-01-05 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/105616 title Mozilla Firefox < 57.0.4 Speculative Execution Side-Channel Attack Vulnerability (Spectre) NASL family Red Hat Local Security Checks NASL id REDHAT-RHSA-2018-0151.NASL description An update for kernel is now available for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7. Red Hat Product Security has rated this update as having a security impact of Important. A Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) base score, which gives a detailed severity rating, is available for each vulnerability from the CVE link(s) in the References section. The kernel packages contain the Linux kernel, the core of any Linux operating system. Security Fix(es) : An industry-wide issue was found in the way many modern microprocessor designs have implemented speculative execution of instructions (a commonly used performance optimization). There are three primary variants of the issue which differ in the way the speculative execution can be exploited. Note: This issue is present in hardware and cannot be fully fixed via software update. The updated kernel packages provide software mitigation for this hardware issue at a cost of potential performance penalty. Please refer to References section for further information about this issue and the performance impact. In this update initial mitigations for IBM Power (PowerPC) and IBM zSeries (S390) architectures are provided. * Variant CVE-2017-5715 triggers the speculative execution by utilizing branch target injection. It relies on the presence of a precisely-defined instruction sequence in the privileged code as well as the fact that memory accesses may cause allocation into the microprocessor last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 106330 published 2018-01-25 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/106330 title RHEL 7 : kernel (RHSA-2018:0151) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family Misc. NASL id VMWARE_ESXI_VMSA-2017-0021.NASL description The remote VMware ESXi host is version 5.5, 6.0, or 6.5 and is missing a security patch. It is, therefore, affected by multiple vulnerabilities that can allow code execution in a virtual machine via the authenticated VNC session as well as cause information disclosure from one virtual machine to another virtual machine on the same host. last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 105486 published 2017-12-29 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2017-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/105486 title ESXi 5.5 / 6.0 / 6.5 / Multiple Vulnerabilities (VMSA-2017-0021) (VMSA-2018-0002) (Spectre) (remote check) NASL family Oracle Linux Local Security Checks NASL id ORACLELINUX_ELSA-2018-4071.NASL description The remote Oracle Linux host is missing a security update for the Unbreakable Enterprise kernel package(s). last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 109156 published 2018-04-19 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/109156 title Oracle Linux 6 / 7 : Unbreakable Enterprise kernel (ELSA-2018-4071) (Dirty COW) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family Misc. NASL id VMWARE_VCENTER_VMSA-2018-0007.NASL description The version of VMware vCenter Server installed on the remote host is 6.5.x prior to 6.5u1f. It is, therefore, affected by multiple vulnerabilities. See advisory for details. last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 106950 published 2018-02-22 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018 Tenable Network Security, Inc. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/106950 title VMware vCenter Server 6.5.x < 6.5u1f Multiple Vulnerabilities (VMSA-2018-0007) (Spectre-1) (Meltdown) NASL family Red Hat Local Security Checks NASL id REDHAT-RHSA-2018-0022.NASL description An update for kernel is now available for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6.5 Advanced Update Support. Red Hat Product Security has rated this update as having a security impact of Important. A Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) base score, which gives a detailed severity rating, is available for each vulnerability from the CVE link(s) in the References section. The kernel packages contain the Linux kernel, the core of any Linux operating system. Security Fix(es) : An industry-wide issue was found in the way many modern microprocessor designs have implemented speculative execution of instructions (a commonly used performance optimization). There are three primary variants of the issue which differ in the way the speculative execution can be exploited. Note: This issue is present in hardware and cannot be fully fixed via software update. The updated kernel packages provide software mitigation for this hardware issue at a cost of potential performance penalty. Please refer to References section for further information about this issue and the performance impact. In this update mitigations for x86-64 architecture are provided. Variant CVE-2017-5753 triggers the speculative execution by performing a bounds-check bypass. It relies on the presence of a precisely-defined instruction sequence in the privileged code as well as the fact that memory accesses may cause allocation into the microprocessor last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 105563 published 2018-01-04 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/105563 title RHEL 6 : kernel (RHSA-2018:0022) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family AIX Local Security Checks NASL id AIX_IJ03032.NASL description Systems with microprocessors utilizing speculative execution and indirect branch prediction may allow unauthorized disclosure of information to an attacker with local user access via a side-channel analysis. last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 106312 published 2018-01-25 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/106312 title AIX 7.1 TL 4 : spectre_meltdown (IJ03032) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family SuSE Local Security Checks NASL id SUSE_SU-2018-0171-1.NASL description The SUSE Linux Enterprise 11 SP3 LTSS kernel was updated to receive various security and bugfixes. This update is only provided as a fix update for IBM Z platform. - CVE-2017-5753 / last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 106260 published 2018-01-23 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/106260 title SUSE SLES11 Security Update : kernel (SUSE-SU-2018:0171-1) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family Ubuntu Local Security Checks NASL id UBUNTU_USN-3540-2.NASL description USN-3540-1 addressed vulnerabilities in the Linux kernel for Ubuntu 16.04 LTS. This update provides the corresponding updates for the Linux Hardware Enablement (HWE) kernel from Ubuntu 16.04 LTS for Ubuntu 14.04 LTS. Jann Horn discovered that microprocessors utilizing speculative execution and branch prediction may allow unauthorized memory reads via sidechannel attacks. This flaw is known as Spectre. A local attacker could use this to expose sensitive information, including kernel memory. This update provides mitigations for the i386 (CVE-2017-5753 only), amd64, ppc64el, and s390x architectures. (CVE-2017-5715, CVE-2017-5753) USN-3522-2 mitigated CVE-2017-5754 (Meltdown) for the amd64 architecture in the Linux Hardware Enablement (HWE) kernel from Ubuntu 16.04 LTS for Ubuntu 14.04 LTS. This update provides the corresponding mitigations for the ppc64el architecture. Jann Horn discovered that microprocessors utilizing speculative execution and indirect branch prediction may allow unauthorized memory reads via sidechannel attacks. This flaw is known as Meltdown. A local attacker could use this to expose sensitive information, including kernel memory. (CVE-2017-5754). Note that Tenable Network Security has extracted the preceding description block directly from the Ubuntu security advisory. Tenable has attempted to automatically clean and format it as much as possible without introducing additional issues. last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 106269 published 2018-01-23 reporter Ubuntu Security Notice (C) 2018-2019 Canonical, Inc. / NASL script (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/106269 title Ubuntu 14.04 LTS : linux-lts-xenial, linux-aws vulnerabilities (USN-3540-2) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family OracleVM Local Security Checks NASL id ORACLEVM_OVMSA-2018-0006.NASL description The remote OracleVM system is missing necessary patches to address critical security updates : please see Oracle VM Security Advisory OVMSA-2018-0006 for details. last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 105718 published 2018-01-10 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/105718 title OracleVM 3.4 : xen (OVMSA-2018-0006) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family CentOS Local Security Checks NASL id CENTOS_RHSA-2018-0151.NASL description An update for kernel is now available for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7. Red Hat Product Security has rated this update as having a security impact of Important. A Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) base score, which gives a detailed severity rating, is available for each vulnerability from the CVE link(s) in the References section. The kernel packages contain the Linux kernel, the core of any Linux operating system. Security Fix(es) : An industry-wide issue was found in the way many modern microprocessor designs have implemented speculative execution of instructions (a commonly used performance optimization). There are three primary variants of the issue which differ in the way the speculative execution can be exploited. Note: This issue is present in hardware and cannot be fully fixed via software update. The updated kernel packages provide software mitigation for this hardware issue at a cost of potential performance penalty. Please refer to References section for further information about this issue and the performance impact. In this update initial mitigations for IBM Power (PowerPC) and IBM zSeries (S390) architectures are provided. * Variant CVE-2017-5715 triggers the speculative execution by utilizing branch target injection. It relies on the presence of a precisely-defined instruction sequence in the privileged code as well as the fact that memory accesses may cause allocation into the microprocessor last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 106353 published 2018-01-26 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/106353 title CentOS 7 : kernel (CESA-2018:0151) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family Scientific Linux Local Security Checks NASL id SL_20180103_KERNEL_ON_SL6_X.NASL description Security Fix(es) : An industry-wide issue was found in the way many modern microprocessor designs have implemented speculative execution of instructions (a commonly used performance optimization). There are three primary variants of the issue which differ in the way the speculative execution can be exploited. Note: This issue is present in hardware and cannot be fully fixed via software update. The updated kernel packages provide software mitigation for this hardware issue at a cost of potential performance penalty. The performance impact of these patches may vary considerably based on workload and hardware configuration. In this update mitigations for x86-64 architecture are provided. Variant CVE-2017-5753 triggers the speculative execution by performing a bounds-check bypass. It relies on the presence of a precisely-defined instruction sequence in the privileged code as well as the fact that memory accesses may cause allocation into the microprocessor last seen 2020-03-18 modified 2018-01-04 plugin id 105534 published 2018-01-04 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2020 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/105534 title Scientific Linux Security Update : kernel on SL6.x i386/x86_64 (20180103) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family Debian Local Security Checks NASL id DEBIAN_DSA-4187.NASL description Several vulnerabilities have been discovered in the Linux kernel that may lead to a privilege escalation, denial of service or information leaks. - CVE-2015-9016 Ming Lei reported a race condition in the multiqueue block layer (blk-mq). On a system with a driver using blk-mq (mtip32xx, null_blk, or virtio_blk), a local user might be able to use this for denial of service or possibly for privilege escalation. - CVE-2017-0861 Robb Glasser reported a potential use-after-free in the ALSA (sound) PCM core. We believe this was not possible in practice. - CVE-2017-5715 Multiple researchers have discovered a vulnerability in various processors supporting speculative execution, enabling an attacker controlling an unprivileged process to read memory from arbitrary addresses, including from the kernel and all other processes running on the system. This specific attack has been named Spectre variant 2 (branch target injection) and is mitigated for the x86 architecture (amd64 and i386) by using the last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 109517 published 2018-05-02 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2020 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/109517 title Debian DSA-4187-1 : linux - security update (Spectre) NASL family MacOS X Local Security Checks NASL id MACOSX_FIREFOX_57_0_4.NASL description The version of Mozilla Firefox installed on the remote macOS or Mac OS X host is prior to 57.0.4. It is, therefore, vulnerable to a speculative execution side-channel attack. Code from a malicious web page could read data from other web sites or private data from the browser itself. last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 105615 published 2018-01-05 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/105615 title Mozilla Firefox < 57.0.4 Speculative Execution Side-Channel Attack Vulnerability (Spectre) (macOS) NASL family SuSE Local Security Checks NASL id SUSE_SU-2018-0219-1.NASL description This update for webkit2gtk3 fixes the following issues: Update to version 2.18.5 : + Disable SharedArrayBuffers from Web API. + Reduce the precision of last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 106370 published 2018-01-26 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/106370 title SUSE SLED12 / SLES12 Security Update : webkit2gtk3 (SUSE-SU-2018:0219-1) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family Red Hat Local Security Checks NASL id REDHAT-RHSA-2018-0182.NASL description An update for kernel is now available for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.3 Extended Update Support. Red Hat Product Security has rated this update as having a security impact of Important. A Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) base score, which gives a detailed severity rating, is available for each vulnerability from the CVE link(s) in the References section. The kernel packages contain the Linux kernel, the core of any Linux operating system. Security Fix(es) : An industry-wide issue was found in the way many modern microprocessor designs have implemented speculative execution of instructions (a commonly used performance optimization). There are three primary variants of the issue which differ in the way the speculative execution can be exploited. Note: This issue is present in hardware and cannot be fully fixed via software update. The updated kernel packages provide software mitigation for this hardware issue at a cost of potential performance penalty. Please refer to References section for further information about this issue and the performance impact. In this update initial mitigations for IBM Power (PowerPC) and IBM zSeries (S390) architectures are provided. Variant CVE-2017-5753 triggers the speculative execution by performing a bounds-check bypass. It relies on the presence of a precisely-defined instruction sequence in the privileged code as well as the fact that memory accesses may cause allocation into the microprocessor last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 106335 published 2018-01-25 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/106335 title RHEL 7 : kernel (RHSA-2018:0182) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family Red Hat Local Security Checks NASL id REDHAT-RHSA-2018-0047.NASL description An update for redhat-virtualization-host is now available for RHEV 4.X, RHEV-H, and Agents for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7. Red Hat Product Security has rated this update as having a security impact of Important. A Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) base score, which gives a detailed severity rating, is available for each vulnerability from the CVE link(s) in the References section. The ovirt-node-ng packages provide the Red Hat Virtualization Host. These packages include redhat-release-virtualization-host, ovirt-node, and rhev-hypervisor. Red Hat Virtualization Hosts (RHVH) are installed using a special build of Red Hat Enterprise Linux with only the packages required to host virtual machines. RHVH features a Cockpit user interface for monitoring the host last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 105678 published 2018-01-09 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/105678 title RHEL 7 : redhat-virtualization-host (RHSA-2018:0047) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family Oracle Linux Local Security Checks NASL id ORACLELINUX_ELSA-2018-4110.NASL description The remote Oracle Linux host is missing a security update for the Unbreakable Enterprise kernel package(s). last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 109881 published 2018-05-17 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/109881 title Oracle Linux 6 : Unbreakable Enterprise kernel (ELSA-2018-4110) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family SuSE Local Security Checks NASL id SUSE_SU-2019-2430-1.NASL description The SUSE Linux Enterprise 15 SP1 RT kernel was updated to receive various security and bugfixes. The following security bugs were fixed : CVE-2018-12126 CVE-2018-12127 CVE-2018-12130: Microarchitectural Store Buffer Data Sampling (MSBDS): Stored buffers on some microprocessors utilizing speculative execution which may have allowed an authenticated user to potentially enable information disclosure via a side channel with local access. A list of impacted products can be found here : https://www.intel.com/content/dam/www/public/us/en/documents/corporate -info rmation/SA00233-microcode-update-guidance_05132019. (bsc#1103186)CVE-2019-11091: Microarchitectural Data Sampling Uncacheable Memory (MDSUM): Uncacheable memory on some microprocessors utilizing speculative execution may have allowed an authenticated user to potentially enable information disclosure via a side channel with local access. A list of impacted products can be found here : https://www.intel.com/content/dam/www/public/us/en/documents/corporate -info rmation/SA00233-microcode-update-guidance_05132019. (bsc#1111331)CVE-2019-12382: An issue was discovered in drm_load_edid_firmware in drivers/gpu/drm/drm_edid_load.c in the Linux kernel There was an unchecked kstrdup of fwstr, which might allow an attacker to cause a denial of service (NULL pointer dereference and system crash). (bsc#1136586) CVE-2019-10124: An issue was discovered in the hwpoison implementation in mm/memory-failure.c in the Linux kernel. When soft_offline_in_use_page() runs on a thp tail page after pmd is split, an attacker could cause a denial of service (bsc#1130699). CVE-2019-11486: The Siemens R3964 line discipline driver in drivers/tty/n_r3964.c in the Linux kernel has multiple race conditions. (bsc#1133188) CVE-2019-11811: An issue was discovered in the Linux kernel There was a use-after-free upon attempted read access to /proc/ioports after the ipmi_si module was removed, related to drivers/char/ipmi/ipmi_si_intf.c, drivers/char/ipmi/ipmi_si_mem_io.c, and drivers/char/ipmi/ipmi_si_port_io.c. (bsc#1134397) CVE-2019-11487: The Linux kernel allowed page reference count overflow, with resultant use-after-free issues, if about 140 GiB of RAM exists. This is related to fs/fuse/dev.c, fs/pipe.c, fs/splice.c, include/linux/mm.h, include/linux/pipe_fs_i.h, kernel/trace/trace.c, mm/gup.c, and mm/hugetlb.c. It could occur with FUSE requests. (bsc#1133190) CVE-2019-12818: The nfc_llcp_build_tlv function in net/nfc/llcp_commands.c may return NULL. If the caller does not check for this, it will trigger a NULL pointer dereference. This will cause denial of service. This used to affect nfc_llcp_build_gb in net/nfc/llcp_core.c. (bsc#1138293) CVE-2019-11833: fs/ext4/extents.c in the Linux kernel did not zero out the unused memory region in the extent tree block, which might allow local users to obtain sensitive information by reading uninitialized data in the filesystem. (bsc#1135281) CVE-2019-5489: The mincore() implementation in mm/mincore.c in the Linux kernel allowed local attackers to observe page cache access patterns of other processes on the same system, potentially allowing sniffing of secret information. (Fixing this affects the output of the fincore program.) Limited remote exploitation may be possible, as demonstrated by latency differences in accessing public files from an Apache HTTP Server. (bsc#1120843) CVE-2018-7191: In the tun subsystem in the Linux kernel, dev_get_valid_name was not called before register_netdevice. This allowed local users to cause a denial of service (NULL pointer dereference and panic) via an ioctl(TUNSETIFF) call with a dev name containing a / character. (bsc#1135603) CVE-2019-11884: The do_hidp_sock_ioctl function in net/bluetooth/hidp/sock.c in the Linux kernel allowed a local user to obtain potentially sensitive information from kernel stack memory via a hidPCONNADD command, because a name field may not end with a last seen 2020-05-12 modified 2019-09-24 plugin id 129284 published 2019-09-24 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2019-2020 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/129284 title SUSE SLED15 / SLES15 Security Update : kernel-source-rt (SUSE-SU-2019:2430-1) (MDSUM/RIDL) (MFBDS/RIDL/ZombieLoad) (MLPDS/RIDL) (MSBDS/Fallout) (SACK Panic) (SACK Slowness) (Spectre) NASL family OracleVM Local Security Checks NASL id ORACLEVM_OVMSA-2018-0248.NASL description The remote OracleVM system is missing necessary patches to address critical security updates : please see Oracle VM Security Advisory OVMSA-2018-0248 for details. last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 111992 published 2018-08-20 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/111992 title OracleVM 3.4 : xen (OVMSA-2018-0248) (Bunker Buster) (Foreshadow) (Meltdown) (POODLE) (Spectre) NASL family SuSE Local Security Checks NASL id OPENSUSE-2018-762.NASL description The openSUSE Leap 15 kernel was updated to