Security News > 2023 > April > Charming Kitten's New BellaCiao Malware Discovered in Multi-Country Attacks
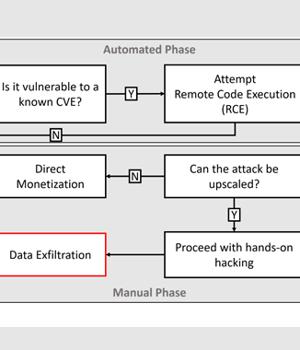
The prolific Iranian nation-state group known as Charming Kitten targeted multiple victims in the U.S., Europe, the Middle East and India with a novel malware dubbed BellaCiao, adding to its ever-expanding list of custom tools.
Discovered by Bitdefender Labs, BellaCiao is a "Personalized dropper" that's capable of delivering other malware payloads onto a victim machine based on commands received from an actor-controlled server.
The development comes as the threat actor was attributed by Microsoft to retaliatory attacks aimed at critical infrastructure entities in the U.S. between late 2021 to mid-2022 using bespoke malware such as harmPower, Drokbk, and Soldier.
"The resolved IP address is like the real public IP address, but with slight modifications that allow BellaCiao to receive further instructions," Zugec explained.
"The best protection against modern attacks involves implementing a defense-in-depth architecture," Zugec concluded.
"The first step in this process is to reduce the attack surface, which involves limiting the number of entry points that attackers can use to gain access to your systems and prompt patching of newly discovered vulnerabilities."
News URL
https://thehackernews.com/2023/04/charming-kittens-new-bellaciao-malware.html
Related news
- Multi-Stage Malware Attack Uses .JSE and PowerShell to Deploy Agent Tesla and XLoader (source)
- Nebulous Mantis Targets NATO-Linked Entities with Multi-Stage Malware Attacks (source)
- New TCESB Malware Found in Active Attacks Exploiting ESET Security Scanner (source)
- New Android malware steals your credit cards for NFC relay attacks (source)
- Hackers Abuse Russian Bulletproof Host Proton66 for Global Attacks and Malware Delivery (source)
- SuperCard X Android Malware Enables Contactless ATM and PoS Fraud via NFC Relay Attacks (source)
- SK Telecom warns customer USIM data exposed in malware attack (source)
- DslogdRAT Malware Deployed via Ivanti ICS Zero-Day CVE-2025-0282 in Japan Attacks (source)
- Malware Attack Targets World Uyghur Congress Leaders via Trojanized UyghurEdit++ Tool (source)
- Disney Slack attack wasn't Russian protesters, just a Cali dude with malware (source)