Security News > 2021 > January > NSA Suggests Enterprises Use 'Designated' DNS-over-HTTPS' Resolvers
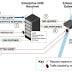
The U.S. National Security Agency on Friday said DNS over HTTPS - if configured appropriately in enterprise environments - can help prevent "Numerous" initial access, command-and-control, and exfiltration techniques used by threat actors.
"DNS over Hypertext Transfer Protocol over Transport Layer Security, often referred to as DNS over HTTPS, encrypts DNS requests by using HTTPS to provide privacy, integrity, and 'last mile' source authentication with a client's DNS resolver," according to the NSA's new guidance.
One of the major shortcomings with current DNS lookups is that even when someone visits a site that uses HTTPS, the DNS query and its response is sent over an unencrypted connection, thus allowing third-party eavesdropping on the network to track every website a user is visiting.
To that effect, the NSA recommends using only designated enterprise DNS resolvers to achieve the desired cybersecurity defense, while warning that individual client applications that enable DoH using third-party DoH resolvers can completely circumvent the enterprise DNS service.
One consequence is that "Malware can also leverage DoH to perform DNS lookups that bypass enterprise DNS resolvers and network monitoring tools, often for command and control or exfiltration purposes."
The gateway, which is used to forward the query to external authoritative DNS servers in the event the enterprise DNS resolver does not have the DNS response cached, should be designed to block DNS, DoH, and DNS over TLS requests to external resolvers and DNS servers that are not from the enterprise resolver, the agency added.