receive various security and bugfixes. The following security bugs were fixed : - CVE-2018-13406: An integer overflow in the uvesafb_setcmap function could have result in local attackers being able to crash the kernel or potentially elevate privileges because kmalloc_array is not used (bnc#1100418) - CVE-2018-13053: The alarm_timer_nsleep function had an integer overflow via a large relative timeout because ktime_add_safe was not used (bnc#1099924) - CVE-2018-9385: Prevent overread of the last seen 2020-06-05 modified 2018-07-30 plugin id 111414 published 2018-07-30 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2020 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/111414 title openSUSE Security Update : the Linux Kernel (openSUSE-2018-762) (Spectre) NASL family Debian Local Security Checks NASL id DEBIAN_DLA-1422.NASL description The previous update to linux failed to build for the armhf (ARM EABI hard-float) architecture. This update corrects that. For all other architectures, there is no need to upgrade or reboot again. For reference, the relevant part of the original advisory text follows. Several vulnerabilities have been discovered in the Linux kernel that may lead to a privilege escalation, denial of service or information leaks. CVE-2017-5715 Multiple researchers have discovered a vulnerability in various processors supporting speculative execution, enabling an attacker controlling an unprivileged process to read memory from arbitrary addresses, including from the kernel and all other processes running on the system. This specific attack has been named Spectre variant 2 (branch target injection) and is mitigated for the x86 architecture (amd64 and i386) by using new microcoded features. This mitigation requires an update to the processor last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 111082 published 2018-07-16 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/111082 title Debian DLA-1422-2 : linux security update (Spectre) NASL family Debian Local Security Checks NASL id DEBIAN_DSA-4469.NASL description Two vulnerabilities were discovered in Libvirt, a virtualisation abstraction library, allowing an API client with read-only permissions to execute arbitrary commands via the virConnectGetDomainCapabilities API, or read or execute arbitrary files via the virDomainSaveImageGetXMLDesc API. Additionally the libvirt last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 126128 published 2019-06-24 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2019-2020 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/126128 title Debian DSA-4469-1 : libvirt - security update NASL family SuSE Local Security Checks NASL id SUSE_SU-2018-0113-1.NASL description The SUSE Linux Enterprise 12 SP3 kernel was updated to receive various security and bugfixes. This update is only provided as a fix update for IBM Z platform. - CVE-2017-5753 / last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 106127 published 2018-01-18 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/106127 title SUSE SLES12 Security Update : kernel (SUSE-SU-2018:0113-1) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family Red Hat Local Security Checks NASL id REDHAT-RHSA-2018-0009.NASL description An update for kernel is now available for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.3 Extended Update Support. Red Hat Product Security has rated this update as having a security impact of Important. A Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) base score, which gives a detailed severity rating, is available for each vulnerability from the CVE link(s) in the References section. The kernel packages contain the Linux kernel, the core of any Linux operating system. Security Fix(es) : An industry-wide issue was found in the way many modern microprocessor designs have implemented speculative execution of instructions (a commonly used performance optimization). There are three primary variants of the issue which differ in the way the speculative execution can be exploited. Note: This issue is present in hardware and cannot be fully fixed via software update. The updated kernel packages provide software mitigation for this hardware issue at a cost of potential performance penalty. Please refer to References section for further information about this issue and the performance impact. In this update mitigations for x86-64 architecture are provided. Variant CVE-2017-5753 triggers the speculative execution by performing a bounds-check bypass. It relies on the presence of a precisely-defined instruction sequence in the privileged code as well as the fact that memory accesses may cause allocation into the microprocessor last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 105525 published 2018-01-04 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/105525 title RHEL 7 : kernel (RHSA-2018:0009) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family Huawei Local Security Checks NASL id EULEROS_SA-2019-2599.NASL description According to the versions of the kernel packages installed, the EulerOS installation on the remote host is affected by the following vulnerabilities : - The kernel package contains the Linux kernel (vmlinuz), the core of any Linux operating system. The kernel handles the basic functions of the operating system: memory allocation, process allocation, device input and output, etc.Security Fix(es):** DISPUTED ** Multiple integer overflows in the lzo1x_decompress_safe function in lib/lzo/lzo1x_decompress_safe.c in the LZO decompressor in the Linux kernel before 3.15.2 allow context-dependent attackers to cause a denial of service (memory corruption) via a crafted Literal Run. NOTE: the author of the LZO algorithms says last seen 2020-05-08 modified 2019-12-18 plugin id 132134 published 2019-12-18 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2019-2020 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/132134 title EulerOS 2.0 SP3 : kernel (EulerOS-SA-2019-2599) NASL family Windows : Microsoft Bulletins NASL id SMB_NT_MS18_JAN_4056893.NASL description The remote Windows host is missing security update 4056893 or 4075199. It is, therefore, affected by multiple vulnerabilities : - An vulnerability exists within microprocessors utilizing speculative execution and indirect branch prediction, which may allow an attacker with local user access to disclose information via a side-channel analysis. (CVE-2017-5715, CVE-2017-5753, CVE-2017-5754) - An elevation of privilege vulnerability exists when the Windows kernel fails to properly handle objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could run arbitrary code in kernel mode. An attacker could then install programs; view, change, or delete data; or create new accounts with full user rights. (CVE-2018-0744) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists in the way that the scripting engine handles objects in memory in Microsoft Edge. The vulnerability could corrupt memory in such a way that an attacker could execute arbitrary code in the context of the current user. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could gain the same user rights as the current user. (CVE-2018-0758, CVE-2018-0769, CVE-2018-0770, CVE-2018-0776, CVE-2018-0777) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists in the Windows kernel that could allow an attacker to retrieve information that could lead to a Kernel Address Space Layout Randomization (ASLR) bypass. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could retrieve the memory address of a kernel object. (CVE-2018-0746, CVE-2018-0747) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists when the scripting engine does not properly handle objects in memory in Microsoft Edge. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could obtain information to further compromise the users system. (CVE-2018-0780) - An elevation of privilege vulnerability exists when Microsoft Edge does not properly enforce cross-domain policies, which could allow an attacker to access information from one domain and inject it into another domain. (CVE-2018-0803) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists in Windows Adobe Type Manager Font Driver (ATMFD.dll) when it fails to properly handle objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could potentially read data that was not intended to be disclosed. Note that this vulnerability would not allow an attacker to execute code or to elevate their user rights directly, but it could be used to obtain information that could be used to try to further compromise the affected system. (CVE-2018-0754) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists in the way the scripting engine handles objects in memory in Microsoft browsers. The vulnerability could corrupt memory in such a way that an attacker could execute arbitrary code in the context of the current user. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could gain the same user rights as the current user. (CVE-2018-0762, CVE-2018-0772) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists when Microsoft Edge PDF Reader improperly handles objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could obtain information to further compromise the users system. (CVE-2018-0766) - An elevation of privilege vulnerability exists in the way that the Windows Kernel API enforces permissions. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could impersonate processes, interject cross-process communication, or interrupt system functionality. (CVE-2018-0748, CVE-2018-0751, CVE-2018-0752) - An elevation of privilege vulnerability exists in the Microsoft Server Message Block (SMB) Server when an attacker with valid credentials attempts to open a specially crafted file over the SMB protocol on the same machine. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could bypass certain security checks in the operating system. (CVE-2018-0749) - A denial of service vulnerability exists in the way that Windows handles objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could cause a target system to stop responding. Note that the denial of service condition would not allow an attacker to execute code or to elevate user privileges. However, the denial of service condition could prevent authorized users from using system resources. The security update addresses the vulnerability by correcting how Windows handles objects in memory. (CVE-2018-0753) last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 105551 published 2018-01-04 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018 Tenable Network Security, Inc. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/105551 title KB4056893: Windows 10 LTSB January 2018 Security Update (Meltdown)(Spectre) NASL family AIX Local Security Checks NASL id AIX_IJ03033.NASL description Systems with microprocessors utilizing speculative execution and indirect branch prediction may allow unauthorized disclosure of information to an attacker with local user access via a side-channel analysis. last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 106313 published 2018-01-25 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/106313 title AIX 7.1 TL 5 : spectre_meltdown (IJ03033) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family Red Hat Local Security Checks NASL id REDHAT-RHSA-2018-1129.NASL description An update for kernel is now available for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.3 Extended Update Support. Red Hat Product Security has rated this update as having a security impact of Important. A Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) base score, which gives a detailed severity rating, is available for each vulnerability from the CVE link(s) in the References section. The kernel packages contain the Linux kernel, the core of any Linux operating system. Security Fix(es) : * An industry-wide issue was found in the way many modern microprocessor designs have implemented speculative execution of instructions (a commonly used performance optimization). There are three primary variants of the issue which differ in the way the speculative execution can be exploited. Variant CVE-2017-5754 relies on the fact that, on impacted microprocessors, during speculative execution of instruction permission faults, exception generation triggered by a faulting access is suppressed until the retirement of the whole instruction block. In a combination with the fact that memory accesses may populate the cache even when the block is being dropped and never committed (executed), an unprivileged local attacker could use this flaw to read privileged (kernel space) memory by conducting targeted cache side-channel attacks. (CVE-2017-5754, Important, KVM for Power) Red Hat would like to thank Google Project Zero for reporting this issue. Bug Fix(es) : These updated kernel packages include also numerous bug fixes. Space precludes documenting all of these bug fixes in this advisory. See the bug fix descriptions in the related Knowledge Article: https://access.redhat.com/articles/3413511 last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 109115 published 2018-04-18 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/109115 title RHEL 7 : kernel (RHSA-2018:1129) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family Oracle Linux Local Security Checks NASL id ORACLELINUX_ELSA-2018-0007.NASL description From Red Hat Security Advisory 2018:0007 : An update for kernel is now available for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7. Red Hat Product Security has rated this update as having a security impact of Important. A Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) base score, which gives a detailed severity rating, is available for each vulnerability from the CVE link(s) in the References section. The kernel packages contain the Linux kernel, the core of any Linux operating system. Security Fix(es) : An industry-wide issue was found in the way many modern microprocessor designs have implemented speculative execution of instructions (a commonly used performance optimization). There are three primary variants of the issue which differ in the way the speculative execution can be exploited. Note: This issue is present in hardware and cannot be fully fixed via software update. The updated kernel packages provide software mitigation for this hardware issue at a cost of potential performance penalty. Please refer to References section for further information about this issue and the performance impact. In this update mitigations for x86-64 architecture are provided. Variant CVE-2017-5753 triggers the speculative execution by performing a bounds-check bypass. It relies on the presence of a precisely-defined instruction sequence in the privileged code as well as the fact that memory accesses may cause allocation into the microprocessor last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 105598 published 2018-01-05 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/105598 title Oracle Linux 7 : kernel (ELSA-2018-0007) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family CentOS Local Security Checks NASL id CENTOS_RHSA-2018-0007.NASL description An update for kernel is now available for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7. Red Hat Product Security has rated this update as having a security impact of Important. A Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) base score, which gives a detailed severity rating, is available for each vulnerability from the CVE link(s) in the References section. The kernel packages contain the Linux kernel, the core of any Linux operating system. Security Fix(es) : An industry-wide issue was found in the way many modern microprocessor designs have implemented speculative execution of instructions (a commonly used performance optimization). There are three primary variants of the issue which differ in the way the speculative execution can be exploited. Note: This issue is present in hardware and cannot be fully fixed via software update. The updated kernel packages provide software mitigation for this hardware issue at a cost of potential performance penalty. Please refer to References section for further information about this issue and the performance impact. In this update mitigations for x86-64 architecture are provided. Variant CVE-2017-5753 triggers the speculative execution by performing a bounds-check bypass. It relies on the presence of a precisely-defined instruction sequence in the privileged code as well as the fact that memory accesses may cause allocation into the microprocessor last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 105588 published 2018-01-05 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/105588 title CentOS 7 : kernel (CESA-2018:0007) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family Windows : Microsoft Bulletins NASL id SMB_NT_MS18_MAR_4088876.NASL description The remote Windows host is missing security update 4088879 or cumulative update 4088876. It is, therefore, affected by multiple vulnerabilities : - An vulnerability exists within microprocessors utilizing speculative execution and indirect branch prediction, which may allow an attacker with local user access to disclose information via a side-channel analysis. (CVE-2017-5715, CVE-2017-5753, CVE-2017-5754) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists when Windows Remote Assistance incorrectly processes XML External Entities (XXE). An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could obtain information to further compromise the users system. (CVE-2018-0878) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists when Internet Explorer improperly handles objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could obtain information to further compromise the users system. (CVE-2018-0929) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists when Windows Shell does not properly validate file copy destinations. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could run arbitrary code in the context of the current user. If the current user is logged on with administrative user rights, an attacker could take control of the affected system. An attacker could then install programs; view, change, or delete data; or create new accounts with full user rights. Users whose accounts are configured to have fewer user rights on the system could be less impacted than users who operate with administrative user rights. (CVE-2018-0883) - An elevation of privilege vulnerability exists in Windows when the Microsoft Video Control mishandles objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could run arbitrary code in system mode. An attacker could then install programs; view, change, or delete data; or create new accounts with full user rights. (CVE-2018-0881) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists when affected Microsoft browsers improperly handle objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could obtain information to further compromise the users system. (CVE-2018-0927, CVE-2018-0932) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists in the way that the scripting engine handles objects in memory in Internet Explorer. The vulnerability could corrupt memory in such a way that an attacker could execute arbitrary code in the context of the current user. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could gain the same user rights as the current user. (CVE-2018-0889, CVE-2018-0935) - An elevation of privilege vulnerability exists when Internet Explorer fails a check, allowing sandbox escape. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could use the sandbox escape to elevate privileges on an affected system. This vulnerability by itself does not allow arbitrary code execution; however, it could allow arbitrary code to be run if the attacker uses it in combination with another vulnerability (such as a remote code execution vulnerability or another elevation of privilege vulnerability) that is capable of leveraging the elevated privileges when code execution is attempted. The update addresses the vulnerability by correcting how Internet Explorer handles zone and integrity settings. (CVE-2018-0942) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists when the Windows kernel improperly initializes objects in memory. (CVE-2018-0811, CVE-2018-0813, CVE-2018-0814) - A denial of service vulnerability exists when Microsoft Hyper-V Network Switch on a host server fails to properly validate input from a privileged user on a guest operating system. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could cause the host server to crash. (CVE-2018-0885) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists in the Credential Security Support Provider protocol (CredSSP). An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could relay user credentials and use them to execute code on the target system. CredSSP is an authentication provider which processes authentication requests for other applications; any application which depends on CredSSP for authentication may be vulnerable to this type of attack. As an example of how an attacker would exploit this vulnerability against Remote Desktop Protocol, the attacker would need to run a specially crafted application and perform a man-in-the-middle attack against a Remote Desktop Protocol session. An attacker could then install programs; view, change, or delete data; or create new accounts with full user rights. The security update addresses the vulnerability by correcting how Credential Security Support Provider protocol (CredSSP) validates requests during the authentication process. To be fully protected against this vulnerability users must enable Group Policy settings on their systems and update their Remote Desktop clients. The Group Policy settings are disabled by default to prevent connectivity problems and users must follow the instructions documented HERE to be fully protected. (CVE-2018-0886) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists in the Windows kernel that could allow an attacker to retrieve information that could lead to a Kernel Address Space Layout Randomization (ASLR) bypass. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could retrieve the memory address of a kernel object. (CVE-2018-0894, CVE-2018-0895, CVE-2018-0896, CVE-2018-0897, CVE-2018-0898, CVE-2018-0899, CVE-2018-0900, CVE-2018-0901, CVE-2018-0904) - An elevation of privilege vulnerability exists in the Windows Installer when the Windows Installer fails to properly sanitize input leading to an insecure library loading behavior. A locally authenticated attacker could run arbitrary code with elevated system privileges. An attacker could then install programs; view, change, or delete data; or create new accounts with full user rights. The security update addresses the vulnerability by correcting the input sanitization error to preclude unintended elevation. (CVE-2018-0868) - An elevation of privilege vulnerability exists in the way that the Windows Graphics Device Interface (GDI) handles objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could run arbitrary code in kernel mode. An attacker could then install programs; view, change, or delete data; or create new accounts with full user rights. (CVE-2018-0816, CVE-2018-0817) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists when Windows Hyper-V on a host operating system fails to properly validate input from an authenticated user on a guest operating system. (CVE-2018-0888) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists when the scripting engine does not properly handle objects in memory in Microsoft browsers. