Vulnerabilities > CVE-2017-0199 - Remote Code Execution vulnerability in Microsoft Office OLE Feature
Attack vector
NETWORK Attack complexity
MEDIUM Privileges required
NONE Confidentiality impact
COMPLETE Integrity impact
COMPLETE Availability impact
COMPLETE Summary
Microsoft Office 2007 SP3, Microsoft Office 2010 SP2, Microsoft Office 2013 SP1, Microsoft Office 2016, Microsoft Windows Vista SP2, Windows Server 2008 SP2, Windows 7 SP1, Windows 8.1 allow remote attackers to execute arbitrary code via a crafted document, aka "Microsoft Office/WordPad Remote Code Execution Vulnerability w/Windows API."
Vulnerable Configurations
| Part | Description | Count |
|---|---|---|
| Application | 4 | |
| OS | 5 |
Exploit-Db
description Microsoft Excel - OLE Arbitrary Code Execution. CVE-2017-0199. Dos exploit for Windows platform file exploits/windows/dos/42995.txt id EDB-ID:42995 last seen 2017-10-17 modified 2017-09-30 platform windows port published 2017-09-30 reporter Exploit-DB source https://www.exploit-db.com/download/42995/ title Microsoft Excel - OLE Arbitrary Code Execution type dos description Microsoft Word - '.RTF' Remote Code Execution. CVE-2017-0199. Remote exploit for Windows platform file exploits/windows/remote/41894.py id EDB-ID:41894 last seen 2017-04-19 modified 2017-04-18 platform windows port published 2017-04-18 reporter Exploit-DB source https://www.exploit-db.com/download/41894/ title Microsoft Word - '.RTF' Remote Code Execution type remote description Microsoft Office Word - Malicious Hta Execution (Metasploit). CVE-2017-0199. Remote exploit for Windows platform. Tags: Metasploit Framework file exploits/windows/remote/41934.rb id EDB-ID:41934 last seen 2017-04-25 modified 2017-04-25 platform windows port published 2017-04-25 reporter Exploit-DB source https://www.exploit-db.com/download/41934/ title Microsoft Office Word - Malicious Hta Execution (Metasploit) type remote description Microsoft Office - 'Composite Moniker Remote Code Execution. CVE-2017-8570. Local exploit for Windows platform id EDB-ID:44263 last seen 2018-05-24 modified 2018-01-09 published 2018-01-09 reporter Exploit-DB source https://www.exploit-db.com/download/44263/ title Microsoft Office - 'Composite Moniker Remote Code Execution
Metasploit
Nessus
NASL family Windows : Microsoft Bulletins NASL id SMB_NT_MS17_APR_4015549.NASL description The remote Windows host is missing security update 4015546 or cumulative update 4015549. It is, therefore, affected by multiple vulnerabilities : - An information disclosure vulnerability exists in the open-source libjpeg image processing library due to improper handling of objects in memory. An unauthenticated, remote attacker can exploit this to disclose sensitive information that can be utilized to bypass ASLR security protections. (CVE-2013-6629) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists in the win32k component due to improper handling of kernel information. A local attacker can exploit this, via a specially crafted application, to disclose sensitive information. (CVE-2017-0058) - Multiple privilege escalation vulnerabilities exist in the Microsoft Graphics Component due to improper handling of objects in memory. A local attacker can exploit this, via a specially crafted application, to execute arbitrary code with elevated privileges. (CVE-2017-0155, CVE-2017-0156) - A flaw exists in the VBScript engine due to improper handling of objects in memory. An unauthenticated, remote attacker can exploit this, by convincing a user to visit a malicious website or open a specially crafted document