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could obtain information to further compromise the users system. (CVE-2018-0891) last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 108291 published 2018-03-13 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/108291 title KB4088879: Windows 8.1 and Windows Server 2012 R2 March 2018 Security Update (Meltdown)(Spectre) NASL family SuSE Local Security Checks NASL id SUSE_SU-2018-0601-1.NASL description This update for xen fixes several issues. These security issues were fixed : - CVE-2017-5753, CVE-2017-5715, CVE-2017-5754: Prevent information leaks via side effects of speculative execution, aka last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 107140 published 2018-03-06 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/107140 title SUSE SLES12 Security Update : xen (SUSE-SU-2018:0601-1) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family SuSE Local Security Checks NASL id SUSE_SU-2018-0438-1.NASL description This update for xen fixes several issues. These security issues were fixed : - CVE-2017-5753, CVE-2017-5715, CVE-2017-5754: Prevent information leaks via side effects of speculative execution, aka last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 106834 published 2018-02-15 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/106834 title SUSE SLED12 / SLES12 Security Update : xen (SUSE-SU-2018:0438-1) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family OracleVM Local Security Checks NASL id ORACLEVM_OVMSA-2018-0020.NASL description The remote OracleVM system is missing necessary patches to address critical security updates : - BUILDINFO: OVMF commit=173bf5c847e3ca8b42c11796ce048d8e2e916ff8 - BUILDINFO: xen commit=9ccc143584e12027a8db854d19ce8a120d22cfac - BUILDINFO: QEMU upstream commit=8bff6989bd0bafcc0ddf859c23ce6a2ff21a80ff - BUILDINFO: QEMU traditional commit=346fdd7edd73f8287d0d0a2bab9c67b71bc6b8ba - BUILDINFO: IPXE commit=9a93db3f0947484e30e753bbd61a10b17336e20e - BUILDINFO: SeaBIOS commit=7d9cbe613694924921ed1a6f8947d711c5832eee - gnttab: don last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 107129 published 2018-03-05 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/107129 title OracleVM 3.4 : xen (OVMSA-2018-0020) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family Fedora Local Security Checks NASL id FEDORA_2018-0590E4AF13.NASL description This update includes improvements to mitigate the effects of Spectre ([CVE-2017-5753](https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-20 17-5753) and [CVE-2017-5715](https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-201 7-5715)) : - Disable SharedArrayBuffers from Web API. - Reduce the precision of “high” resolution time to 1ms. Additional fixes : - Fix API documentation generation with newer gtk-doc. Note that Tenable Network Security has extracted the preceding description block directly from the Fedora update system website. Tenable has attempted to automatically clean and format it as much as possible without introducing additional issues. last seen 2020-06-05 modified 2018-01-15 plugin id 106022 published 2018-01-15 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2020 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/106022 title Fedora 27 : webkitgtk4 (2018-0590e4af13) (Spectre) NASL family SuSE Local Security Checks NASL id SUSE_SU-2019-0222-1.NASL description The SUSE Linux Enterprise 12 SP4 kernel for Azure was updated to receive various security and bugfixes. The following security bugs were fixed : CVE-2018-19407: The vcpu_scan_ioapic function in arch/x86/kvm/x86.c allowed local users to cause a denial of service (NULL pointer dereference and BUG) via crafted system calls that reach a situation where ioapic was uninitialized (bnc#1116841). CVE-2018-16884: NFS41+ shares mounted in different network namespaces at the same time can make bc_svc_process() use wrong back-channel IDs and cause a use-after-free vulnerability. Thus a malicious container user can cause a host kernel memory corruption and a system panic. Due to the nature of the flaw, privilege escalation cannot be fully ruled out (bnc#1119946). CVE-2018-20169: The USB subsystem mishandled size checks during the reading of an extra descriptor, related to __usb_get_extra_descriptor in drivers/usb/core/usb.c (bnc#1119714). CVE-2018-9568: In sk_clone_lock of sock.c, there is a possible memory corruption due to type confusion. This could lead to local escalation of privilege with no additional execution privileges needed. User interaction is not needed for exploitation (bnc#1118319). CVE-2018-16862: A security flaw was found in the way that the cleancache subsystem clears an inode after the final file truncation (removal). The new file created with the same inode may contain leftover pages from cleancache and the old file data instead of the new one (bnc#1117186). CVE-2018-14625: A flaw was found where an attacker may be able to have an uncontrolled read to kernel-memory from within a vm guest. A race condition between connect() and close() function may allow an attacker using the AF_VSOCK protocol to gather a 4 byte information leak or possibly intercept or corrupt AF_VSOCK messages destined to other clients (bnc#1106615). CVE-2018-19985: The function hso_probe read if_num from the USB device (as an u8) and used it without a length check to index an array, resulting in an OOB memory read in hso_probe or hso_get_config_data that could be used by local attackers (bnc#1120743). CVE-2018-12232: In net/socket.c there is a race condition between fchownat and close in cases where they target the same socket file descriptor, related to the sock_close and sockfs_setattr functions. fchownat did not increment the file descriptor reference count, which allowed close to set the socket to NULL during fchownat last seen 2020-03-18 modified 2019-02-04 plugin id 121569 published 2019-02-04 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2019-2020 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/121569 title SUSE SLES12 Security Update : kernel (SUSE-SU-2019:0222-1) (Spectre) NASL family Oracle Linux Local Security Checks NASL id ORACLELINUX_ELSA-2018-4017.NASL description Description of changes: [4.1.12-112.14.13.el7uek] - Revert last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 106225 published 2018-01-22 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/106225 title Oracle Linux 6 / 7 : Unbreakable Enterprise kernel (ELSA-2018-4017) (Spectre) NASL family Slackware Local Security Checks NASL id SLACKWARE_SSA_2018-057-01.NASL description New kernel packages are available for Slackware 14.2 to mitigate the speculative side channel attack known as Spectre variant 1. last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 107006 published 2018-02-27 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/107006 title Slackware 14.2 : Slackware 14.2 kernel (SSA:2018-057-01) (Spectre) NASL family SuSE Local Security Checks NASL id SUSE_SU-2018-2092-1.NASL description The SUSE Linux Enterprise 15 kernel was updated to receive various security and bugfixes. The following new feature was added : - NVDIMM memory error notification (ACPI 6.2) The following security bugs were fixed : - CVE-2018-13406: An integer overflow in the uvesafb_setcmap function could have result in local attackers being able to crash the kernel or potentially elevate privileges because kmalloc_array is not used (bnc#1100418) - CVE-2018-13053: The alarm_timer_nsleep function had an integer overflow via a large relative timeout because ktime_add_safe was not used (bnc#1099924) - CVE-2018-9385: Prevent overread of the last seen 2020-03-21 modified 2019-01-02 plugin id 120067 published 2019-01-02 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2019-2020 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/120067 title SUSE SLED15 / SLES15 Security Update : kernel (SUSE-SU-2018:2092-1) (Spectre) NASL family Scientific Linux Local Security Checks NASL id SL_20180125_KERNEL_ON_SL7_X.NASL description Security Fix(es) : An industry-wide issue was found in the way many modern microprocessor designs have implemented speculative execution of instructions (a commonly used performance optimization). There are three primary variants of the issue which differ in the way the speculative execution can be exploited. Note: This issue is present in hardware and cannot be fully fixed via software update. The updated kernel packages provide software mitigation for this hardware issue at a cost of potential performance penalty. * Variant CVE-2017-5715 triggers the speculative execution by utilizing branch target injection. It relies on the presence of a precisely-defined instruction sequence in the privileged code as well as the fact that memory accesses may cause allocation into the microprocessor last seen 2020-03-18 modified 2018-01-25 plugin id 106340 published 2018-01-25 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2020 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/106340 title Scientific Linux Security Update : kernel on SL7.x x86_64 (20180125) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family Red Hat Local Security Checks NASL id REDHAT-RHSA-2018-0046.NASL description An update for rhev-hypervisor7 is now available for RHEV 3.X Hypervisor and Agents for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 and RHEV 3.X Hypervisor and Agents for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 ELS. Red Hat Product Security has rated this update as having a security impact of Important. A Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) base score, which gives a detailed severity rating, is available for each vulnerability from the CVE link(s) in the References section. The rhev-hypervisor7 package provides a Red Hat Enterprise Virtualization Hypervisor ISO disk image. The Red Hat Enterprise Virtualization Hypervisor is a dedicated Kernel-based Virtual Machine (KVM) hypervisor. It includes everything necessary to run and manage virtual machines: A subset of the Red Hat Enterprise Linux operating environment and the Red Hat Enterprise Virtualization Agent. Security Fix(es) : An industry-wide issue was found in the way many modern microprocessor designs have implemented speculative execution of instructions (a commonly used performance optimization). There are three primary variants of the issue which differ in the way the speculative execution can be exploited. Note: This issue is present in hardware and cannot be fully fixed via software update. The updated kernel packages provide software mitigation for this hardware issue at a cost of potential performance penalty. Please refer to References section for further information about this issue and the performance impact. Variant CVE-2017-5753 triggers the speculative execution by performing a bounds-check bypass. It relies on the presence of a precisely-defined instruction sequence in the privileged code as well as the fact that memory accesses may cause allocation into the microprocessor last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 105677 published 2018-01-09 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/105677 title RHEL 6 / 7 : rhev-hypervisor7 (RHSA-2018:0046) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family SuSE Local Security Checks NASL id SUSE_SU-2018-0114-1.NASL description The SUSE Linux Enterprise 12 SP1 LTSS kernel was updated to receive various security and bugfixes. This update is only provided as a fix update for IBM Z platform. - CVE-2017-5753 / last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 106094 published 2018-01-17 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/106094 title SUSE SLES12 Security Update : kernel (SUSE-SU-2018:0114-1) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family Red Hat Local Security Checks NASL id REDHAT-RHSA-2018-0020.NASL description An update for kernel is now available for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6.2 Advanced Update Support. Red Hat Product Security has rated this update as having a security impact of Important. A Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) base score, which gives a detailed severity rating, is available for each vulnerability from the CVE link(s) in the References section. The kernel packages contain the Linux kernel, the core of any Linux operating system. Security Fix(es) : An industry-wide issue was found in the way many modern microprocessor designs have implemented speculative execution of instructions (a commonly used performance optimization). There are three primary variants of the issue which differ in the way the speculative execution can be exploited. Note: This issue is present in hardware and cannot be fully fixed via software update. The updated kernel packages provide software mitigation for this hardware issue at a cost of potential performance penalty. Please refer to References section for further information about this issue and the performance impact. In this update mitigations for x86-64 architecture are provided. Variant CVE-2017-5753 triggers the speculative execution by performing a bounds-check bypass. It relies on the presence of a precisely-defined instruction sequence in the privileged code as well as the fact that memory accesses may cause allocation into the microprocessor last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 105562 published 2018-01-04 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/105562 title RHEL 6 : kernel (RHSA-2018:0020) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family Oracle Linux Local Security Checks NASL id ORACLELINUX_ELSA-2018-0512.NASL description From Red Hat Security Advisory 2018:0512 : An update for kernel is now available for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6. Red Hat Product Security has rated this update as having a security impact of Important. A Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) base score, which gives a detailed severity rating, is available for each vulnerability from the CVE link(s) in the References section. The kernel packages contain the Linux kernel, the core of any Linux operating system. Security Fix(es) : * hw: cpu: speculative execution branch target injection (s390-only) (CVE-2017-5715, Important) * hw: cpu: speculative execution bounds-check bypass (s390 and powerpc) (CVE-2017-5753, Important) * hw: cpu: speculative execution permission faults handling (powerpc-only) (CVE-2017-5754) For more details about the security issue(s), including the impact, a CVSS score, acknowledgments, and other related information, refer to the CVE page(s) listed in the References section. Bug Fixes : * If a fibre channel (FC) switch was powered down and then powered on again, the SCSI device driver stopped permanently the SCSI device last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 108358 published 2018-03-15 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/108358 title Oracle Linux 6 : kernel (ELSA-2018-0512) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family Red Hat Local Security Checks NASL id REDHAT-RHSA-2018-0292.NASL description An update for kernel is now available for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5 Extended Lifecycle Support. Red Hat Product Security has rated this update as having a security impact of Important. A Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) base score, which gives a detailed severity rating, is available for each vulnerability from the CVE link(s) in the References section. The kernel packages contain the Linux kernel, the core of any Linux operating system. Security Fix(es): An industry-wide issue was found in the way many modern microprocessor designs have implemented speculative execution of instructions (a commonly used performance optimization). There are three primary variants of the issue which differ in the way the speculative execution can be exploited. Note: This issue is present in hardware and cannot be fully fixed via software update. The updated kernel packages provide software mitigation for this hardware issue at a cost of potential performance penalty. Please refer to References section for further information about this issue and the performance impact. In this update mitigations for IBM zSeries (S390) and x86-64 architectures are provided. Variant CVE-2017-5753 triggers the speculative execution by performing a bounds-check bypass. It relies on the presence of a precisely-defined instruction sequence in the privileged code as well as the fact that memory accesses may cause allocation into the microprocessor last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 107058 published 2018-02-28 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 Tenable Network Security, Inc. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/107058 title RHEL 5 : kernel (RHSA-2018:0292) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family OracleVM Local Security Checks NASL id ORACLEVM_OVMSA-2018-0021.NASL description The remote OracleVM system is missing necessary patches to address critical security updates : - BUILDINFO: xen commit=b2a6db11ced11291a472bc1bda20ce329eda4d66 - BUILDINFO: QEMU upstream commit=8bff6989bd0bafcc0ddf859c23ce6a2ff21a80ff - BUILDINFO: QEMU traditional commit=346fdd7edd73f8287d0d0a2bab9c67b71bc6b8ba - BUILDINFO: IPXE commit=9a93db3f0947484e30e753bbd61a10b17336e20e - BUILDINFO: SeaBIOS commit=7d9cbe613694924921ed1a6f8947d711c5832eee - gnttab: don last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 107130 published 2018-03-05 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/107130 title OracleVM 3.4 : xen (OVMSA-2018-0021) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family Misc. NASL id RANCHEROS_1_4_0.NASL description The remote host is running a version of RancherOS prior to 1.4.0, hence is exposted to a side-channel vulnerabilities: - Systems with microprocessors utilizing speculative execution and branch prediction may allow unauthorized disclosure of information to an attacker with local user access via a side-channel analysis.(CVE-2017-5753) - A statement in the System Programming Guide of the Intel 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developerâs Manual (SDM) was mishandled in the development of some or all operating-system kernels, resulting in unexpected behavior for #DB exceptions that are deferred by MOV SS or POP SS, as demonstrated by (for example) privilege escalation in Windows, macOS, some Xen configurations, or FreeBSD, or a Linux kernel crash. (CVE-2018-8897) last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 132252 published 2019-12-19 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/132252 title Security Updates for RancherOS Information Disclosure NASL family SuSE Local Security Checks NASL id SUSE_SU-2018-0012-1.NASL description The SUSE Linux Enterprise 12 SP2 kernel was updated to receive various security and bugfixes. This update adds mitigations for various side channel attacks against modern CPUs that could disclose content of otherwise unreadable memory (bnc#1068032). - CVE-2017-5753 / last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 105576 published 2018-01-04 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/105576 title SUSE SLED12 / SLES12 Security Update : kernel (SUSE-SU-2018:0012-1) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family Windows : Microsoft Bulletins NASL id SMB_NT_MS18_MAR_4088875.NASL description The remote Windows host is missing security update 4088878 or cumulative update 4088875. It is, therefore, affected by multiple vulnerabilities : - An vulnerability exists within microprocessors utilizing speculative execution and indirect branch prediction, which may allow an attacker with local user access to disclose information via a side-channel analysis. Note: this patch applies to only 32-bit Windows 7 systems. (CVE-2017-5715, CVE-2017-5753, CVE-2017-5754) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists when Windows Remote Assistance incorrectly processes XML External Entities (XXE). An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could obtain information to further compromise the users system. (CVE-2018-0878) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists when Internet Explorer improperly handles objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could obtain information to further compromise the users system. (CVE-2018-0929) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists when Windows Shell does not properly validate file copy destinations. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could run arbitrary code in the context of the current user. If the current user is logged on with administrative user rights, an attacker could take control of the affected system. An attacker could then install programs; view, change, or delete data; or create new accounts with full user rights. Users whose accounts are configured to have fewer user rights on the system could be less impacted than users who operate with administrative user rights. (CVE-2018-0883) - An elevation of privilege vulnerability exists in Windows when the Microsoft Video Control mishandles objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could run arbitrary code in system mode. An attacker could then install programs; view, change, or delete data; or create new accounts with full user rights. (CVE-2018-0881) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists when affected Microsoft browsers improperly handle objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could obtain information to further compromise the users system. (CVE-2018-0927, CVE-2018-0932) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists in the way that the scripting engine handles objects in memory in Internet Explorer. The vulnerability could corrupt memory in such a way that an attacker could execute arbitrary code in the context of the current user. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could gain the same user rights as the current user. (CVE-2018-0889, CVE-2018-0935) - An elevation of privilege vulnerability exists when Internet Explorer fails a check, allowing sandbox escape. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could use the sandbox escape to elevate privileges on an affected system. This vulnerability by itself does not allow arbitrary code execution; however, it could allow arbitrary code to be run if the attacker uses it in combination with another vulnerability (such as a remote code execution vulnerability or another elevation of privilege vulnerability) that is capable of leveraging the elevated privileges when code execution is attempted. The update addresses the vulnerability by correcting how Internet Explorer handles zone and integrity settings. (CVE-2018-0942) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists when the Windows kernel improperly initializes objects in memory. (CVE-2018-0811, CVE-2018-0813, CVE-2018-0814) - A denial of service vulnerability exists when Microsoft Hyper-V Network Switch on a host server fails to properly validate input from a privileged user on a guest operating system. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could cause the host server to crash. (CVE-2018-0885) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists in the Windows kernel that could allow an attacker to retrieve information that could lead to a Kernel Address Space Layout Randomization (ASLR) bypass. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could retrieve the memory address of a kernel object. (CVE-2018-0894, CVE-2018-0895, CVE-2018-0896, CVE-2018-0897, CVE-2018-0898, CVE-2018-0899, CVE-2018-0900, CVE-2018-0901, CVE-2018-0904) - An elevation of privilege vulnerability exists in the Windows Installer when the Windows Installer fails to properly sanitize input leading to an insecure library loading behavior. A locally authenticated attacker could run arbitrary code with elevated system privileges. An attacker could then install programs; view, change, or delete data; or create new accounts with full user rights. The security update addresses the vulnerability by correcting the input sanitization error to preclude unintended elevation. (CVE-2018-0868) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists in the Credential Security Support Provider protocol (CredSSP). An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could relay user credentials and use them to execute code on the target system. CredSSP is an authentication provider which processes authentication requests for other applications; any application which depends on CredSSP for authentication may be vulnerable to this type of attack. As an example of how an attacker would exploit this vulnerability against Remote Desktop Protocol, the attacker would need to run a specially crafted application and perform a man-in-the-middle attack against a Remote Desktop Protocol session. An attacker could then install programs; view, change, or delete data; or create new accounts with full user rights. The security update addresses the vulnerability by correcting how Credential Security Support Provider protocol (CredSSP) validates requests during the authentication process. To be fully protected against this vulnerability users must enable Group Policy settings on their systems and update their Remote Desktop clients. The Group Policy settings are disabled by default to prevent connectivity problems and users must follow the instructions documented HERE to be fully protected. (CVE-2018-0886) - An elevation of privilege vulnerability exists in the way that the Windows Graphics Device Interface (GDI) handles objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could run arbitrary code in kernel mode. An attacker could then install programs; view, change, or delete data; or create new accounts with full user rights. (CVE-2018-0815, CVE-2018-0816, CVE-2018-0817) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists when Windows Hyper-V on a host operating system fails to properly validate input from an authenticated user on a guest operating system. (CVE-2018-0888) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists when the scripting engine does not properly handle objects in memory in Microsoft browsers. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could obtain information to further compromise the users system. (CVE-2018-0891) last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 108290 published 2018-03-13 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/108290 title KB4088878: Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2 March 2018 Security Update (Meltdown)(Spectre) NASL family SuSE Local Security Checks NASL id SUSE_SU-2018-1368-1.NASL description The SUSE Linux Enterprise 11 SP4 kernel was updated to receive various security and bugfixes. The following security bugs were fixed : - CVE-2018-3639: Information leaks using last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 110035 published 2018-05-23 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/110035 title SUSE SLES11 Security Update : kernel (SUSE-SU-2018:1368-1) (Spectre) NASL family Ubuntu Local Security Checks NASL id UBUNTU_USN-3597-2.NASL description USN-3597-1 fixed vulnerabilities in the Linux kernel for Ubuntu 17.10. This update provides the corresponding updates for the Linux Hardware Enablement (HWE) kernel from Ubuntu 17.10 for Ubuntu 16.04 LTS. USNS 3541-2 and 3523-2 provided mitigations for Spectre and Meltdown (CVE-2017-5715, CVE-2017-5753, CVE-2017-5754) for the i386, amd64, and ppc64el architectures for Ubuntu 16.04 LTS. This update provides the corresponding mitigations for the arm64 architecture. Original advisory details : Jann Horn discovered that microprocessors utilizing speculative execution and indirect branch prediction may allow unauthorized memory reads via sidechannel attacks. This flaw is known as Meltdown. A local attacker could use this to expose sensitive information, including kernel memory. (CVE-2017-5754) Jann Horn discovered that microprocessors utilizing speculative execution and branch prediction may allow unauthorized memory reads via sidechannel attacks. This flaw is known as Spectre. A local attacker could use this to expose sensitive information, including kernel memory. (CVE-2017-5715, CVE-2017-5753). Note that Tenable Network Security has extracted the preceding description block directly from the Ubuntu security advisory. Tenable has attempted to automatically clean and format it as much as possible without introducing additional issues. last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 108372 published 2018-03-15 reporter Ubuntu Security Notice (C) 2018-2019 Canonical, Inc. / NASL script (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/108372 title Ubuntu 16.04 LTS : linux-hwe vulnerabilities (USN-3597-2) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family SuSE Local Security Checks NASL id SUSE_SU-2018-0131-1.NASL description The SUSE Linux Enterprise 11 SP4 kernel was updated to receive various security and bugfixes. This update is only provided as a fix update for IBM Z platform. - CVE-2017-5753 / last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 106185 published 2018-01-19 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/106185 title SUSE SLES11 Security Update : kernel (SUSE-SU-2018:0131-1) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family Virtuozzo Local Security Checks NASL id VIRTUOZZO_VZA-2018-003.NASL description According to the versions of the crit / criu / criu-devel / ksm-vz / libcompel / etc packages installed, the Virtuozzo installation on the remote host is affected by the following vulnerabilities : - CVE-2017-5715 triggers the speculative execution by utilizing branch target injection. It relies on the presence of a precisely-defined instruction sequence in the privileged code as well as the fact that memory accesses may cause allocation into the microprocessor last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 105657 published 2018-01-09 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/105657 title Virtuozzo 7 : crit / criu / criu-devel / ksm-vz / libcompel / etc (VZA-2018-003) NASL family PhotonOS Local Security Checks NASL id PHOTONOS_PHSA-2018-1_0-0098.NASL description An update of [linux] packages for PhotonOS has been released. This kernel update mitigates vulnerabilities [CVE-2017-5753](https://web.nv d.nist.gov/view/vuln/detail?vulnId=CVE-2017-5753) and [CVE-2017-5715]( https://web.nvd.nist.gov/view/vuln/detail?vulnId=CVE-2017-5715) which are referred to as the variants of Spectre vulnerability. last seen 2019-02-21 modified 2019-02-07 plugin id 111911 published 2018-08-17 reporter Tenable source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/index.php?view=single&id=111911 title Photon OS 1.0: Linux PHSA-2018-1.0-0098 (deprecated) NASL family SuSE Local Security Checks NASL id SUSE_SU-2018-0909-1.NASL description This update for xen fixes the following issues: Update to Xen 4.7.5 bug fix only release (bsc#1027519) Security issues fixed : - CVE-2018-7540: Fixed DoS via non-preemptable L3/L4 pagetable freeing (XSA-252) (bsc#1080635) - CVE-2018-7541: A grant table v2 -> v1 transition may crash Xen (XSA-255) (bsc#1080662) - CVE-2017-5753,CVE-2017-5715,CVE-2017-5754 Fixed information leaks via side effects of speculative execution (XSA-254). Includes Spectre v2 mitigation. (bsc#1074562) - Preserve xen-syms from xen-dbg.gz to allow processing vmcores with crash(1) (bsc#1087251) - Xen HVM: Fixed unchecked MSR access error (bsc#1072834) - Add script, udev rule and systemd service to watch for vcpu online/offline events in a HVM domU They are triggered via xl vcpu-set domU N (fate#324965) - Make sure tools and tools-domU require libs from the very same build Note that Tenable Network Security has extracted the preceding description block directly from the SUSE security advisory. Tenable has attempted to automatically clean and format it as much as possible without introducing additional issues. last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 109001 published 2018-04-11 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/109001 title SUSE SLED12 / SLES12 Security Update : xen (SUSE-SU-2018:0909-1) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family SuSE Local Security Checks NASL id SUSE_SU-2018-0191-1.NASL description This update for wireshark to version 2.2.12 fixes the following issues : - CVE-2018-5334: IxVeriWave file could crash (bsc#1075737) - CVE-2018-5335: WCP dissector could crash (bsc#1075738) - CVE-2018-5336: Multiple dissector crashes (bsc#1075739) - CVE-2017-17935: Incorrect handling of last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 106342 published 2018-01-25 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/106342 title SUSE SLED12 / SLES12 Security Update : wireshark (SUSE-SU-2018:0191-1) (Spectre) NASL family SuSE Local Security Checks NASL id OPENSUSE-2018-3.NASL description The openSUSE Leap 42.2 kernel was updated to 4.4.104 to receive various security and bugfixes. This update adds mitigations for various side channel attacks against modern CPUs that could disclose content of otherwise unreadable memory (bnc#1068032). - CVE-2017-5753 / last seen 2020-06-05 modified 2018-01-08 plugin id 105636 published 2018-01-08 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2020 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/105636 title openSUSE Security Update : the Linux Kernel (openSUSE-2018-3) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family Ubuntu Local Security Checks NASL id UBUNTU_USN-3549-1.NASL description Jann Horn discovered that microprocessors utilizing speculative execution and branch prediction may allow unauthorized memory reads via sidechannel attacks. This flaw is known as Spectre. A local attacker could use this to expose sensitive information, including kernel memory. (CVE-2017-5715, CVE-2017-5753). Note that Tenable Network Security has extracted the preceding description block directly from the Ubuntu security advisory. Tenable has attempted to automatically clean and format it as much as possible without introducing additional issues. last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 106483 published 2018-01-30 reporter Ubuntu Security Notice (C) 2018-2019 Canonical, Inc. / NASL script (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/106483 title Ubuntu 16.04 LTS : linux-kvm vulnerabilities (USN-3549-1) (Spectre) NASL family AIX Local Security Checks NASL id AIX_IJ03036.NASL description Systems with microprocessors utilizing speculative execution and indirect branch prediction may allow unauthorized disclosure of information to an attacker with local user access via a side-channel analysis. last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 106316 published 2018-01-25 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/106316 title AIX 7.2 TL 2 : spectre_meltdown (IJ03036) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family SuSE Local Security Checks NASL id SUSE_SU-2018-0031-1.NASL description The SUSE Linux Enterprise 12 SP1 LTSS kernel was updated to receive various security and bugfixes. This update adds mitigations for various side channel attacks against modern CPUs that could disclose content of otherwise unreadable memory (bnc#1068032). - CVE-2017-5753 / last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 105647 published 2018-01-08 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/105647 title SUSE SLES12 Security Update : kernel (SUSE-SU-2018:0031-1) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family Red Hat Local Security Checks NASL id REDHAT-RHSA-2018-0018.NASL description An update for kernel is now available for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6.4 Advanced Update Support. Red Hat Product Security has rated this update as having a security impact of Important. A Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) base score, which gives a detailed severity rating, is available for each vulnerability from the CVE link(s) in the References section. The kernel packages contain the Linux kernel, the core of any Linux operating system. Security Fix(es) : An industry-wide issue was found in the way many modern microprocessor designs have implemented speculative execution of instructions (a commonly used performance optimization). There are three primary variants of the issue which differ in the way the speculative execution can be exploited. Note: This issue is present in hardware and cannot be fully fixed via software update. The updated kernel packages provide software mitigation for this hardware issue at a cost of potential performance penalty. Please refer to References section for further information about this issue and the performance impact. In this update mitigations for x86-64 architecture are provided. Variant CVE-2017-5753 triggers the speculative execution by performing a bounds-check bypass. It relies on the presence of a precisely-defined instruction sequence in the privileged code as well as the fact that memory accesses may cause allocation into the microprocessor last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 105561 published 2018-01-04 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/105561 title RHEL 6 : kernel (RHSA-2018:0018) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family Misc. NASL id XEN_SERVER_XSA-254.NASL description According to its self-reported version number, the Xen hypervisor installed on the remote host is affected by multiple vulnerabilities. Note that Nessus has checked the changeset versions based on the xen.git change log. Nessus did not check guest hardware configurations or if patches were applied manually to the source code before a recompile and reinstall. last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 106902 published 2018-02-20 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/106902 title Xen Multiple Vulnerabilities (Spectre) (Meltdown) (XSA-254) NASL family Windows : Microsoft Bulletins NASL id SMB_NT_MS18_FEB_4074596.NASL description The remote Windows host is missing security update 4074596. It is, therefore, affected by multiple vulnerabilities : - An vulnerability exists within microprocessors utilizing speculative execution and indirect branch prediction, which may allow an attacker with local user access to disclose information via a side-channel analysis. (CVE-2017-5715, CVE-2017-5753, CVE-2017-5754) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists in the way that the scripting engine handles objects in memory in Internet Explorer. The vulnerability could corrupt memory in such a way that an attacker could execute arbitrary code in the context of the current user. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could gain the same user rights as the current user. (CVE-2018-0866) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists when the Windows kernel improperly handles objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could obtain information to further compromise the users system. (CVE-2018-0757, CVE-2018-0829, CVE-2018-0830) - An elevation of privilege vulnerability exists in the way that the Windows Kernel handles objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could execute code with elevated permissions. (CVE-2018-0742, CVE-2018-0756, CVE-2018-0820) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists when VBScript improperly discloses the contents of its memory, which could provide an attacker with information to further compromise the users computer or data. (CVE-2018-0847) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists in StructuredQuery when the software fails to properly handle objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could run arbitrary code in the context of the current user. If the current user is logged on with administrative user rights, an attacker could take control of the affected system. An attacker could then install programs; view, change, or delete data; or create new accounts with full user rights. (CVE-2018-0825) - An elevation of privilege vulnerability exists when NTFS improperly handles objects. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could run processes in an elevated context. (CVE-2018-0822) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists in the way that the scripting engine handles objects in memory in Microsoft Edge. The vulnerability could corrupt memory in such a way that an attacker could execute arbitrary code in the context of the current user. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could gain the same user rights as the current user. (CVE-2018-0834, CVE-2018-0835, CVE-2018-0837, CVE-2018-0838, CVE-2018-0857, CVE-2018-0859, CVE-2018-0860) - An elevation of privilege vulnerability exists when AppContainer improperly implements constrained impersonation. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could run processes in an elevated context. (CVE-2018-0821) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists when Windows improperly handles objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited these vulnerabilities could take control of an affected system. (CVE-2018-0842) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists in the way the scripting engine handles objects in memory in Microsoft browsers. The vulnerability could corrupt memory in such a way that an attacker could execute arbitrary code in the context of the current user. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could gain the same user rights as the current user. (CVE-2018-0840) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists in the Windows kernel that could allow an attacker to retrieve information that could lead to a Kernel Address Space Layout Randomization (ASLR) bypass. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could retrieve the memory address of a kernel object. (CVE-2018-0832) - An elevation of privilege vulnerability exists when the Windows Common Log File System (CLFS) driver improperly handles objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could run processes in an elevated context. (CVE-2018-0844, CVE-2018-0846) last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 106801 published 2018-02-13 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/106801 title KB4074596: Windows 10 February 2018 Security Update (Meltdown)(Spectre) NASL family Amazon Linux Local Security Checks NASL id AL2_ALAS-2018-956.NASL description Stack-based out-of-bounds read via vmcall instruction Linux kernel compiled with the KVM virtualization (CONFIG_KVM) support is vulnerable to an out-of-bounds read access issue. It could occur when emulating vmcall instructions invoked by a guest. A guest user/process could use this flaw to disclose kernel memory bytes.