file, to execute arbitrary code. (CVE-2017-0158) - Multiple flaws exist in Windows Hyper-V Network Switch due to improper validation of input from the guest operating system. A local attacker can exploit these, via a specially crafted application on the guest, to execute arbitrary code on the host system. (CVE-2017-0163, CVE-2017-0180) - A flaw exists in LDAP due to buffer request lengths not being properly calculated. An unauthenticated, remote attacker can exploit this, via specially crafted traffic sent to a Domain Controller, to run processes with elevated privileges. (CVE-2017-0166) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists in Windows Hyper-V Network Switch due to improper validation of user-supplied input. A guest attacker can exploit this to disclose sensitive information on the host server. (CVE-2017-0168) - Multiple denial of service vulnerabilities exist in Windows Hyper-V Network Switch due to improper validation of input from the guest operating system. A local attacker on the guest can exploit these vulnerabilities, via a specially crafted application, to crash the host system. (CVE-2017-0182, CVE-2017-0183) - A denial of service vulnerability exists in Hyper-V due to improper validation of input from a privileged user on a guest operating system. A local attacker on the guest can exploit this, via a specially crafted application, to cause the host system to crash. (CVE-2017-0184) - A flaw exists in Windows due to improper handling of objects in memory that allows an attacker to cause a denial of service condition. (CVE-2017-0191) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists in the Adobe Type Manager Font Driver (ATMFD.dll) due to improper handling of objects in memory. An unauthenticated, remote attacker can exploit this, by convincing a user to open a specially crafted document or visit a malicious web page, to disclose sensitive information. (CVE-2017-0192) - An arbitrary code execution vulnerability exists in Microsoft Office and Windows WordPad due to improper handling of specially crafted files. An unauthenticated, remote attacker can exploit this, by convincing a user to open a malicious file, to execute arbitrary code in the context of the current user. Note that this vulnerability is being utilized to spread the Petya ransomware. (CVE-2017-0199) - A memory corruption issue exists in Internet Explorer due to improper validation of user-supplied input. An unauthenticated, remote attacker can exploit this, by convincing a user to visit a malicious website, to execute arbitrary code. (CVE-2017-0202) - A privilege escalation vulnerability exists in Internet Explorer due to a failure to properly enforce cross-domain policies. An unauthenticated, remote attacker can exploit this to inject arbitrary content and gain elevated privileges. (CVE-2017-0210) last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 99304 published 2017-04-12 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2017-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/99304 title Windows 7 and Windows 2008 R2 April 2017 Security Updates (Petya) NASL family Windows : Microsoft Bulletins NASL id SMB_NT_MS17_APR_OFFICE.NASL description The Microsoft Office application, Office Web Apps, or SharePoint Server installed on the remote Windows host is missing a security update. It is, therefore, affected by multiple vulnerabilities : - An arbitrary code execution vulnerability exists in Microsoft Outlook due to improper parsing of email messages. An unauthenticated, remote attacker can exploit this, via a specially crafted email message, to execute arbitrary code. (CVE-2017-0106) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists in Microsoft Office due to improper handling of objects in memory. An unauthenticated, remote attacker can exploit this, by convincing a user to open a specially crafted Excel file, to disclose the contents of memory. (CVE-2017-0194) - A cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerability exists in Office Web Apps Server due to improper validation of input before returning it to users. An authenticated, remote attacker can exploit this, via a specially crafted request, to execute arbitrary script code in a user last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 99314 published 2017-04-12 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2017-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/99314 title Security Update for Microsoft Office Products (April 2017) (Petya) NASL family Windows : Microsoft Bulletins NASL id SMB_NT_MS17_APR_4014793.NASL description The remote Windows host is missing security update KB4014793. It is, therefore, affected by a remote code execution vulnerability in Windows WordPad due to improper validation of user-supplied input. An unauthenticated, remote attacker can exploit this, by convincing a user to open a specially crafted file, to execute arbitrary code. last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 104044 published 2017-10-20 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2017-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/104044 title KB4014793: Microsoft Wordpad Remote Code Execution vulnerability (April 2017) NASL family Windows : Microsoft Bulletins NASL id SMB_NT_MS17-APR_4015551.NASL description The remote Windows host is missing security update 4015548 or cumulative update 4015551. It is, therefore, affected by multiple vulnerabilities : - An information disclosure vulnerability exists in the open-source libjpeg image processing library due to improper handling of objects in memory. An unauthenticated, remote attacker can exploit this to disclose sensitive information that can be utilized to bypass ASLR security protections. (CVE-2013-6629) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists in Windows DirectShow due to improper handling of objects in memory. Any unauthenticated, remote attacker can exploit this, by convincing a user to visit a website with specially crafted media content, to disclose sensitive information. (CVE-2017-0042) - Multiple information disclosure vulnerabilities exist in the win32k component due to improper handling of kernel information. A local attacker can exploit these vulnerabilities, via a specially crafted application, to disclose sensitive information. (CVE-2017-0058, CVE-2017-0188) - Multiple flaws exist in Windows Hyper-V Network Switch due to improper validation of input from the guest operating system. A local attacker can exploit these, via a specially crafted application on the guest, to execute arbitrary code on the host system. (CVE-2017-0163, CVE-2017-0180) - A flaw exists in LDAP due to buffer request lengths not being properly calculated. An unauthenticated, remote attacker can exploit this, via specially crafted traffic sent to a Domain Controller, to run processes with elevated privileges. (CVE-2017-0166) - Multiple information disclosure vulnerabilities exist in Windows Hyper-V Network Switch due to improper validation of user-supplied input. A guest attacker can exploit these to disclose sensitive information on the host server. (CVE-2017-0168, CVE-2017-0169) - Multiple denial