(CVE-2017-17741) drivers/block/loop.c mishandles lo_release serialization allowing denial-of-service A flaw was found in the Linux kernel last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 109127 published 2018-04-18 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/109127 title Amazon Linux 2 : kernel (ALAS-2018-956) (Dirty COW) (Spectre) NASL family Misc. NASL id NVIDIA_UNIX_CVE_2017_5753.NASL description The NVIDIA GPU display driver software on the remote host is missing a security update. It is, therefore, affected by multiple vulnerabilities. last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 105776 published 2018-01-12 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/105776 title NVIDIA Linux GPU Display Driver 384.x < 384.111 / 390.x < 390.12 Multiple Vulnerabilities (Meltdown)(Spectre) NASL family SuSE Local Security Checks NASL id SUSE_SU-2018-0472-1.NASL description This update for xen fixes several issues. These security issues were fixed : - CVE-2017-5753, CVE-2017-5715, CVE-2017-5754: Prevent information leaks via side effects of speculative execution, aka last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 106901 published 2018-02-20 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/106901 title SUSE SLED12 / SLES12 Security Update : xen (SUSE-SU-2018:0472-1) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family SuSE Local Security Checks NASL id OPENSUSE-2018-118.NASL description This update for webkit2gtk3 fixes the following issues : Update to version 2.18.5 : + Disable SharedArrayBuffers from Web API. + Reduce the precision of last seen 2020-06-05 modified 2018-02-01 plugin id 106549 published 2018-02-01 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2020 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/106549 title openSUSE Security Update : webkit2gtk3 (openSUSE-2018-118) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family MacOS X Local Security Checks NASL id MACOSX_SAFARI11_0_2_PATCH_2018_01_08.NASL description The version of Apple Safari installed on the remote macOS or Mac OS X host is prior to 11.0.2, or is 11.0.2 and missing the January 8th patch. It is, therefore, affected by a vulnerability that exists within microprocessors utilizing speculative execution and indirect branch prediction, which may allow an attacker with local user access to disclose information via a side-channel analysis. last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 105689 published 2018-01-09 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/105689 title macOS : Apple Safari <= 11.0.2 (11604.4.7.1.6 / 12604.4.7.1.6 / 13604.4.7.10.6) Information Disclosure (Spectre) NASL family OracleVM Local Security Checks NASL id ORACLEVM_OVMSA-2018-0012.NASL description The remote OracleVM system is missing necessary patches to address critical security updates : - Revert last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 106226 published 2018-01-22 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/106226 title OracleVM 3.4 : Unbreakable / etc (OVMSA-2018-0012) (Spectre) NASL family Red Hat Local Security Checks NASL id REDHAT-RHSA-2018-0654.NASL description An update for kernel-alt is now available for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7. Red Hat Product Security has rated this update as having a security impact of Important. A Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) base score, which gives a detailed severity rating, is available for each vulnerability from the CVE link(s) in the References section. The kernel-alt packages provide the Linux kernel version 4.x. The following packages have been upgraded to a later upstream version: kernel-alt (4.14.0). (BZ#1492717) Security Fix(es) : * An industry-wide issue was found in the way many modern microprocessor designs have implemented speculative execution of instructions (a commonly used performance optimization). There are three primary variants of the issue which differ in the way the speculative execution can be exploited. Variant CVE-2017-5715 triggers the speculative execution by utilizing branch target injection. It relies on the presence of a precisely-defined instruction sequence in the privileged code as well as the fact that memory accesses may cause allocation into the microprocessor last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 108942 published 2018-04-10 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/108942 title RHEL 7 : kernel-alt (RHSA-2018:0654) NASL family NewStart CGSL Local Security Checks NASL id NEWSTART_CGSL_NS-SA-2019-0049_KERNEL-RT.NASL description The remote NewStart CGSL host, running version CORE 5.04 / MAIN 5.04, has kernel-rt packages installed that are affected by multiple vulnerabilities: - A buffer overflow vulnerability due to a lack of input filtering of incoming fragmented datagrams was found in the IP-over-1394 driver [firewire-net] in a fragment handling code in the Linux kernel. The vulnerability exists since firewire supported IPv4, i.e. since version 2.6.31 (year 2009) till version v4.9-rc4. A maliciously formed fragment with a respectively large datagram offset would cause a memcpy() past the datagram buffer, which would cause a system panic or possible arbitrary code execution. The flaw requires [firewire-net] module to be loaded and is remotely exploitable from connected firewire devices, but not over a local network. (CVE-2016-8633) - The Linux Kernel imposes a size restriction on the arguments and environmental strings passed through RLIMIT_STACK/RLIMIT_INFINITY, but does not take the argument and environment pointers into account, which allows attackers to bypass this limitation. (CVE-2017-1000365) - A bug in the 32-bit compatibility layer of the ioctl handling code of the v4l2 video driver in the Linux kernel has been found. A memory protection mechanism ensuring that user-provided buffers always point to a userspace memory were disabled, allowing destination address to be in a kernel space. This flaw could be exploited by an attacker to overwrite a kernel memory from an unprivileged userspace process, leading to privilege escalation. (CVE-2017-13166) - The timer_create syscall implementation in kernel/time/posix-timers.c in the Linux kernel doesn last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 127233 published 2019-08-12 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/127233 title NewStart CGSL CORE 5.04 / MAIN 5.04 : kernel-rt Multiple Vulnerabilities (NS-SA-2019-0049) NASL family CentOS Local Security Checks NASL id CENTOS_RHSA-2018-0008.NASL description An update for kernel is now available for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6. Red Hat Product Security has rated this update as having a security impact of Important. A Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) base score, which gives a detailed severity rating, is available for each vulnerability from the CVE link(s) in the References section. [Updated 23rd January 2019] The text has been updated to correct the list of architectures addressed by the CVE-2017-5753 mitigation. No changes have been made to the packages. The kernel packages contain the Linux kernel, the core of any Linux operating system. Security Fix(es) : An industry-wide issue was found in the way many modern microprocessor designs have implemented speculative execution of instructions (a commonly used performance optimization). There are three primary variants of the issue which differ in the way the speculative execution can be exploited. Note: This issue is present in hardware and cannot be fully fixed via software update. The updated kernel packages provide software mitigation for this hardware issue at a cost of potential performance penalty. Please refer to References section for further information about this issue and the performance impact. In this update, mitigations for x86 (CVE-2017-5753) and x86-64 (CVE-2017-5753, CVE-2017-5715, and CVE-2017-5754) architectures are provided. Variant CVE-2017-5753 triggers the speculative execution by performing a bounds-check bypass. It relies on the presence of a precisely-defined instruction sequence in the privileged code as well as the fact that memory accesses may cause allocation into the microprocessor last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 105589 published 2018-01-05 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/105589 title CentOS 6 : kernel (CESA-2018:0008) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family OracleVM Local Security Checks NASL id ORACLEVM_OVMSA-2018-0005.NASL description The remote OracleVM system is missing necessary patches to address critical security updates : please see Oracle VM Security Advisory OVMSA-2018-0005 for details. last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 105717 published 2018-01-10 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/105717 title OracleVM 3.4 : xen (OVMSA-2018-0005) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family Gentoo Local Security Checks NASL id GENTOO_GLSA-201810-06.NASL description The remote host is affected by the vulnerability described in GLSA-201810-06 (Xen: Multiple vulnerabilities) Multiple vulnerabilities have been discovered in Xen. Please review the referenced CVE identifiers for details. Impact : A local attacker could cause a Denial of Service condition or disclose sensitive information. Workaround : There is no known workaround at this time. last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 118506 published 2018-10-31 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/118506 title GLSA-201810-06 : Xen: Multiple vulnerabilities (Foreshadow) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family Debian Local Security Checks NASL id DEBIAN_DSA-4188.NASL description Several vulnerabilities have been discovered in the Linux kernel that may lead to a privilege escalation, denial of service or information leaks. - CVE-2017-5715 Multiple researchers have discovered a vulnerability in various processors supporting speculative execution, enabling an attacker controlling an unprivileged process to read memory from arbitrary addresses, including from the kernel and all other processes running on the system. This specific attack has been named Spectre variant 2 (branch target injection) and is mitigated for the x86 architecture (amd64 and i386) by using the last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 109518 published 2018-05-02 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/109518 title Debian DSA-4188-1 : linux - security update (Spectre) NASL family VMware ESX Local Security Checks NASL id VMWARE_VMSA-2018-0002.NASL description Bounds Check bypass and Branch Target Injection issues CPU data cache timing can be abused to efficiently leak information out of mis-speculated CPU execution, leading to (at worst) arbitrary virtual memory read vulnerabilities across local security boundaries in various contexts. (Speculative execution is an automatic and inherent CPU performance optimization used in all modern processors.) ESXi, Workstation and Fusion are vulnerable to Bounds Check Bypass and Branch Target Injection issues resulting from this vulnerability. Result of exploitation may allow for information disclosure from one Virtual Machine to another Virtual Machine that is running on the same host. The remediation listed in the table below is for the known variants of the Bounds Check Bypass and Branch Target Injection issues. The Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures project (cve.mitre.org) has assigned the identifiers CVE-2017-5753 (Bounds Check bypass) and CVE-2017-5715 (Branch Target Injection) to these issues. last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 105584 published 2018-01-04 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/105584 title VMSA-2018-0002 : VMware ESXi, Workstation and Fusion updates address side-channel analysis due to speculative execution. (Spectre) NASL family SuSE Local Security Checks NASL id OPENSUSE-2018-2.NASL description The openSUSE Leap 42.3 kernel was updated to 4.4.104 to receive various security and bugfixes. This update adds mitigations for various side channel attacks against modern CPUs that could disclose content of otherwise unreadable memory (bnc#1068032). - CVE-2017-5753 / last seen 2020-06-05 modified 2018-01-05 plugin id 105597 published 2018-01-05 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2020 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/105597 title openSUSE Security Update : the Linux Kernel (openSUSE-2018-2) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family SuSE Local Security Checks NASL id SUSE_SU-2018-0010-1.NASL description The SUSE Linux Enterprise 12 SP3 kernel was updated to receive various security and bugfixes. This update adds mitigations for various side channel attacks against modern CPUs that could disclose content of otherwise unreadable memory (bnc#1068032). - CVE-2017-5753 / last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 105574 published 2018-01-04 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/105574 title SUSE SLED12 / SLES12 Security Update : kernel (SUSE-SU-2018:0010-1) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family Huawei Local Security Checks NASL id EULEROS_SA-2019-1539.NASL description According to the versions of the kernel packages installed, the EulerOS Virtualization for ARM 64 installation on the remote host is affected by the following vulnerabilities : - An industry-wide issue was found in the way many modern microprocessor designs have implemented speculative execution of instructions past bounds check. The flaw relies on the presence of a precisely-defined instruction sequence in the privileged code and the fact that memory writes occur to an address which depends on the untrusted value. Such writes cause an update into the microprocessor last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 124992 published 2019-05-14 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/124992 title EulerOS Virtualization for ARM 64 3.0.1.0 : kernel (EulerOS-SA-2019-1539) NASL family Windows : Microsoft Bulletins NASL id SMB_NT_MS18_JAN_4056898.NASL description The remote Windows host is missing security update 4056898 or cumulative update 4056895. It is, therefore, affected by multiple vulnerabilities : - An vulnerability exists within microprocessors utilizing speculative execution and indirect branch prediction, which may allow an attacker with local user access to disclose information via a side-channel analysis. (CVE-2017-5715, CVE-2017-5753, CVE-2017-5754) - An elevation of privilege vulnerability exists in Windows Adobe Type Manager Font Driver (ATMFD.dll) when it fails to properly handle objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could execute arbitrary code and take control of an affected system. An attacker could then install programs; view, change, or delete data; or create new accounts with full user rights. (CVE-2018-0788) - An elevation of privilege vulnerability exists when the Windows kernel fails to properly handle objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could run arbitrary code in kernel mode. An attacker could then install programs; view, change, or delete data; or create new accounts with full user rights. (CVE-2018-0744) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists in the Windows kernel that could allow an attacker to retrieve information that could lead to a Kernel Address Space Layout Randomization (ASLR) bypass. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could retrieve the memory address of a kernel object. (CVE-2018-0746, CVE-2018-0747) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists in Windows Adobe Type Manager Font Driver (ATMFD.dll) when it fails to properly handle objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could potentially read data that was not intended to be disclosed. Note that this vulnerability would not allow an attacker to execute code or to elevate their user rights directly, but it could be used to obtain information that could be used to try to further compromise the affected system. (CVE-2018-0754) - A remote code execution vulnerability exists in the way the scripting engine handles objects in memory in Microsoft browsers. The vulnerability could corrupt memory in such a way that an attacker could execute arbitrary code in the context of the current user. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could gain the same user rights as the current user. (CVE-2018-0762, CVE-2018-0772) - An elevation of privilege vulnerability exists in the way that the Windows Kernel API enforces permissions. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could impersonate processes, interject cross-process communication, or interrupt system functionality. (CVE-2018-0748, CVE-2018-0751, CVE-2018-0752) - An elevation of privilege vulnerability exists in the Microsoft Server Message Block (SMB) Server when an attacker with valid credentials attempts to open a specially crafted file over the SMB protocol on the same machine. An attacker who successfully exploited this vulnerability could bypass certain security checks in the operating system. (CVE-2018-0749) - A denial of service vulnerability exists in the way that Windows handles objects in memory. An attacker who successfully exploited the vulnerability could cause a target system to stop responding. Note that the denial of service condition would not allow an attacker to execute code or to elevate user privileges. However, the denial of service condition could prevent authorized users from using system resources. The security update addresses the vulnerability by correcting how Windows handles objects in memory. (CVE-2018-0753) last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 105553 published 2018-01-04 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/105553 title KB4056898: Windows 8.1 and Windows Server 2012 R2 January 2018 Security Update (Meltdown)(Spectre) NASL family SuSE Local Security Checks NASL id OPENSUSE-2019-536.NASL description The openSUSE Leap 15 kernel was updated to receive various security and bugfixes. The following security bugs were fixed : - CVE-2018-13406: An integer overflow in the uvesafb_setcmap function could have result in local attackers being able to crash the kernel or potentially elevate privileges because kmalloc_array is not used (bnc#1100418) - CVE-2018-13053: The alarm_timer_nsleep function had an integer overflow via a large relative timeout because ktime_add_safe was not used (bnc#1099924) - CVE-2018-9385: Prevent overread of the last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 123226 published 2019-03-27 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2019-2020 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/123226 title openSUSE Security Update : the Linux Kernel (openSUSE-2019-536) (Spectre) NASL family SuSE Local Security Checks NASL id OPENSUSE-2018-32.NASL description This update for wireshark to version 2.2.12 fixes the following issues : - CVE-2018-5334: IxVeriWave file could crash (boo#1075737) - CVE-2018-5335: WCP dissector could crash (boo#1075738) - CVE-2018-5336: Multiple dissector crashes (boo#1075739) - CVE-2017-17997: MRDISC dissector could crash (boo#1074171) This release no longers enable the Linux kernel BPF JIT compiler via the net.core.bpf_jit_enable sysctl, as this would make systems more vulnerable to Spectre variant 1 CVE-2017-5753 - (boo#1075748) Further bug fixes and updated protocol support as listed in: https://www.wireshark.org/docs/relnotes/wireshark-2.2.12.html last seen 2020-06-05 modified 2018-01-16 plugin id 106061 published 2018-01-16 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2020 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/106061 title openSUSE Security Update : wireshark (openSUSE-2018-32) (Spectre) NASL family Oracle Linux Local Security Checks NASL id ORACLELINUX_ELSA-2018-0151.NASL description From Red Hat Security Advisory 2018:0151 : An update for kernel is now available for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7. Red Hat Product Security has rated this update as having a security impact of Important. A Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) base score, which gives a detailed severity rating, is available for each vulnerability from the CVE link(s) in the References section. The kernel packages contain the Linux kernel, the core of any Linux operating system. Security Fix(es) : An industry-wide issue was found in the way many modern microprocessor designs have implemented speculative execution of instructions (a commonly used performance optimization). There are three primary variants of the issue which differ in the way the speculative execution can be exploited. Note: This issue is present in hardware and cannot be fully fixed via software update. The updated kernel packages provide software mitigation for this hardware issue at a cost of potential performance penalty. Please refer to References section for further information about this issue and the performance impact. In this update initial mitigations for IBM Power (PowerPC) and IBM zSeries (S390) architectures are provided. * Variant CVE-2017-5715 triggers the speculative execution by utilizing branch target injection. It relies on the presence of a precisely-defined instruction sequence in the privileged code as well as the fact that memory accesses may cause allocation into the microprocessor last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 106364 published 2018-01-26 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/106364 title Oracle Linux 7 : kernel (ELSA-2018-0151) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family Windows : Microsoft Bulletins NASL id SMB_ADV180002_MSSQL.NASL description The remote Microsoft SQL Server is missing a security update. It is, therefore, affected by a vulnerability exists within microprocessors utilizing speculative execution and indirect branch prediction, which may allow an attacker with local user access to disclose information via a side-channel analysis. last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 105613 published 2018-01-05 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/105613 title ADV180002: Microsoft SQL Server January 2018 Security Update (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family Red Hat Local Security Checks NASL id REDHAT-RHSA-2018-0007.NASL description An update for kernel is now available for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7. Red Hat Product Security has rated this update as having a security impact of Important. A Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) base score, which gives a detailed severity rating, is available for each vulnerability from the CVE link(s) in the References section. The kernel packages contain the Linux kernel, the core of any Linux operating system. Security Fix(es) : An industry-wide issue was found in the way many modern microprocessor designs have implemented speculative execution of instructions (a commonly used performance optimization). There are three primary variants of the issue which differ in the way the speculative execution can be exploited. Note: This issue is present in hardware and cannot be fully fixed via software update. The updated kernel packages provide software mitigation for this hardware issue at a cost of potential performance penalty. Please refer to References section for further information about this issue and the performance impact. In this update mitigations for x86-64 architecture are provided. Variant CVE-2017-5753 triggers the speculative execution by performing a bounds-check bypass. It relies on the presence of a precisely-defined instruction sequence in the privileged code as well as the fact that memory accesses may cause allocation into the microprocessor last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 105523 published 2018-01-04 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/105523 title RHEL 7 : kernel (RHSA-2018:0007) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family Red Hat Local Security Checks NASL id REDHAT-RHSA-2018-0021.NASL description An update for kernel-rt is now available for Red Hat Enterprise MRG 2. Red Hat Product Security has rated this update as having a security impact of Important. A Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) base score, which gives a detailed severity rating, is available for each vulnerability from the CVE link(s) in the References section. The kernel-rt packages provide the Real Time Linux Kernel, which enables fine-tuning for systems with extremely high determinism requirements. Security Fix(es) : An industry-wide issue was found in the way many modern microprocessor designs have implemented speculative execution of instructions (a commonly used performance optimization). There are three primary variants of the issue which differ in the way the speculative execution can be exploited. Note: This issue is present in hardware and cannot be fully fixed via software update. The updated kernel packages provide software mitigation for this hardware issue at a cost of potential performance penalty. Please refer to References section for further information about this issue and the performance impact. In this update mitigations for x86-64 architecture