of service vulnerabilities exist in Windows Hyper-V Network Switch due to improper validation of input from the guest operating system. A local attacker on the guest can exploit these vulnerabilities, via a specially crafted application, to crash the host system. (CVE-2017-0182, CVE-2017-0183, CVE-2017-0185, CVE-2017-0186) - Multiple denial of service vulnerabilities exist in Hyper-V due to improper validation of input from a privileged user on a guest operating system. A local attacker on the guest can exploit these, via a specially crafted application, to cause the host system to crash. (CVE-2017-0184) - A flaw exists in Windows due to improper handling of objects in memory that allows an attacker to cause a denial of service condition. (CVE-2017-0191) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists in the Adobe Type Manager Font Driver (ATMFD.dll) due to improper handling of objects in memory. An unauthenticated, remote attacker can exploit this, by convincing a user to open a specially crafted document or visit a malicious web page, to disclose sensitive information. (CVE-2017-0192) - An arbitrary code execution vulnerability exists in Microsoft Office and Windows WordPad due to improper handling of specially crafted files. An unauthenticated, remote attacker can exploit this, by convincing a user to open a malicious file, to execute arbitrary code in the context of the current user. Note that this vulnerability is being utilized to spread the Petya ransomware. (CVE-2017-0199) - A memory corruption issue exists in Internet Explorer in the JScript and VBScript engines due to improper validation of user-supplied input. An unauthenticated, remote attacker can exploit this, by convincing a user to visit a malicious website, to execute arbitrary code. (CVE-2017-0201) - A privilege escalation vulnerability exists in Internet Explorer due to a failure to properly enforce cross-domain policies. An unauthenticated, remote attacker can exploit this to inject arbitrary content and gain elevated privileges. (CVE-2017-0210) - A privilege escalation vulnerability exists in Microsoft Windows OLE due to an unspecified failure in integrity-level checks. An authenticated, remote attacker can exploit this to run an application with limited privileges at a medium integrity level. Note that this vulnerability by itself does not allow arbitrary code execution but can be used in conjunction other vulnerabilities. (CVE-2017-0211) last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 99285 published 2017-04-11 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2017-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/99285 title Windows Server 2012 April 2017 Security Updates (Petya) NASL family Windows NASL id MS17-010.NASL description The remote Windows host is affected by the following vulnerabilities : - Multiple remote code execution vulnerabilities exist in Microsoft Server Message Block 1.0 (SMBv1) due to improper handling of certain requests. An unauthenticated, remote attacker can exploit these vulnerabilities, via a specially crafted packet, to execute arbitrary code. (CVE-2017-0143, CVE-2017-0144, CVE-2017-0145, CVE-2017-0146, CVE-2017-0148) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists in Microsoft Server Message Block 1.0 (SMBv1) due to improper handling of certain requests. An unauthenticated, remote attacker can exploit this, via a specially crafted packet, to disclose sensitive information. (CVE-2017-0147) ETERNALBLUE, ETERNALCHAMPION, ETERNALROMANCE, and ETERNALSYNERGY are four of multiple Equation Group