are provided. Variant CVE-2017-5753 triggers the speculative execution by performing a bounds-check bypass. It relies on the presence of a precisely-defined instruction sequence in the privileged code as well as the fact that memory accesses may cause allocation into the microprocessor last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 105672 published 2018-01-09 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/105672 title RHEL 6 : MRG (RHSA-2018:0021) (Meltdown) (Spectre) NASL family Virtuozzo Local Security Checks NASL id VIRTUOZZO_VZA-2018-002.NASL description According to the versions of the parallels-server-bm-release / vzkernel / etc packages installed, the Virtuozzo installation on the remote host is affected by the following vulnerabilities : - CVE-2017-5715 triggers the speculative execution by utilizing branch target injection. It relies on the presence of a precisely-defined instruction sequence in the privileged code as well as the fact that memory accesses may cause allocation into the microprocessor last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 105619 published 2018-01-08 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/105619 title Virtuozzo 6 : parallels-server-bm-release / vzkernel / etc (VZA-2018-002) NASL family Virtuozzo Local Security Checks NASL id VIRTUOZZO_VZA-2018-006.NASL description According to the versions of the cpupools / cpupools-features / etc packages installed, the Virtuozzo installation on the remote host is affected by the following vulnerabilities : - CVE-2017-5715 triggers the speculative execution by utilizing branch target injection. It relies on the presence of a precisely-defined instruction sequence in the privileged code as well as the fact that memory accesses may cause allocation into the microprocessor last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 106587 published 2018-02-05 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/106587 title Virtuozzo 6 : cpupools / cpupools-features / etc (VZA-2018-006) NASL family Huawei Local Security Checks NASL id EULEROS_SA-2018-1001.NASL description According to the versions of the kernel packages installed, the EulerOS installation on the remote host is affected by the following vulnerabilities : - The recent speculative execution CVEs address three potential attacks across a wide variety of architectures and hardware platforms. - Note: This issue is present in hardware and cannot be fully fixed via software update. The nature of these vulnerabilities and their fixes introduces the possibility of reduced performance on patched systems. The performance impact depends on the hardware and the applications in place. - The first two variants abuse speculative execution to perform bounds-check bypass (CVE-2017-5753), or by utilizing branch target injection (CVE-2017-5715) to cause kernel code at an address under attacker control to execute speculatively. Collectively these are known as last seen 2020-05-06 modified 2018-01-08 plugin id 105618 published 2018-01-08 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2020 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/105618 title EulerOS 2.0 SP2 : kernel (EulerOS-SA-2018-1001) NASL family Windows NASL id GOOGLE_CHROME_64_0_3282_119.NASL description The version of Google Chrome installed on the remote Windows host is prior to 64.0.3282.119. It is, therefore, affected by multiple security vulnerabilities as noted in Chrome stable channel update release notes for January 24th, 2018. Please refer to the release notes for additional information. Note that Nessus has not attempted to exploit these issues but has instead relied only on the application last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 106485 published 2018-01-30 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/106485 title Google Chrome < 64.0.3282.119 Multiple Vulnerabilities (Spectre) NASL family PhotonOS Local Security Checks NASL id PHOTONOS_PHSA-2018-2_0-0011.NASL description An update of [linux] packages for PhotonOS has been released. This kernel update mitigates vulnerabilities CVE-2017-5753 and CVE-2017-5715 which are referred to as the variants of Spectre vulnerability. last seen 2019-02-21 modified 2019-02-07 plugin id 111282 published 2018-07-24 reporter Tenable source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/index.php?view=single&id=111282 title Photon OS 2.0 : linux (PhotonOS-PHSA-2018-2.0-0011) (Spectre) (deprecated) NASL family SuSE Local Security Checks NASL id SUSE_SU-2018-0115-1.NASL description The SUSE Linux Enterprise 12 GA LTSS kernel was updated to receive various security and bugfixes. This update adds mitigations for various side channel attacks against modern CPUs that could disclose content of otherwise unreadable memory (bnc#1068032). - CVE-2017-5753 / last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 106095 published 2018-01-17 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/106095 title SUSE SLES12 Security Update : kernel (SUSE-SU-2018:0115-1) (Meltdown) (Spectre)
Packetstorm
| data source | https://packetstormsecurity.com/files/download/145645/spectre-disclose.txt |
| id | PACKETSTORM:145645 |
| last seen | 2018-01-05 |
| published | 2018-01-04 |
| reporter | Yuval Yarom |
| source | https://packetstormsecurity.com/files/145645/Spectre-Information-Disclosure-Proof-Of-Concept.html |
| title | Spectre Information Disclosure Proof Of Concept |
Redhat
| advisories |
|
Seebug
| bulletinFamily | exploit |
| description | We have discovered that CPU data cache timing can be abused to efficiently leak information out of mis-speculated execution, leading to (at worst) arbitrary virtual memory read vulnerabilities across local security boundaries in various contexts. Variants of this issue are known to affect many modern processors, including certain processors by Intel, AMD and ARM. For a few Intel and AMD CPU models, we have exploits that work against real software. We reported this issue to Intel, AMD and ARM on 2017-06-01 [1]. So far, there are three known variants of the issue: * Variant 1: bounds check bypass (CVE-2017-5753) * Variant 2: branch target injection (CVE-2017-5715) * Variant 3: rogue data cache load (CVE-2017-5754) Before the issues described here were publicly disclosed, Daniel Gruss, Moritz Lipp, Yuval Yarom, Paul Kocher, Daniel Genkin, Michael Schwarz, Mike Hamburg, Stefan Mangard, Thomas Prescher and Werner Haas also reported them; their [writeups/blogposts/paper drafts] are at: * [Spectre](https://spectreattack.com/spectre.pdf) (variants 1 and 2) * [Meltdown](https://meltdownattack.com/meltdown.pdf) (variant 3) During the course of our research, we developed the following proofs of concept (PoCs): 1. A PoC that demonstrates the basic principles behind variant 1 in userspace on the tested Intel Haswell Xeon CPU, the AMD FX CPU, the AMD PRO CPU and an ARM Cortex A57 [2]. This PoC only tests for the ability to read data inside mis-speculated execution within the same process, without crossing any privilege boundaries. 2. A PoC for variant 1 that, when running with normal user privileges under a modern Linux kernel with a distro-standard config, can perform arbitrary reads in a 4GiB range [3] in kernel virtual memory on the Intel Haswell Xeon CPU. If the kernel's BPF JIT is enabled (non-default configuration), it also works on the AMD PRO CPU. On the Intel Haswell Xeon CPU, kernel virtual memory can be read at a rate of around 2000 bytes per second after around 4 seconds of startup time. [4] 3. A PoC for variant 2 that, when running with root privileges inside a KVM guest created using virt-manager on the Intel Haswell Xeon CPU, with a specific (now outdated) version of Debian's distro kernel [5] running on the host, can read host kernel memory at a rate of around 1500 bytes/second, with room for optimization. Before the attack can be performed, some initialization has to be performed that takes roughly between 10 and 30 minutes for a machine with 64GiB of RAM; the needed time should scale roughly linearly with the amount of host RAM. (If 2MB hugepages are available to the guest, the initialization should be much faster, but that hasn't been tested.) 4. A PoC for variant 3 that, when running with normal user privileges, can read kernel memory on the Intel Haswell Xeon CPU under some precondition. We believe that this precondition is that the targeted kernel memory is present in the L1D cache. For interesting resources around this topic, look down into the "Literature" section. A warning regarding explanations about processor internals in this blogpost: This blogpost contains a lot of speculation about hardware internals based on observed behavior, which might not necessarily correspond to what processors are actually doing. We have some ideas on possible mitigations and provided some of those ideas to the processor vendors; however, we believe that the processor vendors are in a much better position than we are to design and evaluate mitigations, and we expect them to be the source of authoritative guidance. The PoC code and the writeups that we sent to the CPU vendors will be made available at a later date. ### Tested Processors * Intel(R) Xeon(R) CPU E5-1650 v3 @ 3.50GHz (called "Intel Haswell Xeon CPU" in the rest of this document) * AMD FX(tm)-8320 Eight-Core Processor (called "AMD FX CPU" in the rest of this document) * AMD PRO A8-9600 R7, 10 COMPUTE CORES 4C+6G (called "AMD PRO CPU" in the rest of this document) * An ARM Cortex A57 core of a Google Nexus 5x phone [6] (called "ARM Cortex A57" in the rest of this document) ### Glossary retire: An instruction retires when its results, e.g. register writes and memory writes, are committed and made visible to the rest of the system. Instructions can be executed out of order, but must always retire in order. logical processor core: A logical processor core is what the operating system sees as a processor core. With hyperthreading enabled, the number of logical cores is a multiple of the number of physical cores. cached/uncached data: In this blogpost, "uncached" data is data that is only present in main memory, not in any of the cache levels of the CPU. Loading uncached data will typically take over 100 cycles of CPU time. speculative execution: A processor can execute past a branch without knowing whether it will be taken or where its target is, therefore executing instructions before it is known whether they should be executed. If this speculation turns out to have been incorrect, the CPU can discard the resulting state without architectural effects and continue execution on the correct execution path. Instructions do not retire before it is known that they are on the correct execution path. mis-speculation window: The time window during which the CPU speculatively executes the wrong code and has not yet detected that mis-speculation has occurred. ### Variant 1: Bounds check bypass This section explains the common theory behind all three variants and the theory behind our PoC for variant 1 that, when running in userspace under a Debian distro kernel, can perform arbitrary reads in a 4GiB region of kernel memory in at least the following configurations: * Intel Haswell Xeon CPU, eBPF JIT is off (default state) * Intel Haswell Xeon CPU, eBPF JIT is on (non-default state) * AMD PRO CPU, eBPF JIT is on (non-default state) The state of the eBPF JIT can be toggled using the net.core.bpf_jit_enable sysctl. ### Theoretical explanation The Intel [Optimization Reference Manual](https://www.intel.com/content/dam/www/public/us/en/documents/manuals/64-ia-32-architectures-optimization-manual.pdf) says the following regarding Sandy Bridge (and later microarchitectural revisions) in section 2.3.2.3 ("Branch Prediction"): Branch prediction predicts the branch target and enables the processor to begin executing instructions long before the branch true execution path is known. In section 2.3.5.2 ("L1 DCache"): Loads can: [...] * Be carried out speculatively, before preceding branches are resolved. * Take cache misses out of order and in an overlapped manner. Intel's Software Developer's Manual [7] states in Volume 3A, section 11.7 ("Implicit Caching (Pentium 4, Intel Xeon, and P6 family processors"): Implicit caching occurs when a memory element is made potentially cacheable, although the element may never have been accessed in the normal von Neumann sequence. Implicit caching occurs on the P6 and more recent processor families due to aggressive prefetching, branch prediction, and TLB miss handling. Implicit caching is an extension of the behavior of existing Intel386, Intel486, and Pentium processor systems, since software running on these processor families also has not been able to deterministically predict the behavior of instruction prefetch. Consider the code sample below. If `arr1->length` is uncached, the processor can speculatively load data from `arr1->data[untrusted_offset_from_caller]`. This is an out-of-bounds read. That should not matter because the processor will effectively roll back the execution state when the branch has executed; none of the speculatively executed instructions will retire (e.g. cause registers etc. to be affected). ``` struct array { unsigned long length; unsigned char data[]; }; struct array *arr1 = ...; unsigned long untrusted_offset_from_caller = ...; if (untrusted_offset_from_caller < arr1->length) { unsigned char value = arr1->data[untrusted_offset_from_caller]; ... } ``` However, in the following code sample, there's an issue. If `arr1->length`, `arr2->data[0x200]` and `arr2->data[0x300]` are not cached, but all other accessed data is, and the branch conditions are predicted as true, the processor can do the following speculatively before `arr1->length` has been loaded and the execution is re-steered: * load value = `arr1->data[untrusted_offset_from_caller]` * start a load from a data-dependent offset in `arr2->data`, loading the corresponding cache line into the L1 cache ``` struct array { unsigned long length; unsigned char data[]; }; struct array *arr1 = ...; /* small array */ struct array *arr2 = ...; /* array of size 0x400 */ /* >0x400 (OUT OF BOUNDS!) */ unsigned long untrusted_offset_from_caller = ...; if (untrusted_offset_from_caller < arr1->length) { unsigned char value = arr1->data[untrusted_offset_from_caller]; unsigned long index2 = ((value&1)*0x100)+0x200; if (index2 < arr2->length) { unsigned char value2 = arr2->data[index2]; } } ``` After the execution has been returned to the non-speculative path because the processor has noticed that `untrusted_offset_from_caller` is bigger than `arr1->length`, the cache line containing `arr2->data[index2]` stays in the L1 cache. By measuring the time required to load `arr2->data[0x200]` and `arr2->data[0x300]`, an attacker can then determine whether the value of index2 during speculative execution was 0x200 or 0x300 - which discloses whether `arr1->data[untrusted_offset_from_caller]`&1 is 0 or 1. To be able to actually use this behavior for an attack, an attacker needs to be able to cause the execution of such a vulnerable code pattern in the targeted context with an out-of-bounds index. For this, the vulnerable code pattern must either be present in existing code, or there must be an interpreter or JIT engine that can be used to generate the vulnerable code pattern. So far, we have not actually identified any existing, exploitable instances of the vulnerable code pattern; the PoC for leaking kernel memory using variant 1 uses the eBPF interpreter or the eBPF JIT engine, which are built into the kernel and accessible to normal users. A minor variant of this could be to instead use an out-of-bounds read to a function pointer to gain control of execution in the mis-speculated path. We did not investigate this variant further. ### Attacking the kernel This section describes in more detail how variant 1 can be used to leak Linux kernel memory using the eBPF bytecode interpreter and JIT engine. While there are many interesting potential targets for variant 1 attacks, we chose to attack the Linux in-kernel eBPF JIT/interpreter because it provides more control to the attacker than most other JITs. The Linux kernel supports eBPF since version 3.18. Unprivileged userspace code can supply bytecode to the kernel that is verified by the kernel and then: * either interpreted by an in-kernel bytecode interpreter * or translated to native machine code that also runs in kernel context using a JIT engine (which translates individual bytecode instructions without performing any further optimizations) Execution of the bytecode can be triggered by attaching the eBPF bytecode to a socket as a filter and then sending data through the other end of the socket. Whether the JIT engine is enabled depends on a run-time configuration setting - but at least on the tested Intel processor, the attack works independent of that setting. Unlike classic BPF, eBPF has data types like data arrays and function pointer arrays into which eBPF bytecode can index. Therefore, it is possible to create the code pattern described above in the kernel using eBPF bytecode. eBPF's data arrays are less efficient than its function pointer arrays, so the attack will use the latter where possible. Both machines on which this was tested have no SMAP, and the PoC relies on that (but it shouldn't be a precondition in principle). Additionally, at least on the Intel machine on which this was tested, bouncing modified cache lines between cores is slow, apparently because the MESI protocol is used for cache coherence [8]. Changing the reference counter of an eBPF array on one physical CPU core causes the cache line containing the reference counter to be bounced over to that CPU core, making reads of the reference counter on all other CPU cores slow until the changed reference counter has been written back to memory. Because the length and the reference counter of an eBPF array are stored in the same cache line, this also means that changing the reference counter on one physical CPU core causes reads of the eBPF array's length to be slow on other physical CPU cores (intentional false sharing). The attack uses two eBPF programs. The first one tail-calls through a page-aligned eBPF function pointer array prog_map at a configurable index. In simplified terms, this program is used to determine the address of prog_map by guessing the offset from prog_map to a userspace address and tail-calling through prog_map at the guessed offsets. To cause the branch prediction to predict that the offset is below the length of prog_map, tail calls to an in-bounds index are performed in between. To increase the mis-speculation window, the cache line containing the length of prog_map is bounced to another core. To test whether an offset guess was successful, it can be tested whether the userspace address has been loaded into the cache. Because such straightforward brute-force guessing of the address would be slow, the following optimization is used: 215 adjacent userspace memory mappings [9], each consisting of 24 pages, are created at the userspace address user_mapping_area, covering a total area of 231 bytes. Each mapping maps the same physical pages, and all mappings are present in the pagetables. 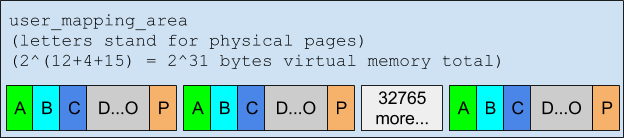 This permits the attack to be carried out in steps of 2^31 bytes. For each step, after causing an out-of-bounds access through prog_map, only one cache line each from the first 2^4 pages of user_mapping_area have to be tested for cached memory. Because the L3 cache is physically indexed, any access to a virtual address mapping a physical page will cause all other virtual addresses mapping the same physical page to become cached as well. When this attack finds a hit—a cached memory location—the upper 33 bits of the kernel address are known (because they can be derived from the address guess at which the hit occurred), and the low 16 bits of the address are also known (from the offset inside user_mapping_area at which the hit was found). The remaining part of the address of user_mapping_area is the middle. 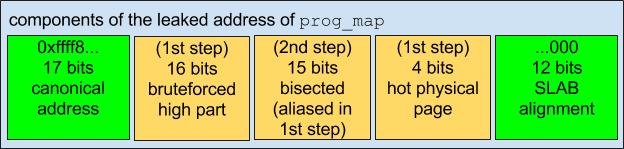 The remaining bits in the middle can be determined by bisecting the remaining address space: Map two physical pages to adjacent ranges of virtual addresses, each virtual address range the size of half of the remaining search space, then determine the remaining address bit-wise. At this point, a second eBPF program can be used to actually leak data. In pseudocode, this program looks as follows: ``` uint64_t bitmask = <runtime-configurable>; uint64_t bitshift_selector = <runtime-configurable>; uint64_t prog_array_base_offset = <runtime-configurable>; uint64_t secret_data_offset = <runtime-configurable>; // index will be bounds-checked by the runtime, // but the bounds check will be bypassed speculatively uint64_t secret_data = bpf_map_read(array=victim_array, index=secret_data_offset); // select a single bit, move it to a specific position, and add the base offset uint64_t progmap_index = (((secret_data & bitmask) >> bitshift_selector) << 7) + prog_array_base_offset; bpf_tail_call(prog_map, progmap_index); ``` This program reads 8-byte-aligned 64-bit values from an eBPF data array "victim_map" at a runtime-configurable offset and bitmasks and bit-shifts the value so that one bit is mapped to one of two values that are 27 bytes apart (sufficient to not land in the same or adjacent cache lines when used as an array index). Finally it adds a 64-bit offset, then uses the resulting value as an offset into prog_map for a tail call. This program can then be used to leak memory by repeatedly calling the eBPF program with an out-of-bounds offset into victim_map that specifies the data to leak and an out-of-bounds offset into prog_map that causes prog_map + offset to point to a userspace memory area. Misleading the branch prediction and bouncing the cache lines works the same way as for the first eBPF program, except that now, the cache line holding the length of victim_map must also be bounced to another core. ### Variant 2: Branch target injection This section describes the theory behind our PoC for variant 2 that, when running with root privileges inside a KVM guest created using virt-manager on the Intel Haswell Xeon CPU, with a specific version of Debian's distro kernel running on the host, can read host kernel memory at a rate of around 1500 bytes/second. #### Basics Prior research (see the Literature section at the end) has shown that it is possible for code in separate security contexts to influence each other's branch prediction. So far, this has only been used to infer information about where code is located (in other words, to create interference from the victim to the attacker); however, the basic hypothesis of this attack variant is that it can also be used to redirect execution of code in the victim context (in other words, to create interference from the attacker to the victim; the other way around). 