vulnerabilities and exploits disclosed on 2017/04/14 by a group known as the Shadow Brokers. WannaCry / WannaCrypt is a ransomware program utilizing the ETERNALBLUE exploit, and EternalRocks is a worm that utilizes seven Equation Group vulnerabilities. Petya is a ransomware program that first utilizes CVE-2017-0199, a vulnerability in Microsoft Office, and then spreads via ETERNALBLUE. last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 97833 published 2017-03-20 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2017-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/97833 title MS17-010: Security Update for Microsoft Windows SMB Server (4013389) (ETERNALBLUE) (ETERNALCHAMPION) (ETERNALROMANCE) (ETERNALSYNERGY) (WannaCry) (EternalRocks) (Petya) (uncredentialed check) NASL family Windows : Microsoft Bulletins NASL id SMB_NT_MS17-010.NASL description The remote Windows host is missing a security update. It is, therefore, affected by the following vulnerabilities : - Multiple remote code execution vulnerabilities exist in Microsoft Server Message Block 1.0 (SMBv1) due to improper handling of certain requests. An unauthenticated, remote attacker can exploit these vulnerabilities, via a specially crafted packet, to execute arbitrary code. (CVE-2017-0143, CVE-2017-0144, CVE-2017-0145, CVE-2017-0146, CVE-2017-0148) - An information disclosure vulnerability exists in Microsoft Server Message Block 1.0 (SMBv1) due to improper handling of certain requests. An unauthenticated, remote attacker can exploit this, via a specially crafted packet, to disclose sensitive information. (CVE-2017-0147) ETERNALBLUE, ETERNALCHAMPION, ETERNALROMANCE, and ETERNALSYNERGY are four of multiple Equation Group vulnerabilities and exploits disclosed on 2017/04/14 by a group known as the Shadow Brokers. WannaCry / WannaCrypt is a ransomware program utilizing the ETERNALBLUE exploit, and EternalRocks is a worm that utilizes seven Equation Group vulnerabilities. Petya is a ransomware program that first utilizes CVE-2017-0199, a vulnerability in Microsoft Office, and then spreads via ETERNALBLUE. last seen 2020-06-01 modified 2020-06-02 plugin id 97737 published 2017-03-15 reporter This script is Copyright (C) 2017-2019 and is owned by Tenable, Inc. or an Affiliate thereof. source https://www.tenable.com/plugins/nessus/97737 title MS17-010: Security Update for Microsoft Windows SMB Server (4013389) (ETERNALBLUE) (ETERNALCHAMPION) (ETERNALROMANCE) (ETERNALSYNERGY) (WannaCry) (EternalRocks) (Petya)
Packetstorm
data source https://packetstormsecurity.com/files/download/143164/mswordmta-exec.txt id PACKETSTORM:143164 last seen 2017-06-28 published 2017-06-27 reporter Juan Sacco source https://packetstormsecurity.com/files/143164/Microsoft-Word-MTA-Handler-Remote-Code-Execution.html title Microsoft Word MTA Handler Remote Code Execution data source https://packetstormsecurity.com/files/download/142211/cve-2017-0199_toolkit.py.txt id PACKETSTORM:142211 last seen 2017-04-20 published 2017-04-19 reporter Bhadresh Patel source https://packetstormsecurity.com/files/142211/Microsoft-RTF-Remote-Code-Execution.html title Microsoft RTF Remote Code Execution data source https://packetstormsecurity.com/files/download/142281/office_word_hta.rb.txt id PACKETSTORM:142281 last seen 2017-04-25 published 2017-04-24 reporter Haifei Li source https://packetstormsecurity.com/files/142281/Microsoft-Office-Word-Malicious-Hta-Execution.html title Microsoft Office Word Malicious Hta Execution
Saint
| bid | 97498 |
| description | Microsoft Word and WordPad RTF HTA handler command execution |