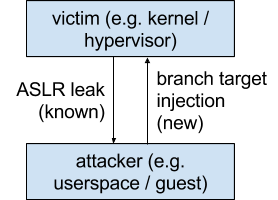 The basic idea for the attack is to target victim code that contains an indirect branch whose target address is loaded from memory and flush the cache line containing the target address out to main memory. Then, when the CPU reaches the indirect branch, it won't know the true destination of the jump, and it won't be able to calculate the true destination until it has finished loading the cache line back into the CPU, which takes a few hundred cycles. Therefore, there is a time window of typically over 100 cycles in which the CPU will speculatively execute instructions based on branch prediction. #### Haswell branch prediction internals Some of the internals of the branch prediction implemented by Intel's processors have already been published; however, getting this attack to work properly required significant further experimentation to determine additional details. This section focuses on the branch prediction internals that were experimentally derived from the Intel Haswell Xeon CPU. Haswell seems to have multiple branch prediction mechanisms that work very differently: * A generic branch predictor that can only store one target per source address; used for all kinds of jumps, like absolute jumps, relative jumps and so on. * A specialized indirect call predictor that can store multiple targets per source address; used for indirect calls. * (There is also a specialized return predictor, according to Intel's optimization manual, but we haven't analyzed that in detail yet. If this predictor could be used to reliably dump out some of the call stack through which a VM was entered, that would be very interesting.) #### Generic predictor The generic branch predictor, as documented in prior research, only uses the lower 31 bits of the address of the last byte of the source instruction for its prediction. If, for example, a branch target buffer (BTB) entry exists for a jump from 0x4141.0004.1000 to 0x4141.0004.5123, the generic predictor will also use it to predict a jump from 0x4242.0004.1000. When the higher bits of the source address differ like this, the higher bits of the predicted destination change together with it—in this case, the predicted destination address will be 0x4242.0004.5123—so apparently this predictor doesn't store the full, absolute destination address. Before the lower 31 bits of the source address are used to look up a BTB entry, they are folded together using XOR. Specifically, the following bits are folded together: 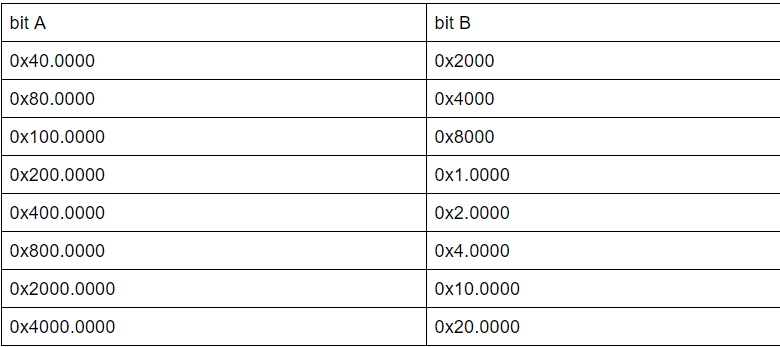 In other words, if a source address is XORed with both numbers in a row of this table, the branch predictor will not be able to distinguish the resulting address from the original source address when performing a lookup. For example, the branch predictor is able to distinguish source addresses 0x100.0000 and 0x180.0000, and it can also distinguish source addresses 0x100.0000 and 0x180.8000, but it can't distinguish source addresses 0x100.0000 and 0x140.2000 or source addresses 0x100.0000 and 0x180.4000. In the following, this will be referred to as aliased source addresses. When an aliased source address is used, the branch predictor will still predict the same target as for the unaliased source address. This indicates that the branch predictor stores a truncated absolute destination address, but that hasn't been verified. Based on observed maximum forward and backward jump distances for different source addresses, the low 32-bit half of the target address could be stored as an absolute 32-bit value with an additional bit that specifies whether the jump from source to target crosses a 232 boundary; if the jump crosses such a boundary, bit 31 of the source address determines whether the high half of the instruction pointer should increment or decrement. #### Indirect call predictor The inputs of the BTB lookup for this mechanism seem to be: * The low 12 bits of the address of the source instruction (we are not sure whether it's the address of the first or the last byte) or a subset of them. * The branch history buffer state. If the indirect call predictor can't resolve a branch, it is resolved by the generic predictor instead. Intel's optimization manual hints at this behavior: "Indirect Calls and Jumps. These may either be predicted as having a monotonic target or as having targets that vary in accordance with recent program behavior." The branch history buffer (BHB) stores information about the last 29 taken branches - basically a fingerprint of recent control flow - and is used to allow better prediction of indirect calls that can have multiple targets. The update function of the BHB works as follows (in pseudocode; src is the address of the last byte of the source instruction, dst is the destination address): ``` void bhb_update(uint58_t *bhb_state, unsigned long src, unsigned long dst) { *bhb_state <<= 2; *bhb_state ^= (dst & 0x3f); *bhb_state ^= (src & 0xc0) >> 6; *bhb_state ^= (src & 0xc00) >> (10 - 2); *bhb_state ^= (src & 0xc000) >> (14 - 4); *bhb_state ^= (src & 0x30) << (6 - 4); *bhb_state ^= (src & 0x300) << (8 - 8); *bhb_state ^= (src & 0x3000) >> (12 - 10); *bhb_state ^= (src & 0x30000) >> (16 - 12); *bhb_state ^= (src & 0xc0000) >> (18 - 14); } ``` Some of the bits of the BHB state seem to be folded together further using XOR when used for a BTB access, but the precise folding function hasn't been understood yet. The BHB is interesting for two reasons. First, knowledge about its approximate behavior is required in order to be able to accurately cause collisions in the indirect call predictor. But it also permits dumping out the BHB state at any repeatable program state at which the attacker can execute code - for example, when attacking a hypervisor, directly after a hypercall. The dumped BHB state can then be used to fingerprint the hypervisor or, if the attacker has access to the hypervisor binary, to determine the low 20 bits of the hypervisor load address (in the case of KVM: the low 20 bits of the load address of kvm-intel.ko). #### Reverse-Engineering Branch Predictor Internals This subsection describes how we reverse-engineered the internals of the Haswell branch predictor. Some of this is written down from memory, since we didn't keep a detailed record of what we were doing. We initially attempted to perform BTB injections into the kernel using the generic predictor, using the knowledge from prior research that the generic predictor only looks at the lower half of the source address and that only a partial target address is stored. This kind of worked - however, the injection success rate was very low, below 1%. (This is the method we used in our preliminary PoCs for method 2 against modified hypervisors running on Haswell.) We decided to write a userspace test case to be able to more easily test branch predictor behavior in different situations. Based on the assumption that branch predictor state is shared between hyperthreads [10], we wrote a program of which two instances are each pinned to one of the two logical processors running on a specific physical core, where one instance attempts to perform branch injections while the other measures how often branch injections are successful. Both instances were executed with ASLR disabled and had the same code at the same addresses. The injecting process performed indirect calls to a function that accesses a (per-process) test variable; the measuring process performed indirect calls to a function that tests, based on timing, whether the per-process test variable is cached, and then evicts it using CLFLUSH. Both indirect calls were performed through the same callsite. Before each indirect call, the function pointer stored in memory was flushed out to main memory using CLFLUSH to widen the speculation time window. Additionally, because of the reference to "recent program behavior" in Intel's optimization manual, a bunch of conditional branches that are always taken were inserted in front of the indirect call. In this test, the injection success rate was above 99%, giving us a base setup for future experiments. 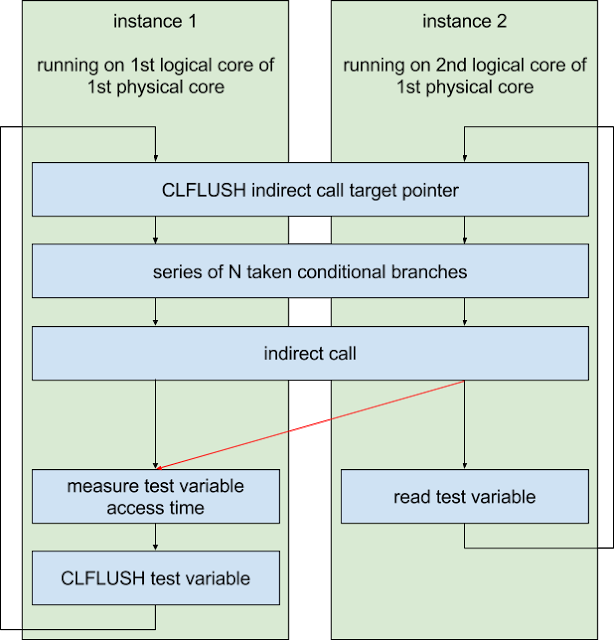 We then tried to figure out the details of the prediction scheme. We assumed that the prediction scheme uses a global branch history buffer of some kind. To determine the duration for which branch information stays in the history buffer, a conditional branch that is only taken in one of the two program instances was inserted in front of the series of always-taken conditional jumps, then the number of always-taken conditional jumps (N) was varied. The result was that for N=25, the processor was able to distinguish the branches (misprediction rate under 1%), but for N=26, it failed to do so (misprediction rate over 99%). Therefore, the branch history buffer had to be able to store information about at least the last 26 branches. The code in one of the two program instances was then moved around in memory. This revealed that only the lower 20 bits of the source and target addresses have an influence on the branch history buffer. Testing with different types of branches in the two program instances revealed that static jumps, taken conditional jumps, calls and returns influence the branch history buffer the same way; non-taken conditional jumps don't influence it; the address of the last byte of the source instruction is the one that counts; IRETQ doesn't influence the history buffer state (which is useful for testing because it permits creating program flow that is invisible to the history buffer). Moving the last conditional branch before the indirect call around in memory multiple times revealed that the branch history buffer contents can be used to distinguish many different locations of that last conditional branch instruction. This suggests that the history buffer doesn't store a list of small history values; instead, it seems to be a larger buffer in which history data is mixed together. However, a history buffer needs to "forget" about past branches after a certain number of new branches have been taken in order to be useful for branch prediction. Therefore, when new data is mixed into the history buffer, this can not cause information in bits that are already present in the history buffer to propagate downwards - and given that, upwards combination of information probably wouldn't be very useful either. Given that branch prediction also must be very fast, we concluded that it is likely that the update function of the history buffer left-shifts the old history buffer, then XORs in the new state (see diagram).  If this assumption is correct, then the history buffer contains a lot of information about the most recent branches, but only contains as many bits of information as are shifted per history buffer update about the last branch about which it contains any data. Therefore, we tested whether flipping different bits in the source and target addresses of a jump followed by 32 always-taken jumps with static source and target allows the branch prediction to disambiguate an indirect call. [11] With 32 static jumps in between, no bit flips seemed to have an influence, so we decreased the number of static jumps until a difference was observable. The result with 28 always-taken jumps in between was that bits 0x1 and 0x2 of the target and bits 0x40 and 0x80 of the source had such an influence; but flipping both 0x1 in the target and 0x40 in the source or 0x2 in the target and 0x80 in the source did not permit disambiguation. This shows that the per-insertion shift of the history buffer is 2 bits and shows which data is stored in the least significant bits of the history buffer. We then repeated this with decreased amounts of fixed jumps after the bit-flipped jump to determine which information is stored in the remaining bits. #### Reading host memory from a KVM guest Locating the host kernel Our PoC locates the host kernel in several steps. The information that is determined and necessary for the next steps of the attack consists of: * lower 20 bits of the address of kvm-intel.ko * full address of kvm.ko * full address of vmlinux Looking back, this is unnecessarily complicated, but it nicely demonstrates the various techniques an attacker can use. A simpler way would be to first determine the address of vmlinux, then bisect the addresses of kvm.ko and kvm-intel.ko. In the first step, the address of kvm-intel.ko is leaked. For this purpose, the branch history buffer state after guest entry is dumped out. Then, for every possible value of bits 12..19 of the load address of kvm-intel.ko, the expected lowest 16 bits of the history buffer are computed based on the load address guess and the known offsets of the last 8 branches before guest entry, and the results are compared against the lowest 16 bits of the leaked history buffer state. The branch history buffer state is leaked in steps of 2 bits by measuring misprediction rates of an indirect call with two targets. One way the indirect call is reached is from a vmcall instruction followed by a series of N branches whose relevant source and target address bits are all zeroes. The second way the indirect call is reached is from a series of controlled branches in userspace that can be used to write arbitrary values into the branch history buffer. Misprediction rates are measured as in the section "Reverse-Engineering Branch Predictor Internals", using one call target that loads a cache line and another one that checks whether the same cache line has been loaded. 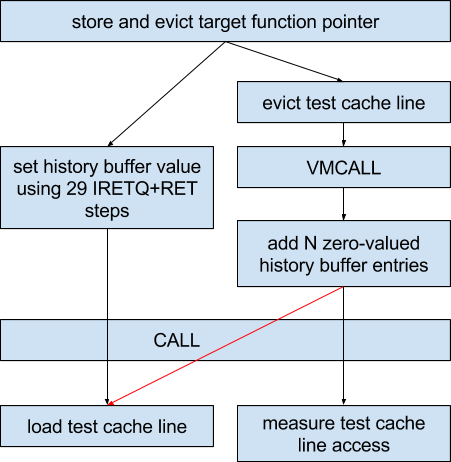 With N=29, mispredictions will occur at a high rate if the controlled branch history buffer value is zero because all history buffer state from the hypercall has been erased. With N=28, mispredictions will occur if the controlled branch history buffer value is one of `0<<(28*2), 1<<(28*2), 2<<(28*2), 3<<(28*2)` - by testing all four possibilities, it can be detected which one is right. Then, for decreasing values of N, the four possibilities are `{0|1|2|3}<<(28*2) | (history_buffer_for(N+1) >> 2)`. By repeating this for decreasing values for N, the branch history buffer value for N=0 can be determined.  At this point, the low 20 bits of kvm-intel.ko are known; the next step is to roughly locate kvm.ko. For this, the generic branch predictor is used, using data inserted into the BTB by an indirect call from kvm.ko to kvm-intel.ko that happens on every hypercall; this means that the source address of the indirect call has to be leaked out of the BTB. kvm.ko will probably be located somewhere in the range from 0xffffffffc0000000 to 0xffffffffc4000000, with page alignment (0x1000). This means that the first four entries in the table in the section "Generic Predictor" apply; there will be 2^4-1=15 aliasing addresses for the correct one. But that is also an advantage: It cuts down the search space from 0x4000 to 0x4000/2^4=1024. To find the right address for the source or one of its aliasing addresses, code that loads data through a specific register is placed at all possible call targets (the leaked low 20 bits of kvm-intel.ko plus the in-module offset of the call target plus a multiple of 2^20) and indirect calls are placed at all possible call sources. Then, alternatingly, hypercalls are performed and indirect calls are performed through the different possible non-aliasing call sources, with randomized history buffer state that prevents the specialized prediction from working. After this step, there are 2^16 remaining possibilities for the load address of kvm.ko. Next, the load address of vmlinux can be determined in a similar way, using an indirect call from vmlinux to kvm.ko. Luckily, none of the bits which are randomized in the load address of vmlinux are folded together, so unlike when locating kvm.ko, the result will directly be unique. vmlinux has an alignment of 2MiB and a randomization range of 1GiB, so there are still only 512 possible addresses. Because (as far as we know) a simple hypercall won't actually cause indirect calls from vmlinux to kvm.ko, we instead use port I/O from the status register of an emulated serial port, which is present in the default configuration of a virtual machine created with virt-manager. The only remaining piece of information is which one of the 16 aliasing load addresses of kvm.ko is actually correct. Because the source address of an indirect call to kvm.ko is known, this can be solved using bisection: Place code at the various possible targets that, depending on which instance of the code is speculatively executed, loads one of two cache lines, and measure which one of the cache lines gets loaded. #### Identifying cache sets The PoC assumes that the VM does not have access to hugepages.To discover eviction sets for all L3 cache sets with a specific alignment relative to a 4KiB page boundary, the PoC first allocates 25600 pages of memory. Then, in a loop, it selects random subsets of all remaining unsorted pages such that the expected number of sets for which an eviction set is contained in the subset is 1, reduces each subset down to an eviction set by repeatedly accessing its cache lines and testing whether the cache lines are always cached (in which case they're probably not part of an eviction set) and attempts to use the new eviction set to evict all remaining unsorted cache lines to determine whether they are in the same cache set [12]. #### Locating the host-virtual address of a guest page Because this attack uses a FLUSH+RELOAD approach for leaking data, it needs to know the host-kernel-virtual address of one guest page. Alternative approaches such as PRIME+PROBE should work without that requirement. The basic idea for this step of the attack is to use a branch target injection attack against the hypervisor to load an attacker-controlled address and test whether that caused the guest-owned page to be loaded. For this, a gadget that simply loads from the memory location specified by R8 can be used - R8-R11 still contain guest-controlled values when the first indirect call after a guest exit is reached on this kernel build. We expected that an attacker would need to either know which eviction set has to be used at this point or brute-force it simultaneously; however, experimentally, using random eviction sets works, too. Our theory is that the observed behavior is actually the result of L1D and L2 evictions, which might be sufficient to permit a few instructions worth of speculative execution. The host kernel maps (nearly?) all physical memory in the physmap area, including memory assigned to KVM guests. However, the location of the physmap is randomized (with a 1GiB alignment), in an area of size 128PiB. Therefore, directly bruteforcing the host-virtual address of a guest page would take a long time. It is not necessarily impossible; as a ballpark estimate, it should be possible within a day or so, maybe less, assuming 12000 successful injections per second and 30 guest pages that are tested in parallel; but not as impressive as doing it in a few minutes. To optimize this, the problem can be split up: First, brute-force the physical address using a gadget that can load from physical addresses, then brute-force the base address of the physmap region. Because the physical address can usually be assumed to be far below 128PiB, it can be brute-forced more efficiently, and brute-forcing the base address of the physmap region afterwards is also easier because then address guesses with 1GiB alignment can be used. To brute-force the physical address, the following gadget can be used: ``` ffffffff810a9def: 4c 89 c0 mov rax,r8 ffffffff810a9df2: 4d 63 f9 movsxd r15,r9d ffffffff810a9df5: 4e 8b 04 fd c0 b3 a6 mov r8,QWORD PTR [r15*8-0x7e594c40] ffffffff810a9dfc: 81 ffffffff810a9dfd: 4a 8d 3c 00 lea rdi,[rax+r8*1] ffffffff810a9e01: 4d 8b a4 00 f8 00 00 mov r12,QWORD PTR [r8+rax*1+0xf8] ffffffff810a9e08: 00 ``` This gadget permits loading an 8-byte-aligned value from the area around the kernel text section by setting R9 appropriately, which in particular permits loading page_offset_base, the start address of the physmap. Then, the value that was originally in R8 - the physical address guess minus 0xf8 - is added to the result of the previous load, 0xfa is added to it, and the result is dereferenced. #### Cache set selection To select the correct L3 eviction set, the attack from the following section is essentially executed with different eviction sets until it works. #### Leaking data At this point, it would normally be necessary to locate gadgets in the host kernel code that can be used to actually leak data by reading from an attacker-controlled location, shifting and masking the result appropriately and then using the result of that as offset to an attacker-controlled address for a load. But piecing gadgets together and figuring out which ones work in a speculation context seems annoying. So instead, we decided to use the eBPF interpreter, which is built into the host kernel - while there is no legitimate way to invoke it from inside a VM, the presence of the code in the host kernel's text section is sufficient to make it usable for the attack, just like with ordinary ROP gadgets. The eBPF interpreter entry point has the following function signature: ``` static unsigned int __bpf_prog_run(void *ctx, const struct bpf_insn *insn) ``` The second parameter is a pointer to an array of statically pre-verified eBPF instructions to be executed - which means that `__bpf_prog_run()` will not perform any type checks or bounds checks. The first parameter is simply stored as part of the initial emulated register state, so its value doesn't matter. The eBPF interpreter provides, among other things: * multiple emulated 64-bit registers * 64-bit immediate writes to emulated registers * memory reads from addresses stored in emulated registers * bitwise operations (including bit shifts) and arithmetic operations To call the interpreter entry point, a gadget that gives RSI and RIP control given R8-R11 control and controlled data at a known memory location is necessary. The following gadget provides this functionality: ``` ffffffff81514edd: 4c 89 ce mov rsi,r9 ffffffff81514ee0: 41 ff 90 b0 00 00 00 call QWORD PTR [r8+0xb0] ``` Now, by pointing R8 and R9 at the mapping of a guest-owned page in the physmap, it is possible to speculatively execute arbitrary unvalidated eBPF bytecode in the host kernel. Then, relatively straightforward bytecode can be used to leak data into the cache. ### Variant 3: Rogue data cache load Basically, read Anders Fogh's blogpost: https://cyber.wtf/2017/07/28/negative-result-reading-kernel-memory-from-user-mode/ In summary, an attack using this variant of the issue attempts to read kernel memory from userspace without misdirecting the control flow of kernel code. This works by using the code pattern that was used for the previous variants, but in userspace. The underlying idea is that the permission check for accessing an address might not be on the critical path for reading data from memory to a register, where the permission check could have significant performance impact. Instead, the memory read could make the result of the read available to following instructions immediately and only perform the permission check asynchronously, setting a flag in the reorder buffer that causes an exception to be raised if the permission check fails. We do have a few additions to make to Anders Fogh's blogpost: ``` "Imagine the following instruction executed in usermode mov rax,[somekernelmodeaddress] It will cause an interrupt when retired, [...]" ``` It is also possible to already execute that instruction behind a high-latency mispredicted branch to avoid taking a page fault. This might also widen the speculation window by increasing the delay between the read from a kernel address and delivery of the associated exception. "First, I call a syscall that touches this memory. Second, I use the prefetcht0 instruction to improve my odds of having the address loaded in L1." When we used prefetch instructions after doing a syscall, the attack stopped working for us, and we have no clue why. Perhaps the CPU somehow stores whether access was denied on the last access and prevents the attack from working if that is the case? "Fortunately I did not get a slow read suggesting that Intel null’s the result when the access is not allowed." That (read from kernel address returns all-zeroes) seems to happen for memory that is not sufficiently cached but for which pagetable entries are present, at least after repeated read attempts. For unmapped memory, the kernel address read does not return a result at all. #### Ideas for further research We believe that our research provides many remaining research topics that we have not yet investigated, and we encourage other public researchers to look into these. This section contains an even higher amount of speculation than the rest of this blogpost - it contains untested ideas that might well be useless. #### Leaking without data cache timing It would be interesting to explore whether there are microarchitectural attacks other than measuring data cache timing that can be used for exfiltrating data out of speculative execution. #### Other microarchitectures Our research was relatively Haswell-centric so far. It would be interesting to see details e.g. on how the branch prediction of other modern processors works and how well it can be attacked. #### Other JIT engines We developed a successful variant 1 attack against the JIT engine built into the Linux kernel. It would be interesting to see whether attacks against more advanced JIT engines with less control over the system are also practical - in particular, JavaScript engines. #### More efficient scanning for host-virtual addresses and cache sets In variant 2, while scanning for the host-virtual address of a guest-owned page, it might make sense to attempt to determine its L3 cache set first. This could be done by performing L3 evictions using an eviction pattern through the physmap, then testing whether the eviction affected the guest-owned page. The same might work for cache sets - use an L1D+L2 eviction set to evict the function pointer in the host kernel context, use a gadget in the kernel to evict an L3 set using physical addresses, then use that to identify which cache sets guest lines belong to until a guest-owned eviction set has been constructed. Dumping the complete BTB state Given that the generic BTB seems to only be able to distinguish 231-8 or fewer source addresses, it seems feasible to dump out the complete BTB state generated by e.g. a hypercall in a timeframe around the order of a few hours. (Scan for jump sources, then for every discovered jump source, bisect the jump target.) This could potentially be used to identify the locations of functions in the host kernel even if the host kernel is custom-built. The source address aliasing would reduce the usefulness somewhat, but because target addresses don't suffer from that, it might be possible to correlate (source,target) pairs from machines with different KASLR offsets and reduce the number of candidate addresses based on KASLR being additive while aliasing is bitwise. This could then potentially allow an attacker to make guesses about the host kernel version or the compiler used to build it based on jump offsets or distances between functions. #### Variant 2: Leaking with more efficient gadgets If sufficiently efficient gadgets are used for variant 2, it might not be necessary to evict host kernel function pointers from the L3 cache at all; it might be sufficient to only evict them from L1D and L2. #### Various speedups In particular the variant 2 PoC is still a bit slow. This is probably partly because: * It only leaks one bit at a time; leaking more bits at a time should be doable. * It heavily uses IRETQ for hiding control flow from the processor. It would be interesting to see what data leak rate can be achieved using variant 2. #### Leaking or injection through the return predictor If the return predictor also doesn't lose its state on a privilege level change, it might be useful for either locating the host kernel from inside a VM (in which case bisection could be used to very quickly discover the full address of the host kernel) or injecting return targets (in particular if the return address is stored in a cache line that can be flushed out by the attacker and isn't reloaded before the return instruction). However, we have not performed any experiments with the return predictor that yielded conclusive results so far. #### Leaking data out of the indirect call predictor We have attempted to leak target information out of the indirect call predictor, but haven't been able to make it work. ### Vendor statements The following statement were provided to us regarding this issue from the vendors to whom Project Zero disclosed this vulnerability: ### Intel No current statement provided at this time. ### AMD AMD provided the following link: http://www.amd.com/en/corporate/speculative-execution ### ARM Arm recognises that the speculation functionality of many modern high-performance processors, despite working as intended, can be used in conjunction with the timing of cache operations to leak some information as described in this blog. Correspondingly, Arm has developed software mitigations that we recommend be deployed. Specific details regarding the affected processors and mitigations can be found at this website: https://developer.arm.com/support/security-update Arm has included a detailed technical whitepaper as well as links to information from some of Arm’s architecture partners regarding their specific implementations and mitigations. ### Literature Note that some of these documents - in particular Intel's documentation - change over time, so quotes from and references to it may not reflect the latest version of Intel's documentation. * https://www.intel.com/content/dam/www/public/us/en/documents/manuals/64-ia-32-architectures-optimization-manual.pdf: Intel's optimization manual has many interesting pieces of optimization advice that hint at relevant microarchitectural behavior; for example: * "Placing data immediately following an indirect branch can cause a performance problem. If the data consists of all zeros, it looks like a long stream of ADDs to memory destinations and this can cause resource conflicts and slow down branch recovery. Also, data immediately following indirect branches may appear as branches to the branch predication [sic] hardware, which can branch off to execute other data pages. This can lead to subsequent self-modifying code problems." * "Loads can:[...]Be carried out speculatively, before preceding branches are resolved." * "Software should avoid writing to a code page in the same 1-KByte subpage that is being executed or fetching code in the same 2-KByte subpage of that is being written. In addition, sharing a page containing directly or speculatively executed code with another processor as a data page can trigger an SMC condition that causes the entire pipeline of the machine and the trace cache to be cleared. This is due to the self-modifying code condition." * "if mapped as WB or WT, there is a potential for speculative processor reads to bring the data into the caches" * "Failure to map the region as WC may allow the line to be speculatively read into the processor caches (via the wrong path of a mispredicted branch)." * https://software.intel.com/en-us/articles/intel-sdm: Intel's Software Developer Manuals * http://www.agner.org/optimize/microarchitecture.pdf: Agner Fog's documentation of reverse-engineered processor behavior and relevant theory was very helpful for this research. * http://www.cs.binghamton.edu/~dima/micro16.pdf and https://github.com/felixwilhelm/mario_baslr: Prior research by Dmitry Evtyushkin, Dmitry Ponomarev and Nael Abu-Ghazaleh on abusing branch target buffer behavior to leak addresses that we used as a starting point for analyzing the branch prediction of Haswell processors. Felix Wilhelm's research based on this provided the basic idea behind variant 2. * https://arxiv.org/pdf/1507.06955.pdf: The rowhammer.js research by Daniel Gruss, Clémentine Maurice and Stefan Mangard contains information about L3 cache eviction patterns that we reused in the KVM PoC to evict a function pointer. * https://xania.org/201602/bpu-part-one: Matt Godbolt blogged about reverse-engineering the structure of the branch predictor on Intel processors. * https://www.sophia.re/thesis.pdf: Sophia D'Antoine wrote a thesis that shows that opcode scheduling can theoretically be used to transmit data between hyperthreads. * https://gruss.cc/files/kaiser.pdf: Daniel Gruss, Moritz Lipp, Michael Schwarz, Richard Fellner, Clémentine Maurice, and Stefan Mangard wrote a paper on mitigating microarchitectural issues caused by pagetable sharing between userspace and the kernel. * https://www.jilp.org/: This journal contains many articles on branch prediction. * http://blog.stuffedcow.net/2013/01/ivb-cache-replacement/: This blogpost by Henry Wong investigates the L3 cache replacement policy used by Intel's Ivy Bridge architecture. ### References * [1] This initial report did not contain any information about variant 3. We had discussed whether direct reads from kernel memory could work, but thought that it was unlikely. We later tested and reported variant 3 prior to the publication of Anders Fogh's work at https://cyber.wtf/2017/07/28/negative-result-reading-kernel-memory-from-user-mode/. * [2] The precise model names are listed in the section "Tested Processors". The code for reproducing this is in the writeup_files.tar archive in our bugtracker, in the folders userland_test_x86 and userland_test_aarch64. * [3] The attacker-controlled offset used to perform an out-of-bounds access on an array by this PoC is a 32-bit value, limiting the accessible addresses to a 4GiB window in the kernel heap area. * [4] This PoC won't work on CPUs with SMAP support; however, that is not a fundamental limitation. * [5] linux-image-4.9.0-3-amd64 at version 4.9.30-2+deb9u2 (available at http://snapshot.debian.org/archive/debian/20170701T224614Z/pool/main/l/linux/linux-image-4.9.0-3-amd64_4.9.30-2%2Bdeb9u2_amd64.deb, sha256 5f950b26aa7746d75ecb8508cc7dab19b3381c9451ee044cd2edfd6f5efff1f8, signed via Release.gpg, Release, Packages.xz); that was the current distro kernel version when I set up the machine. It is very unlikely that the PoC works with other kernel versions without changes; it contains a number of hardcoded addresses/offsets. * [6] The phone was running an Android build from May 2017. * [7] https://software.intel.com/en-us/articles/intel-sdm * [8] https://software.intel.com/en-us/articles/avoiding-and-identifying-false-sharing-among-threads, section "background" * [9] More than 215 mappings would be more efficient, but the kernel places a hard cap of 216 on the number of VMAs that a process can have. * [10] Intel's optimization manual states that "In the first implementation of HT Technology, the physical execution resources are shared and the architecture state is duplicated for each logical processor", so it would be plausible for predictor state to be shared. While predictor state could be tagged by logical core, that would likely reduce performance for multithreaded processes, so it doesn't seem likely. * [11] In case the history buffer was a bit bigger than we had measured, we added some margin - in particular because we had seen slightly different history buffer lengths in different experiments, and because 26 isn't a very round number. * [12] The basic idea comes from http://palms.ee.princeton.edu/system/files/SP_vfinal.pdf, section IV, although the authors of that paper still used hugepages. |
| id | SSV:97059 |
| last seen | 2018-01-04 |
| modified | 2018-01-04 |
| published | 2018-01-04 |
| reporter | Root |
| source | https://www.seebug.org/vuldb/ssvid-97059 |
| title | Reading privileged memory with a side-channel (Meltdown & Spectre) |
The Hacker News
id THN:71C19B8F2C6EDB0AFDA5AA0280A20C00 last seen 2018-07-11 modified 2018-07-11 published 2018-07-11 reporter The Hacker News source https://thehackernews.com/2018/07/intel-spectre-vulnerability.html title Two New Spectre-Class CPU Flaws Discovered—Intel Pays $100K Bounty id THN:7C0B13C9EA246ED9067BDC332C6923AE last seen 2018-07-30 modified 2018-07-27 published 2018-07-27 reporter The Hacker News source https://thehackernews.com/2018/07/netspectre-remote-spectre-attack.html title NetSpectre — New Remote Spectre Attack Steals Data Over the Network id THN:C4C9BC61AD42FB9F46B30ECA56F71393 last seen 2018-05-22 modified 2018-05-22 published 2018-05-22 reporter Swati Khandelwal source https://thehackernews.com/2018/05/fourth-critical-spectre-cpu-flaw.html title New Spectre (Variant 4) CPU Flaw Discovered—Intel, ARM, AMD Affected id THN:788E9312DDA39D9A09855DF379A0FD4D last seen 2018-01-27 modified 2018-01-04 published 2018-01-03 reporter Mohit Kumar source https://thehackernews.com/2018/01/meltdown-spectre-vulnerability.html title Meltdown and Spectre CPU Flaws Affect Intel, ARM, AMD Processors id THN:58CFE19533148E77597FE0AC59963145 last seen 2018-01-27 modified 2018-01-05 published 2018-01-04 reporter Swati Khandelwal source https://thehackernews.com/2018/01/meltdown-spectre-patches.html title [Guide] How to Protect Your Devices Against Meltdown and Spectre Attacks
Related news
- Two New Spectre-Class CPU Flaws Discovered—Intel Pays $100K Bounty (source)
- Intel Pays $100,000 Bounty for New Spectre Variants (source)
- More Chrome OS Devices Receive Meltdown, Spectre Patches (source)
- Intel Shares Details on New CPUs With Spectre, Meltdown Protections (source)
- Microsoft Releases More Patches for Meltdown, Spectre (source)
- Meltdown and Spectre: Data theft hardware bugs affect most modern CPUs (source)
- GhostRace – New Data Leak Vulnerability Affects Modern CPUs (source)
References
- http://lists.opensuse.org/opensuse-security-announce/2018-01/msg00006.html
- http://lists.opensuse.org/opensuse-security-announce/2018-01/msg00006.html
- http://lists.opensuse.org/opensuse-security-announce/2018-01/msg00007.html
- http://lists.opensuse.org/opensuse-security-announce/2018-01/msg00007.html
- http://lists.opensuse.org/opensuse-security-announce/2018-01/msg00008.html
- http://lists.opensuse.org/opensuse-security-announce/2018-01/msg00008.html
- http://lists.opensuse.org/opensuse-security-announce/2018-01/msg00014.html
- http://lists.opensuse.org/opensuse-security-announce/2018-01/msg00014.html
- http://lists.opensuse.org/opensuse-security-announce/2018-01/msg00016.html
- http://lists.opensuse.org/opensuse-security-announce/2018-01/msg00016.html
- http://nvidia.custhelp.com/app/answers/detail/a_id/4609
- http://nvidia.custhelp.com/app/answers/detail/a_id/4609
- http://nvidia.custhelp.com/app/answers/detail/a_id/4611
- http://nvidia.custhelp.com/app/answers/detail/a_id/4611
- http://nvidia.custhelp.com/app/answers/detail/a_id/4613
- http://nvidia.custhelp.com/app/answers/detail/a_id/4613
- http://nvidia.custhelp.com/app/answers/detail/a_id/4614
- http://nvidia.custhelp.com/app/answers/detail/a_id/4614
- http://packetstormsecurity.com/files/145645/Spectre-Information-Disclosure-Proof-Of-Concept.html
- http://packetstormsecurity.com/files/145645/Spectre-Information-Disclosure-Proof-Of-Concept.html
- http://www.arubanetworks.com/assets/alert/ARUBA-PSA-2018-001.txt
- http://www.arubanetworks.com/assets/alert/ARUBA-PSA-2018-001.txt
- http://www.arubanetworks.com/assets/alert/ARUBA-PSA-2019-003.txt
- http://www.arubanetworks.com/assets/alert/ARUBA-PSA-2019-003.txt
- http://www.kb.cert.org/vuls/id/584653
- http://www.kb.cert.org/vuls/id/584653
- http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/security-advisory/cpuapr2018-3678067.html
- http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/security-advisory/cpuapr2018-3678067.html
- http://www.securityfocus.com/bid/102371
- http://www.securityfocus.com/bid/102371
- http://www.securitytracker.com/id/1040071
- http://www.securitytracker.com/id/1040071
- http://xenbits.xen.org/xsa/advisory-254.html
- http://xenbits.xen.org/xsa/advisory-254.html
- https://access.redhat.com/errata/RHSA-2018:0292
- https://access.redhat.com/errata/RHSA-2018:0292
- https://access.redhat.com/security/vulnerabilities/speculativeexecution
- https://access.redhat.com/security/vulnerabilities/speculativeexecution
- https://aws.amazon.com/de/security/security-bulletins/AWS-2018-013/
- https://aws.amazon.com/de/security/security-bulletins/AWS-2018-013/
- https://blog.mozilla.org/security/2018/01/03/mitigations-landing-new-class-timing-attack/
- https://blog.mozilla.org/security/2018/01/03/mitigations-landing-new-class-timing-attack/
- https://cdrdv2.intel.com/v1/dl/getContent/685359
- https://cdrdv2.intel.com/v1/dl/getContent/685359
- https://cert.vde.com/en-us/advisories/vde-2018-002
- https://cert.vde.com/en-us/advisories/vde-2018-002
- https://cert.vde.com/en-us/advisories/vde-2018-003
- https://cert.vde.com/en-us/advisories/vde-2018-003
- https://cert-portal.siemens.com/productcert/pdf/ssa-505225.pdf
- https://cert-portal.siemens.com/productcert/pdf/ssa-505225.pdf
- https://cert-portal.siemens.com/productcert/pdf/ssa-608355.pdf
- https://cert-portal.siemens.com/productcert/pdf/ssa-608355.pdf
- https://developer.arm.com/support/arm-security-updates/speculative-processor-vulnerability
- https://developer.arm.com/support/arm-security-updates/speculative-processor-vulnerability
- https://googleprojectzero.blogspot.com/2018/01/reading-privileged-memory-with-side.html
- https://googleprojectzero.blogspot.com/2018/01/reading-privileged-memory-with-side.html
- https://help.ecostruxureit.com/display/public/UADCO8x/StruxureWare+Data+Center+Operation+Software+Vulnerability+Fixes
- https://help.ecostruxureit.com/display/public/UADCO8x/StruxureWare+Data+Center+Operation+Software+Vulnerability+Fixes
- https://lists.debian.org/debian-lts-announce/2018/07/msg00015.html
- https://lists.debian.org/debian-lts-announce/2018/07/msg00015.html
- https://lists.debian.org/debian-lts-announce/2018/07/msg00016.html
- https://lists.debian.org/debian-lts-announce/2018/07/msg00016.html
- https://lists.debian.org/debian-lts-announce/2018/07/msg00020.html
- https://lists.debian.org/debian-lts-announce/2018/07/msg00020.html
- https://lists.debian.org/debian-lts-announce/2019/03/msg00034.html
- https://lists.debian.org/debian-lts-announce/2019/03/msg00034.html
- https://lists.debian.org/debian-lts-announce/2019/04/msg00004.html
- https://lists.debian.org/debian-lts-announce/2019/04/msg00004.html
- https://portal.msrc.microsoft.com/en-US/security-guidance/advisory/ADV180002
- https://portal.msrc.microsoft.com/en-US/security-guidance/advisory/ADV180002
- https://seclists.org/bugtraq/2019/Jun/36
- https://seclists.org/bugtraq/2019/Jun/36
- https://security.gentoo.org/glsa/201810-06
- https://security.gentoo.org/glsa/201810-06
- https://security.googleblog.com/2018/01/todays-cpu-vulnerability-what-you-need.html
- https://security.googleblog.com/2018/01/todays-cpu-vulnerability-what-you-need.html
- https://security.netapp.com/advisory/ntap-20180104-0001/
- https://security.netapp.com/advisory/ntap-20180104-0001/
- https://spectreattack.com/
- https://spectreattack.com/
- https://support.citrix.com/article/CTX231399
- https://support.citrix.com/article/CTX231399
- https://support.f5.com/csp/article/K91229003
- https://support.f5.com/csp/article/K91229003
- https://support.hpe.com/hpsc/doc/public/display?docId=emr_na-hpesbhf03805en_us
- https://support.hpe.com/hpsc/doc/public/display?docId=emr_na-hpesbhf03805en_us
- https://support.hpe.com/hpsc/doc/public/display?docLocale=en_US&docId=emr_na-hpesbhf03871en_us
- https://support.hpe.com/hpsc/doc/public/display?docLocale=en_US&docId=emr_na-hpesbhf03871en_us
- https://support.lenovo.com/us/en/solutions/LEN-18282
- https://support.lenovo.com/us/en/solutions/LEN-18282
- https://tools.cisco.com/security/center/content/CiscoSecurityAdvisory/cisco-sa-20180104-cpusidechannel
- https://tools.cisco.com/security/center/content/CiscoSecurityAdvisory/cisco-sa-20180104-cpusidechannel
- https://usn.ubuntu.com/3540-1/
- https://usn.ubuntu.com/3540-1/
- https://usn.ubuntu.com/3540-2/
- https://usn.ubuntu.com/3540-2/
- https://usn.ubuntu.com/3541-1/
- https://usn.ubuntu.com/3541-1/
- https://usn.ubuntu.com/3541-2/
- https://usn.ubuntu.com/3541-2/
- https://usn.ubuntu.com/3542-1/
- https://usn.ubuntu.com/3542-1/
- https://usn.ubuntu.com/3542-2/
- https://usn.ubuntu.com/3542-2/
- https://usn.ubuntu.com/3549-1/
- https://usn.ubuntu.com/3549-1/
- https://usn.ubuntu.com/3580-1/
- https://usn.ubuntu.com/3580-1/
- https://usn.ubuntu.com/3597-1/
- https://usn.ubuntu.com/3597-1/
- https://usn.ubuntu.com/3597-2/
- https://usn.ubuntu.com/3597-2/
- https://usn.ubuntu.com/usn/usn-3516-1/
- https://usn.ubuntu.com/usn/usn-3516-1/
- https://www.debian.org/security/2018/dsa-4187
- https://www.debian.org/security/2018/dsa-4187
- https://www.debian.org/security/2018/dsa-4188
- https://www.debian.org/security/2018/dsa-4188
- https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/43427/
- https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/43427/
- https://www.kb.cert.org/vuls/id/180049
- https://www.kb.cert.org/vuls/id/180049
- https://www.mitel.com/en-ca/support/security-advisories/mitel-product-security-advisory-18-0001
- https://www.mitel.com/en-ca/support/security-advisories/mitel-product-security-advisory-18-0001
- https://www.oracle.com/technetwork/security-advisory/cpuapr2019-5072813.html
- https://www.oracle.com/technetwork/security-advisory/cpuapr2019-5072813.html
- https://www.suse.com/c/suse-addresses-meltdown-spectre-vulnerabilities/
- https://www.suse.com/c/suse-addresses-meltdown-spectre-vulnerabilities/
- https://www.synology.com/support/security/Synology_SA_18_01
- https://www.synology.com/support/security/Synology_SA_18_01
- https://www.vmware.com/us/security/advisories/VMSA-2018-0002.html
- https://www.vmware.com/us/security/advisories/VMSA-2018-0002.html