| id | win_patch_office2007,win_patch_office2010,win_patch_office2013,win_patch_office2016 |
| title | microsoft_word_wordpad_rtf |
| type | client |
Seebug
bulletinFamily exploit description Vulnerability details references: * [Office OLE2Link zero-day ](<http://paper.seebug.org/papers/Archive/2017-04%20Office%20OLE2Link%20zero-day%20v0.4.pdf>)from NCCGroup) * [CVE-2017-0199: In the Wild Attacks Leveraging the HTA Handler ](<https://www.fireeye.com/blog/threat-research/2017/04/cve-2017-0199-hta-handler.html>)From FireEye) HTAsThe Microsoft OLE2Link object contains a vulnerability in the way that it processes remotely-linked content. The remote content is opened based on the application associated with the server-provided MIME type. Some MIME types are dangerous, as they can result in code execution. For example, the application/hta mime-type is associated with mshta.exe. Opening arbitrary HTA content is equivalent to executing arbitrary code. This vulnerability is reportedly being exploited in the wild. The exploits used in the wild have the following characteristics: * The document that triggers the OLE2Link vulnerability is an RTF document that masquerades as a Microsoft Word DOC file. * The Trojan connects to a remote server to obtain an execute an HTA file, which contains the VBScript to be executed by the client. Note that depending on the nature of the vulnerability, it may be possible to target Microsoft Windows components other than Microsoft Word. This vulnerability reportedly affects all versions of Microsoft Office, including Office 2016 on Windows 10. It is also reported that [Microsoft Office Protected View ](<https://support.office.com/en-us/article/What-is-Protected-View-d6f09ac7-e6b9-4495-8e43-2bbcdbcb6653>) can help prevent exploitation without user interaction. This vulnerability is reportedly being exploited in the wild. id SSV:92935 last seen 2017-11-19 modified 2017-04-12 published 2017-04-12 reporter Root source https://www.seebug.org/vuldb/ssvid-92935 title Microsoft Office OLE2Link vulnerability (CVE-2017-0199) bulletinFamily exploit description FireEye recently detected a malicious Microsoft Office RTF document that leveraged CVE-2017-8759, a SOAP WSDL parser code injection vulnerability. This vulnerability allows a malicious actor to inject arbitrary code during the parsing of SOAP WSDL definition contents. FireEye analyzed a Microsoft Word document where attackers used the arbitrary code injection to download and execute a Visual Basic script that contained PowerShell commands. FireEye shared the details of the vulnerability with Microsoft and has been coordinating public disclosure timed with the release of a patch to address the vulnerability and security guidance, which can be found here. FireEye email, endpoint and network products detected the malicious documents. ### Vulnerability Used to Target Russian Speakers The malicious document, “Проект.doc” (MD5: fe5c4d6bb78e170abf5cf3741868ea4c), might have been used to target a Russian speaker. Upon successful exploitation of CVE-2017-8759, the document downloads multiple components (details follow), and eventually launches a FINSPY payload (MD5: a7b990d5f57b244dd17e9a937a41e7f5). FINSPY malware, also reported as FinFisher or WingBird, is available for purchase as part of a “lawful intercept” capability. Based on this and previous use of FINSPY, we assess with moderate confidence that this malicious document was used by a nation-state to target a Russian-speaking entity for cyber espionage purposes. Additional detections by FireEye’s Dynamic Threat Intelligence system indicates that related activity, though potentially for a different client, might have occurred as early as July 2017. ### CVE-2017-8759 WSDL Parser Code Injection A code injection vulnerability exists in the WSDL parser module within the PrintClientProxy method (http://referencesource.microsoft.com/ - System.Runtime.Remoting/metadata/wsdlparser.cs,6111). The IsValidUrl does not perform correct validation if provided data that contains a CRLF sequence. This allows an attacker to inject and execute arbitrary code. A portion of the vulnerable code is shown in Figure 1. 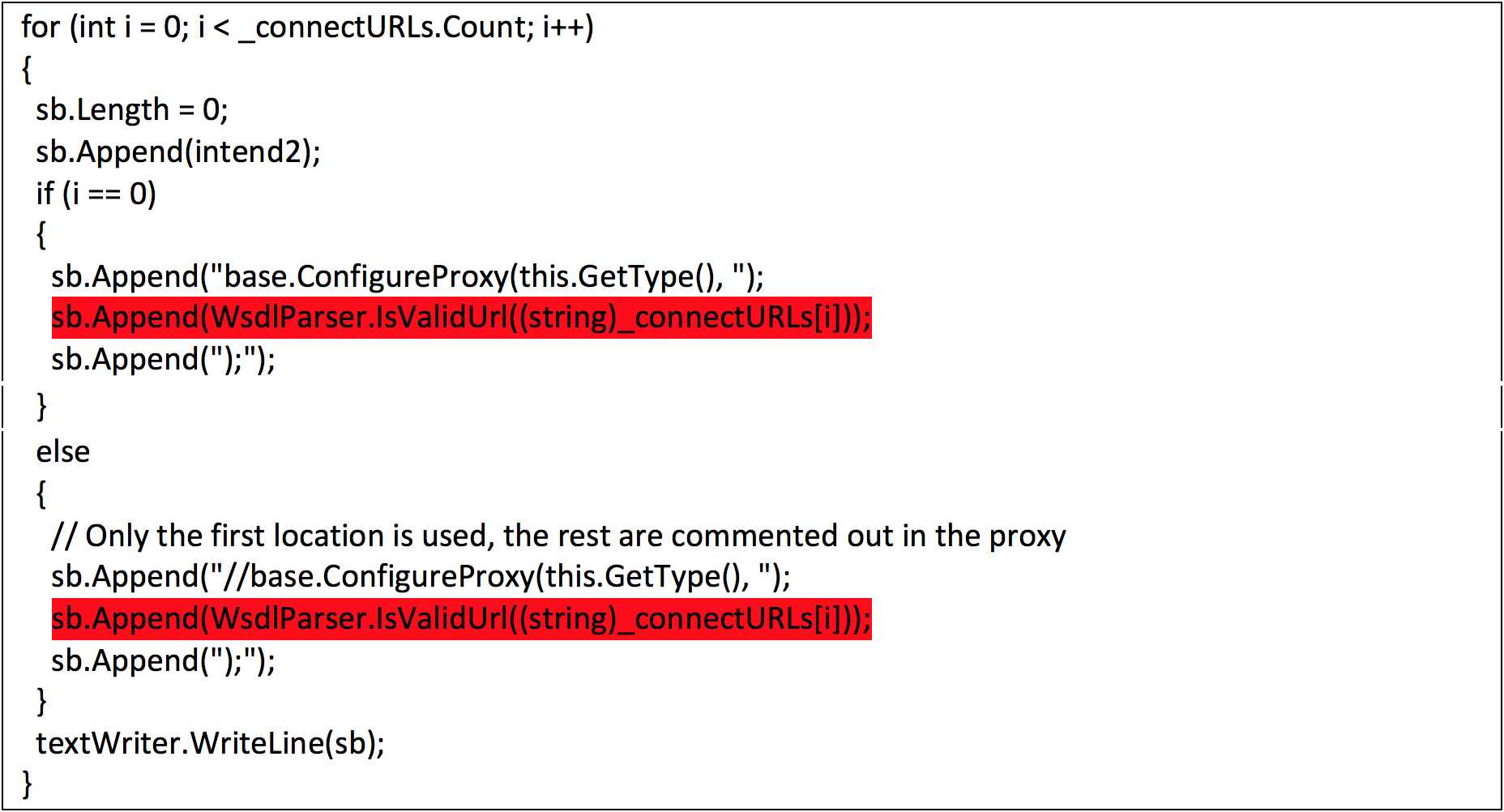 Figure 1: Vulnerable WSDL Parser When multiple address definitions are provided in a SOAP response, the code inserts the “//base.ConfigureProxy(this.GetType(),” string after the first address, commenting out the remaining addresses. However, if a CRLF sequence is in the additional addresses, the code following the CRLF will not be commented out. Figure 2 shows that due to lack validation of CRLF, a System.Diagnostics.Process.Start method call is injected. The generated code will be compiled by csc.exe of .NET framework, and loaded by the Office executables as a DLL. 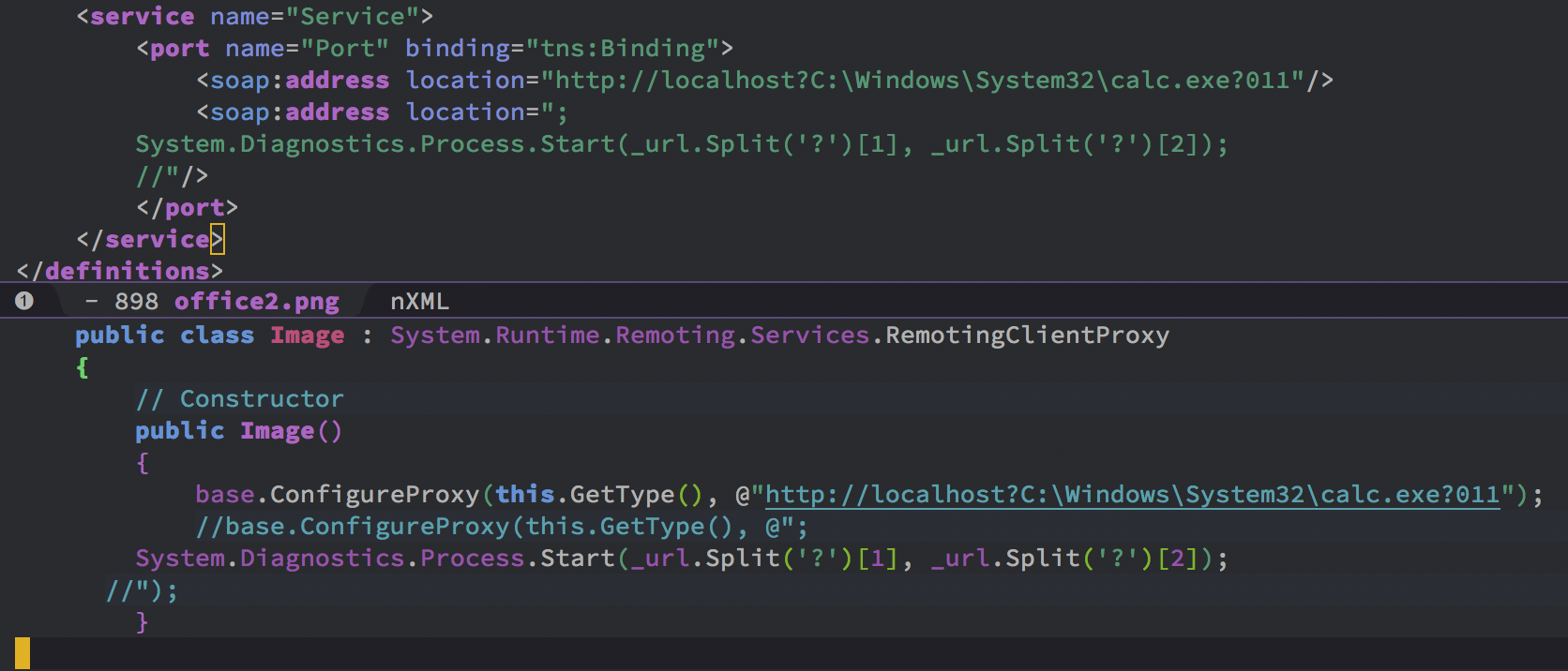 Figure 2: SOAP definition VS Generated code ### The In-the-Wild Attacks The attacks that FireEye observed in the wild leveraged a Rich Text Format (RTF) document, similar to the CVE-2017-0199 documents we previously reported on. The malicious sampled contained an embedded SOAP monikers to facilitate exploitation (Figure 3). 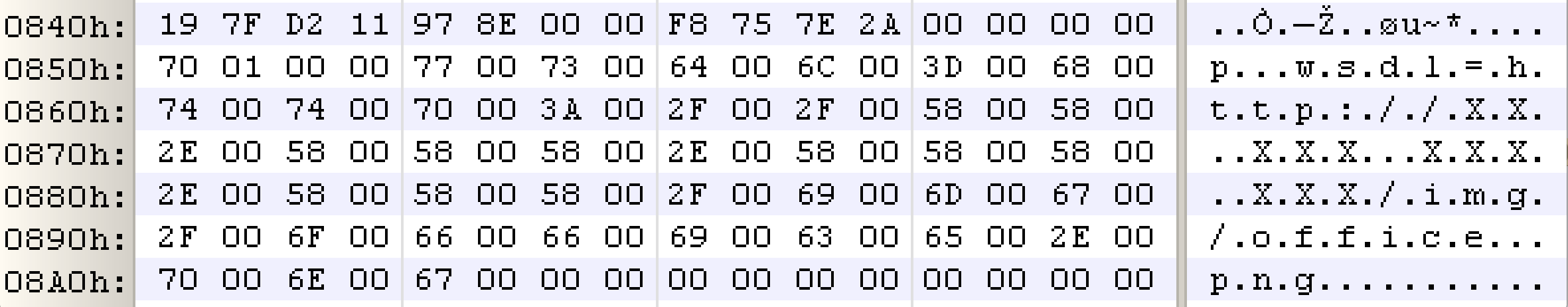 Figure 3: SOAP Moniker The payload retrieves the malicious SOAP WSDL definition from an attacker-controlled server. The WSDL parser, implemented in System.Runtime.Remoting.ni.dll of .NET framework, parses the content and generates a .cs source code at the working directory. The csc.exe of .NET framework then compiles the generated source code into a library, namely http[url path].dll. Microsoft Office then loads the library, completing the exploitation stage. Figure 4 shows an example library loaded as a result of exploitation. 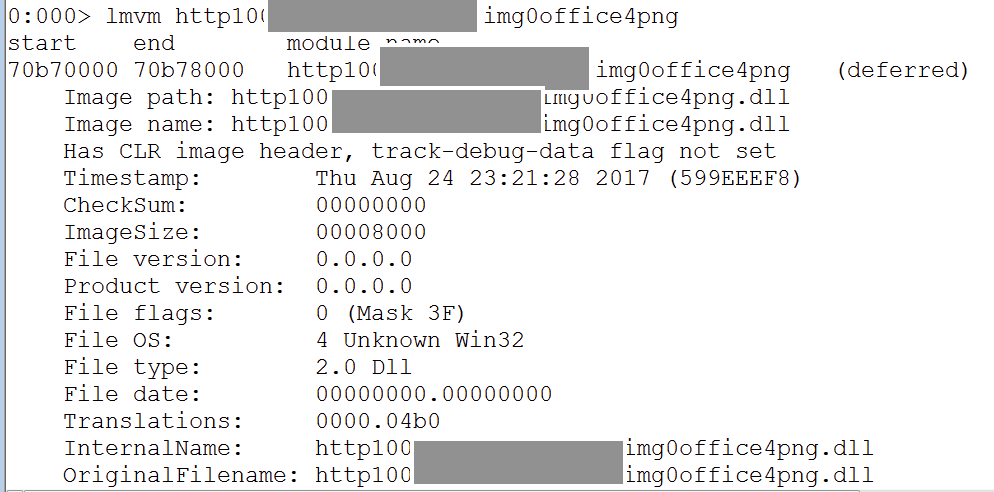 Figure 4: DLL loaded Upon successful exploitation, the injected code creates a new process and leverages mshta.exe to retrieve a HTA script named “word.db” from the same server. The HTA script removes the source code, compiled DLL and the PDB files from disk and then downloads and executes the FINSPY malware named “left.jpg,” which in spite of the .jpg extension and “image/jpeg” content-type, is actually an executable. Figure 5 shows the details of the PCAP of this malware transfer. 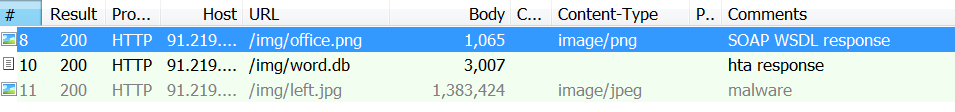 Figure 5: Live requests The malware will be placed at %appdata%\Microsoft\Windows\OfficeUpdte-KB[ 6 random numbers ].exe. Figure 6 shows the process create chain under Process Monitor. 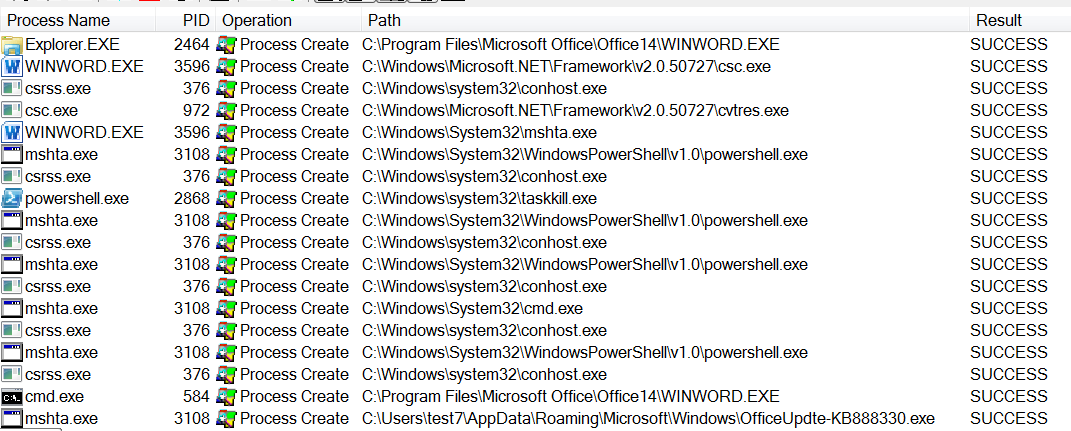 Figure 6: Process Created Chain ### The Malware The “left.jpg” (md5: a7b990d5f57b244dd17e9a937a41e7f5) is a variant of FINSPY. It leverages heavily obfuscated code that employs a built-in virtual machine – among other anti-analysis techniques – to make reversing more difficult. As likely another unique anti-analysis technique, it parses its own full path and searches for the string representation of its own MD5 hash. Many resources, such as analysis tools and sandboxes, rename files/samples to their MD5 hash in order to ensure unique filenames. This variant runs with a mutex of "WininetStartupMutex0". ### Conclusion CVE-2017-8759 is the second zero-day vulnerability used to distribute FINSPY uncovered by FireEye in 2017. These exposures demonstrate the significant resources available to “lawful intercept” companies and their customers. Furthermore, FINSPY has been sold to multiple clients, suggesting the vulnerability was being used against other targets. It is possible that CVE-2017-8759 was being used by additional actors. While we have not found evidence of this, the zero day being used to distribute FINSPY in April 2017, CVE-2017-0199 was simultaneously being used by a financially motivated actor. If the actors behind FINSPY obtained this vulnerability from the same source used previously, it is possible that source sold it to additional actors. id SSV:96484 last seen 2017-11-19 modified 2017-09-14 published 2017-09-14 reporter Root source https://www.seebug.org/vuldb/ssvid-96484 title FireEye Uncovers CVE-2017-8759: Zero-Day Used in the Wild to Distribute FINSPY
The Hacker News
id THN:BAC30CCFD2AEEC91A6E02417A6B55F56 last seen 2018-01-27 modified 2017-06-27 published 2017-06-27 reporter Swati Khandelwal source https://thehackernews.com/2017/06/petya-ransomware-attack.html title Petya Ransomware Spreading Rapidly Worldwide, Just Like WannaCry id THN:F91523FE89728E4535456872C0532560 last seen 2018-01-27 modified 2017-08-14 published 2017-08-14 reporter Mohit Kumar source https://thehackernews.com/2017/08/powerpoint-malware-ms-office.html title How Just Opening A Malicious PowerPoint File Could Compromise Your PC id THN:AE8CC4929BA80C03ABF4AA5FAB5465CC last seen 2018-01-27 modified 2017-07-25 published 2017-07-25 reporter Mohit Kumar source https://thehackernews.com/2017/07/opykittens-cyber-espionage.html title Experts Unveil Cyber Espionage Attacks by CopyKittens Hackers id THN:CB1C2DA47986D8345154BCABBFE41314 last seen 2018-01-27 modified 2017-04-13 published 2017-04-12 reporter Swati Khandelwal source https://thehackernews.com/2017/04/microsoft-word-zeroday.html title Not Just Criminals, But Governments Were Also Using MS Word 0-Day Exploit id THN:2722097C084561C0EE24E84FA6AD506E last seen 2018-01-27 modified 2017-04-12 published 2017-04-11 reporter Swati Khandelwal source https://thehackernews.com/2017/04/microsoft-patch-tuesday.html title Microsoft Issues Patches for Actively Exploited Critical Vulnerabilities
Related news
- New "ThreadKit" Office Exploit Builder Emerges (source)
- The Top Vulnerabilities Exploited by Cybercriminals (source)
- You Can DDoS an Organization for Just $10 per Hour: Cybercrime Report (source)
- How Just Opening A Malicious PowerPoint File Could Compromise Your PC (The Hackers News) (source)
- Not Just Criminals, But Governments Were Also Using MS Word 0-Day Exploit (The Hackers News) (source)
- New Dark Pink APT group targets govt and military with custom malware (source)
References
- http://rewtin.blogspot.nl/2017/04/cve-2017-0199-practical-exploitation-poc.html
- http://www.securityfocus.com/bid/97498
- http://www.securitytracker.com/id/1038224
- https://blog.nviso.be/2017/04/12/analysis-of-a-cve-2017-0199-malicious-rtf-document/
- https://ics-cert.us-cert.gov/advisories/ICSMA-18-058-02
- https://portal.msrc.microsoft.com/en-US/security-guidance/advisory/CVE-2017-0199
- https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/41894/
- https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/41934/
- https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/42995/
- https://www.fireeye.com/blog/threat-research/2017/04/cve-2017-0199_useda.html
- https://www.mdsec.co.uk/2017/04/exploiting-cve-2017-0199-hta-handler-vulnerability/